Evaporative Cooling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics 49 Off
Evaporative Cooling Diagram Evaporative cooling. in subject area: chemistry. evaporative cooling is a process where water evaporates, absorbing latent heat and cooling the surroundings. it is a technique used in dry climates like the middle east to cool buildings by exposing porous materials containing water to dry air streams. As mentioned by dominnguez and de la flor (2016), the evaporation of 1 kg of water can decrease the temperature of 2000 m 3 of water by 1° c. in many cases, the surface temperature of the water may be lower than the ambient temperature, and thus cooling can be provided through convective processes.

Evaporative Cooling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics 49 Off Evaporative cooling is a process in which a dense sample of atoms is cooled by gradually removing the more energetic atoms, leading to a decrease in temperature and an increase in phase space density. this method is commonly used to achieve bose einstein condensation (bec) in physics experiments. 1.1 introduction. this book provides background information, description, and analysis of four major cooling technologies—vapor compression cooling, evaporative cooling, absorption cooling, and gas cooling. vapor compression systems are currently the primary technology used in most standard domestic, commercial, and industrial cooling. An evaporative cooler is a device that chills air by evaporating liquid water into water vapor. other names for an evaporative cooler are a swamp cooler, desert cooler, evaporative air conditioner, or swamp box. while highly effective coolers, evaporative cooling is not appropriate for every situation. for example, if you start with humid air. Evaporative cooling technology (ect) has been deemed as an alternative to the conventional vapor compression air conditioning system for dry climates in recent years due to its simple structure and low operating cost. generally speaking, the ect includes two types of different technologies, direct evaporative cooling (dec) and indirect evaporative cooling (iec). both technologies can.
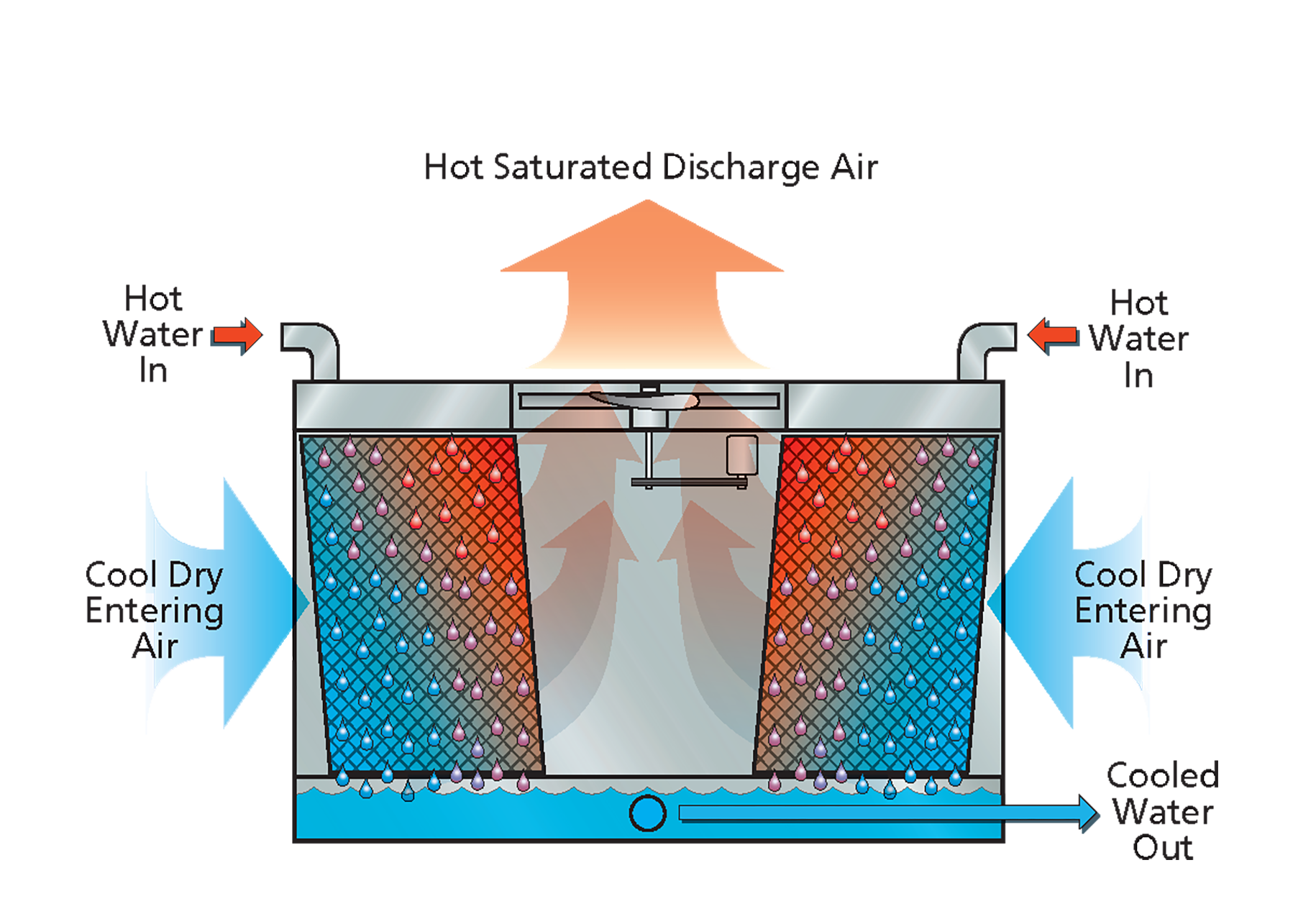
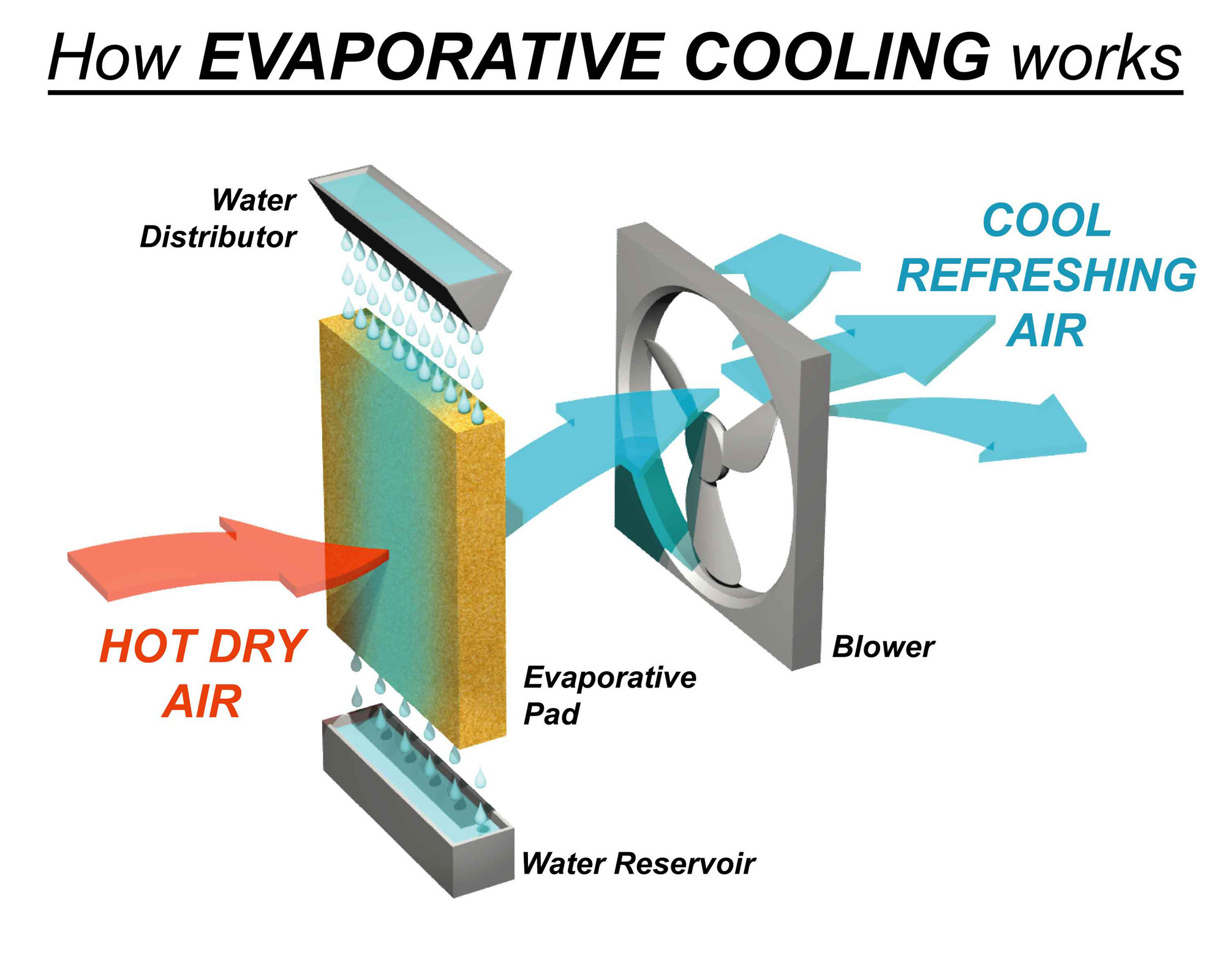
