Feature Based Real Time Computer Aided Diagnosis Of Colorectal Polyps

Feature Based Real Time Computer Aided Diagnosis Of Colorectal Polyps This output was then used as input to a fully connected neural network trained to classify a polyp as neoplastic or non neoplastic based on the detected features. as such, the proposed method provides two outputs: the polyp features observed by the multi label cnn, and the predicted polyp pathology from the resulting polyp features (figure 1). Ai polyp detection tools (so called computer aided polyp detection) during colonoscopy could potentially increase detection of small polyps by up to 50%. 15 while this potentially could increase screening benefit, it also increases health care costs, risk of overtreatment, and patient burden. 16 most additionally detected polyps are small ones.

Computer Aided Diagnosis Of Colorectal Polyp Histology By Using A Real Furthermore, interest in computer aided diagnosis (cadx) has grown, given its potential to assist real time decision making on polyp optical characterization 12,13. Optical colonoscopy with white light (wl) endoscopy is the gold standard for the detection and resection of colorectal mucosal polyps and its adoption in population based screening programs has. Then, cadx ar polyp histology predictions, i.e., neoplastic or non neoplastic, along with the confidence level were displayed on a second monitor in real time and endoscopists were asked to confirm or revise their initial assessment based on the displayed cadx ar prediction and visualization. According to the resect and discard strategy, endoscopists can replace post polypectomy pathology by real time prediction of the histology of the polyp based on its appearance, avoiding the need for pathology assessment when there is high confidence optical diagnosis of both neoplastic and non neoplastic diminutive (≤5 mm) polyps, 1,2 which represent the vast majority of polyps in the colon.

Real Time Artificial Intelligence Based Histologic Classification Of Then, cadx ar polyp histology predictions, i.e., neoplastic or non neoplastic, along with the confidence level were displayed on a second monitor in real time and endoscopists were asked to confirm or revise their initial assessment based on the displayed cadx ar prediction and visualization. According to the resect and discard strategy, endoscopists can replace post polypectomy pathology by real time prediction of the histology of the polyp based on its appearance, avoiding the need for pathology assessment when there is high confidence optical diagnosis of both neoplastic and non neoplastic diminutive (≤5 mm) polyps, 1,2 which represent the vast majority of polyps in the colon. Automatic polyp detection systems using deep learning methods have been proposed for detecting colorectal polyps in real time colonoscopy videos 9,10,11. despite the optimistic results of previous. For unbiased and operator independent real time detection of colorectal polyps, several computer aided detection (cad) systems have recently been developed. apart from initial experiences of ai systems on ex vivo offline images and videos [ 13–18 ], performance of various ai system has been assessed in vivo.
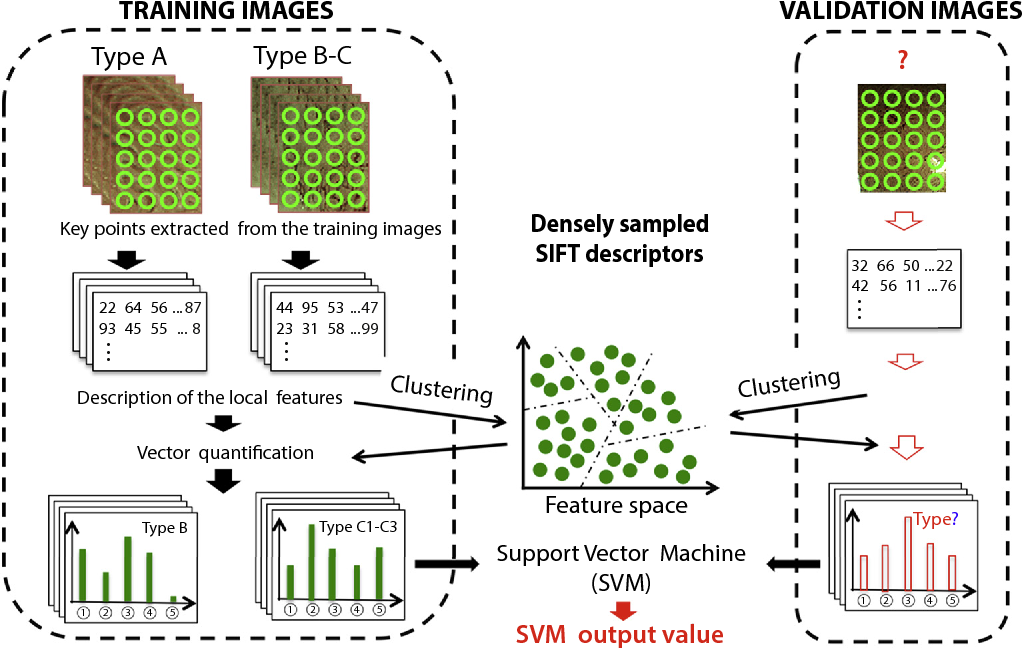
Figure 1 From Computer Aided Diagnosis Of Colorectal Polyp Histology By Automatic polyp detection systems using deep learning methods have been proposed for detecting colorectal polyps in real time colonoscopy videos 9,10,11. despite the optimistic results of previous. For unbiased and operator independent real time detection of colorectal polyps, several computer aided detection (cad) systems have recently been developed. apart from initial experiences of ai systems on ex vivo offline images and videos [ 13–18 ], performance of various ai system has been assessed in vivo.

Comments are closed.