Exterior Angle Theorem Tutorial
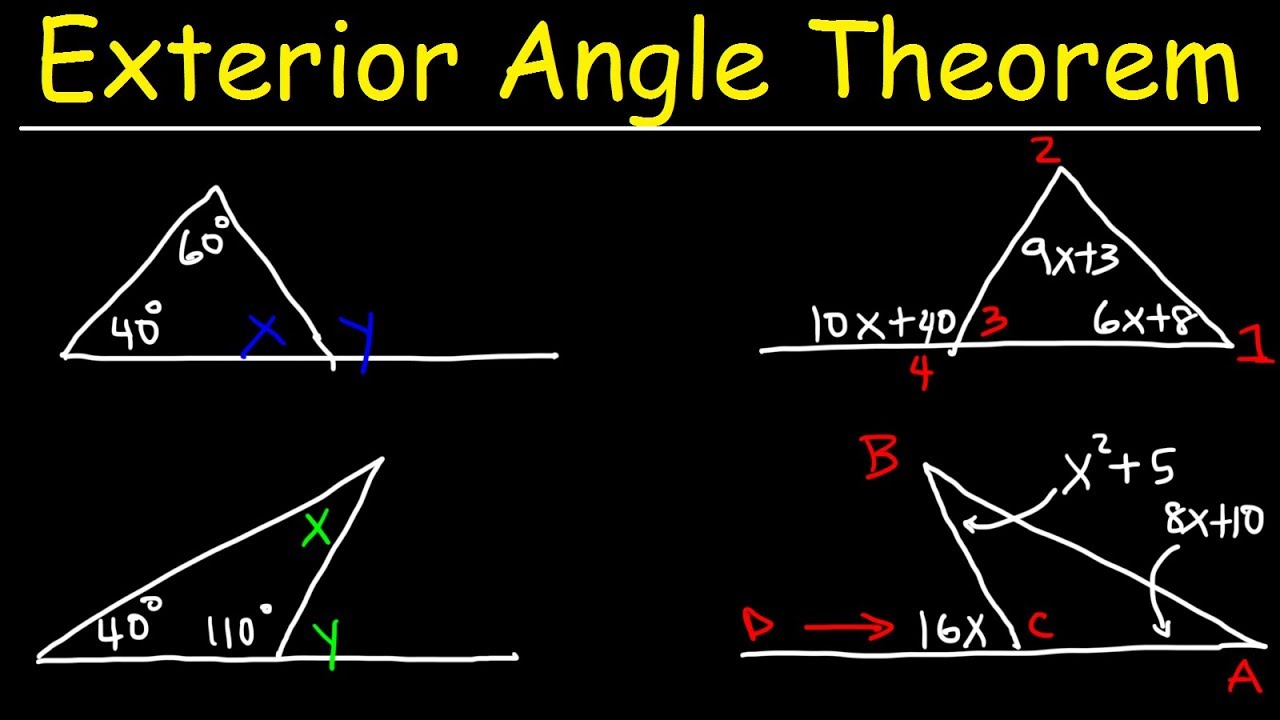
Exterior Angle Theorem For Triangles Practice Problems Geometry Learn how to use the exterior angle theorem in this free math video tutorial by mario's math tutoring. we go through 2 examples as well as the formula in th. Exterior angle theorem. the exterior angle d of a triangle: equals the angles a plus b. is greater than angle a, and. is greater than angle b. example: the exterior angle is 35° 62° = 97°. and 97° > 35°. and 97° > 62°.