How Evaporative Cooler Works At Jeffrey Benson Blog An evaporative cooler is a device that chills air by evaporating liquid water into water vapor. other names for an evaporative cooler are a swamp cooler, desert cooler, evaporative air conditioner, or swamp box. while highly effective coolers, evaporative cooling is not appropriate for every situation. for example, if you start with humid air. Evaporative cooling technology (ect) has been deemed as an alternative to the conventional vapor compression air conditioning system for dry climates in recent years due to its simple structure and low operating cost. generally speaking, the ect includes two types of different technologies, direct evaporative cooling (dec) and indirect evaporative cooling (iec). both technologies can. Direct evaporative cooling systems. in a direct evaporative cooling system outside air is pulled through a water saturated medium (typical cellulose) or air is sprayed with water and cooled by evaporation. the cooled air is circulated by a blower. moisture can be added to the air stream until saturation. dry bulb temperature is reduced. Cooling system. in subject area: agricultural and biological sciences. the evaporative cooling system involves the transfer of mass and heat from sensible heat into latent heat known as the adiabatic process thereby evaporating water and resulting in a reduction in temperature. from: engineering principles, modeling and economics of evaporative.

So What Is Evaporative Cooling And How Does It Work Direct evaporative cooling systems. in a direct evaporative cooling system outside air is pulled through a water saturated medium (typical cellulose) or air is sprayed with water and cooled by evaporation. the cooled air is circulated by a blower. moisture can be added to the air stream until saturation. dry bulb temperature is reduced. Cooling system. in subject area: agricultural and biological sciences. the evaporative cooling system involves the transfer of mass and heat from sensible heat into latent heat known as the adiabatic process thereby evaporating water and resulting in a reduction in temperature. from: engineering principles, modeling and economics of evaporative.
Split System Vs Evaporative Cooling What Is The Difference Gehde

Comments are closed.