Expert Insight Stephane La Barre Coral Reef Food Chains

Expert Insight Stéphane La Barre Coral Reef Food Chains Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Coral reefs are the world’s most diverse marine ecosystem, harboring interaction networks of extraordinary complexity. we show that, despite this complexity, global coral reef food webs are governed by a suite of highly consistent energetic pathways, regardless of regional differences in biodiversity. all networks are characterized by species.
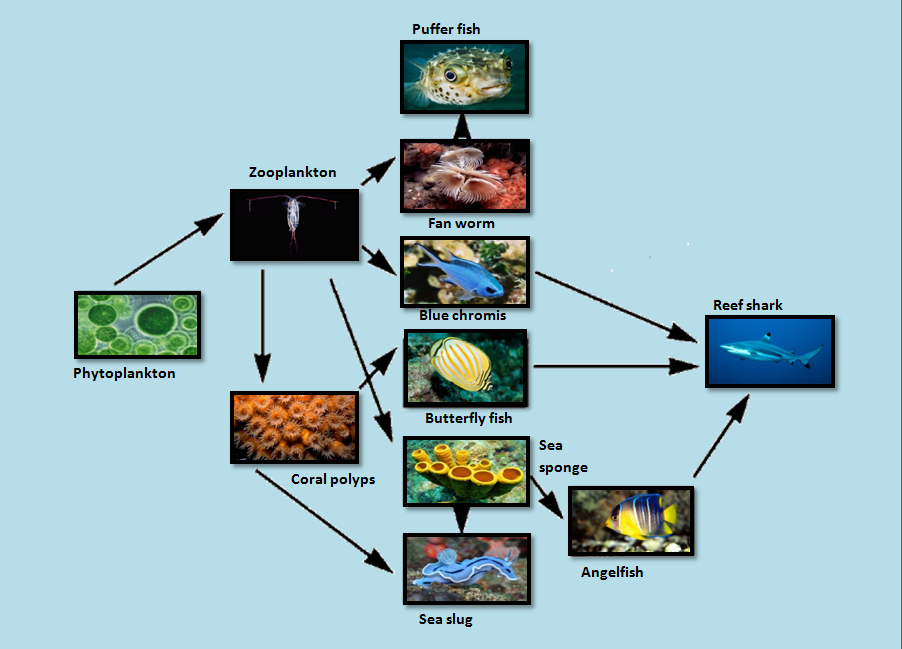
Food Web The Coral Reef Stéphane la barre, senior researcher | cited by 1,614 | of station biologique de roscoff, roscoff | read 80 publications | contact stéphane la barre. Noun. in a food chain or food web, an organism that eats (preys on) herbivores or other first order consumers, but is preyed upon by top predators. marine biology. noun. study of life in the ocean. nutrient. noun. substance an organism needs for energy, growth, and life. ocean. Advances in modelling of energy and nutrient fluxes on coral reefs. (a) four frameworks combine field data, biochemical analyses, and ecological traits to build models that predict energy and nutrient flux for data deficient species. traits may include diet, body size, trophic level, and other covariates relevant to energy and nutrient flux in. Glossary index to learn. chapter 1. the seamost diverse and beautifulwthey are found in warm, shallow ocean waters. evi are one of the planet’s biomes.coral reefs make up les. than 0.2 percent of the ocean floor. but nearly a third of the oc. an’s plants and animals live there. this is why they are. forests of the sea.”coral polypa c.

