Explaining Price Elasticity Of Demand Economics Tutor2u

Explaining Price Elasticity Of Demand Tutor2u Economics Level: gcse, as, a level, ib. board: aqa, edexcel, ocr, ib, eduqas, wjec. last updated 1 jul 2018. share : price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in a product's own price. price elasticity of demand key factors. 7. How does the price elasticity of demand affect a firm’s total revenue? model answer to essay question 1: explain the concept of price elasticity of demand and its importance for businesses and governments. price elasticity of demand (ped) measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to changes in its price.
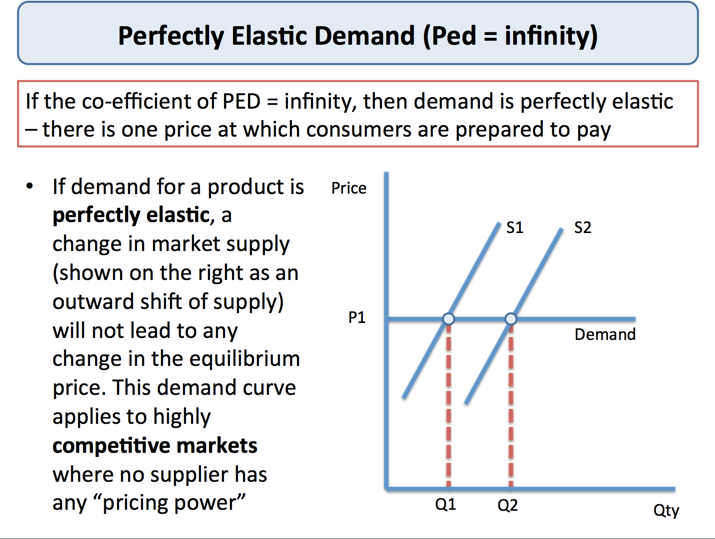
Explaining Price Elasticity Of Demand Tutor2u Economics 4. proportion of a consumer’s income allocated to spending on the good – products that take up a high percentage of income will have a more price elastic demand. 5. time period allowed following a price change – demand is more price elastic, the longer that consumers have to respond to a price change. they have extra time to search for. Definition: demand is price elastic if a change in price leads to a bigger % change in demand; therefore the ped will, therefore, be greater than 1. goods which are elastic, tend to have some or all of the following characteristics. they are luxury goods, e.g. sports cars. they are expensive and a big % of income e.g. sports cars and holidays. Next, we take the results of our calculations and plug them into the formula for price elasticity of supply: price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. The price elasticity comes from the large availability of substitutes. if a good has many substitutes which are available easily then small changes in price will create large changes in demand. the elasticity of these kinds of goods will be greater than 1. draw demand diagrams with different slopes and changes in price and demand.

Explaining Price Elasticity Of Demand Economics Tutor2u Next, we take the results of our calculations and plug them into the formula for price elasticity of supply: price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. The price elasticity comes from the large availability of substitutes. if a good has many substitutes which are available easily then small changes in price will create large changes in demand. the elasticity of these kinds of goods will be greater than 1. draw demand diagrams with different slopes and changes in price and demand. Price elasticity of demand (ped) is introduced and explained in this video.#alevelbusiness #businessrevision #aqabusiness #tutor2ubusiness #alevels #edexcelb. Understanding elasticity. 26 february 2017 by tejvan pettinger. elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. price elasticity of demand (ped) – measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. price elasticity of supply (pes.

Comments are closed.