Exterior Angle Theorem Youtube This geometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the exterior angle theorem for triangles. it explains how to use it solve for x and y. it d. Example 1: find the values of x and y by using the exterior angle theorem of a triangle. solution: ∠x is the exterior angle. ∠x 92 = 180º (linear pair of angles) ∠x = 180 92 = 88º. applying the exterior angle theorem, we get, ∠y 41 = 88. ∠y = 88 41 = 47º. therefore, the values of x and y are 88º and 47º respectively. Using the exterior angle theorem to solve problems. example: find the values of x and y in the following triangle. solution: x 50° = 92° (sum of opposite interior angles = exterior angle) x = 92° – 50° = 42°. y 92° = 180° (interior angle adjacent exterior angle = 180°.) y = 180° – 92° = 88°. Visit doucehouse for more videos like this. in this video, i discuss the exterior angle theorem. i also define what exterior and remote interior ang.
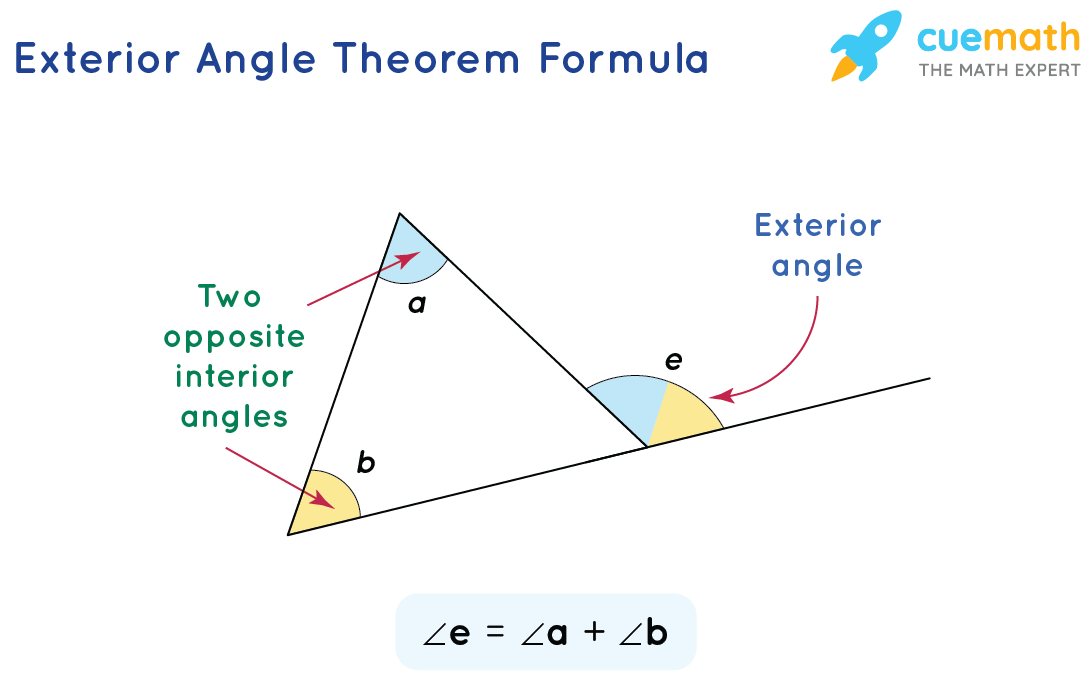
Exterior Angle Formula Concept And Solved Examples Using the exterior angle theorem to solve problems. example: find the values of x and y in the following triangle. solution: x 50° = 92° (sum of opposite interior angles = exterior angle) x = 92° – 50° = 42°. y 92° = 180° (interior angle adjacent exterior angle = 180°.) y = 180° – 92° = 88°. Visit doucehouse for more videos like this. in this video, i discuss the exterior angle theorem. i also define what exterior and remote interior ang. According to the exterior angle theorem, ∠ b c d = ∠ a ∠ b. we can use this theorem to find the measure of an unknown angle in a triangle. example: find x. here, x is the exterior angle with two opposite interior angles measuring 55 ∘ and 45 ∘. by the exterior angle theorem, x = 55 ∘ 45 ∘ = 100 ∘. The exterior angle theorem is proposition 1.16 in euclid's elements, which states that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the measures of the remote interior angles. this is a fundamental result in absolute geometry because its proof does not depend upon the parallel postulate.

Comments are closed.