Coral Reef Food Chain Diagram Advances in modelling of energy and nutrient fluxes on coral reefs. (a) four frameworks combine field data, biochemical analyses, and ecological traits to build models that predict energy and nutrient flux for data deficient species. traits may include diet, body size, trophic level, and other covariates relevant to energy and nutrient flux in. Glossary index to learn. chapter 1. the seamost diverse and beautifulwthey are found in warm, shallow ocean waters. evi are one of the planet’s biomes.coral reefs make up les. than 0.2 percent of the ocean floor. but nearly a third of the oc. an’s plants and animals live there. this is why they are. forests of the sea.”coral polypa c. These species are often of great economic and social value (cinner et al., 2009; gbrmpa, 2014) and play a key functional role in the trophodynamics of coral reef ecosystems, transferring energy up the food chain (polovina, 1984), and potentially offering a stabilizing effect in postdisturbance communities (loeuille, 2010; mccann, hastings. Abstract. this chapter discusses some of the characteristics of reef fish ecology that lead to such a wide range of forms and sizes seen in reef fish. geographic drivers for fish diversity are examined at a range of scales, from global historical events to local scale forces. colour diversity in modern reef fish is examined, along with.
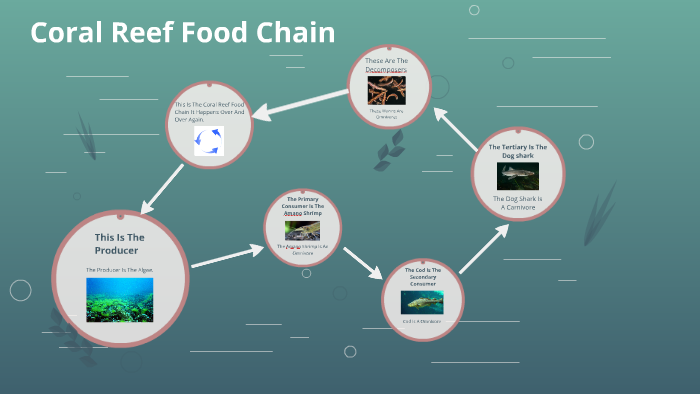
Coral Reef Food Chain Diagram These species are often of great economic and social value (cinner et al., 2009; gbrmpa, 2014) and play a key functional role in the trophodynamics of coral reef ecosystems, transferring energy up the food chain (polovina, 1984), and potentially offering a stabilizing effect in postdisturbance communities (loeuille, 2010; mccann, hastings. Abstract. this chapter discusses some of the characteristics of reef fish ecology that lead to such a wide range of forms and sizes seen in reef fish. geographic drivers for fish diversity are examined at a range of scales, from global historical events to local scale forces. colour diversity in modern reef fish is examined, along with.
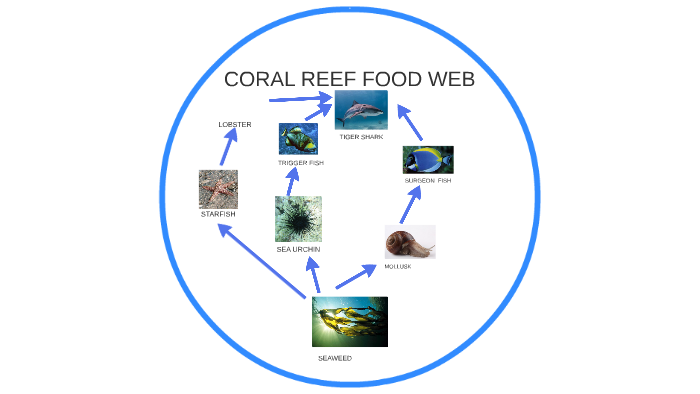
Coral Reef Food Chain Diagram
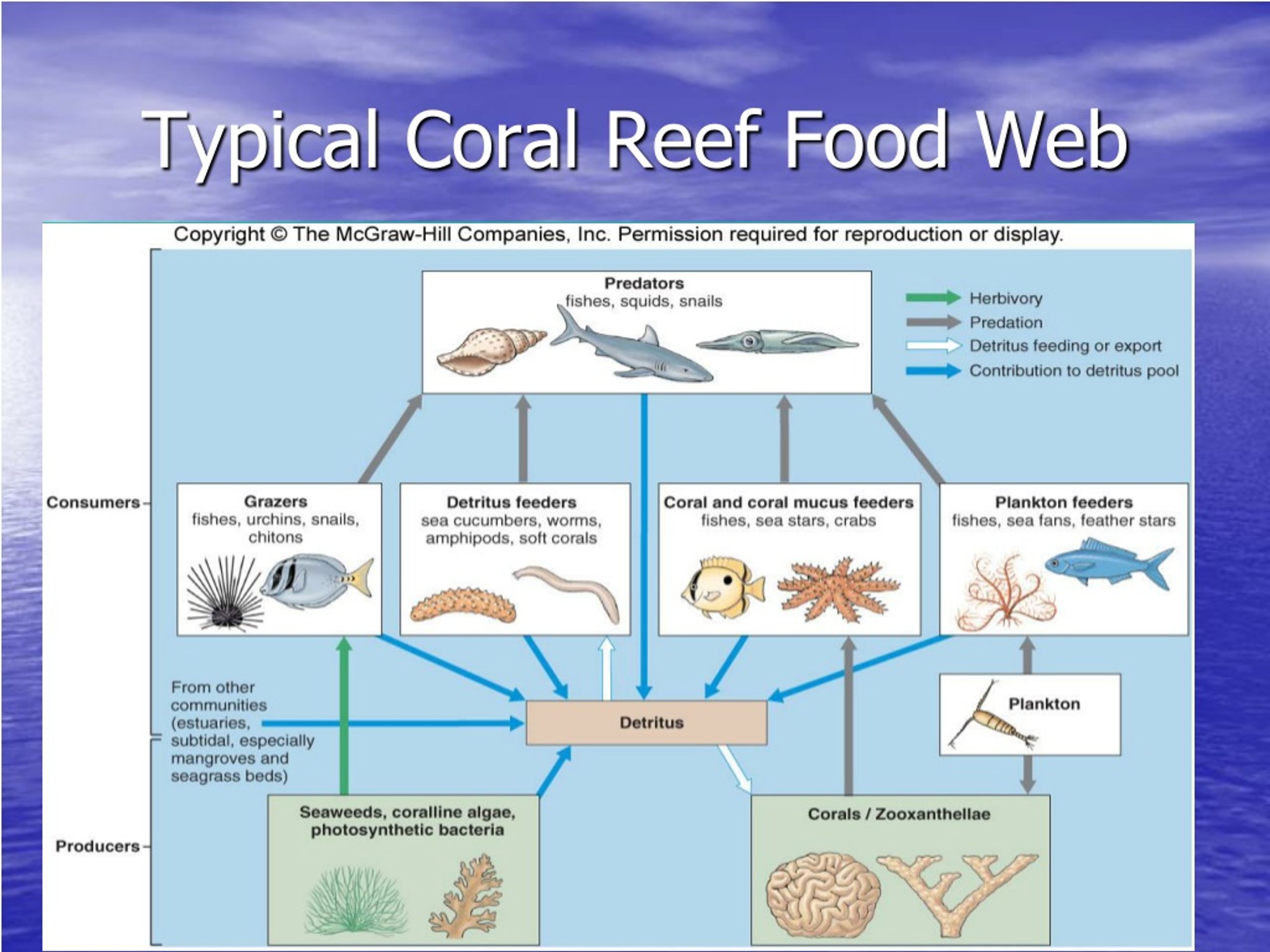
Coral Reef Food Chain Diagram

Comments are closed.