Ep 8 Noise Induced Hearing Loss What To Avoid And How To Diagnose
Noise Induced Hearing Loss Hearing Loss Association Of America Dr. allie and kevin discuss misconceptions, and experiences, with situations that could cause noise induced hearing loss. they share advice on what to avoid,. Evidence that military noise exposure is typically sufficient to cause hearing loss in a substantial proportion of men is provided by figure 1 in moore (2020), showing that about 50% of professional military personnel have hearing loss in the frequency range 6–8 khz, and by figure 2 in moore (2020), showing that the mean hearing loss after 10.

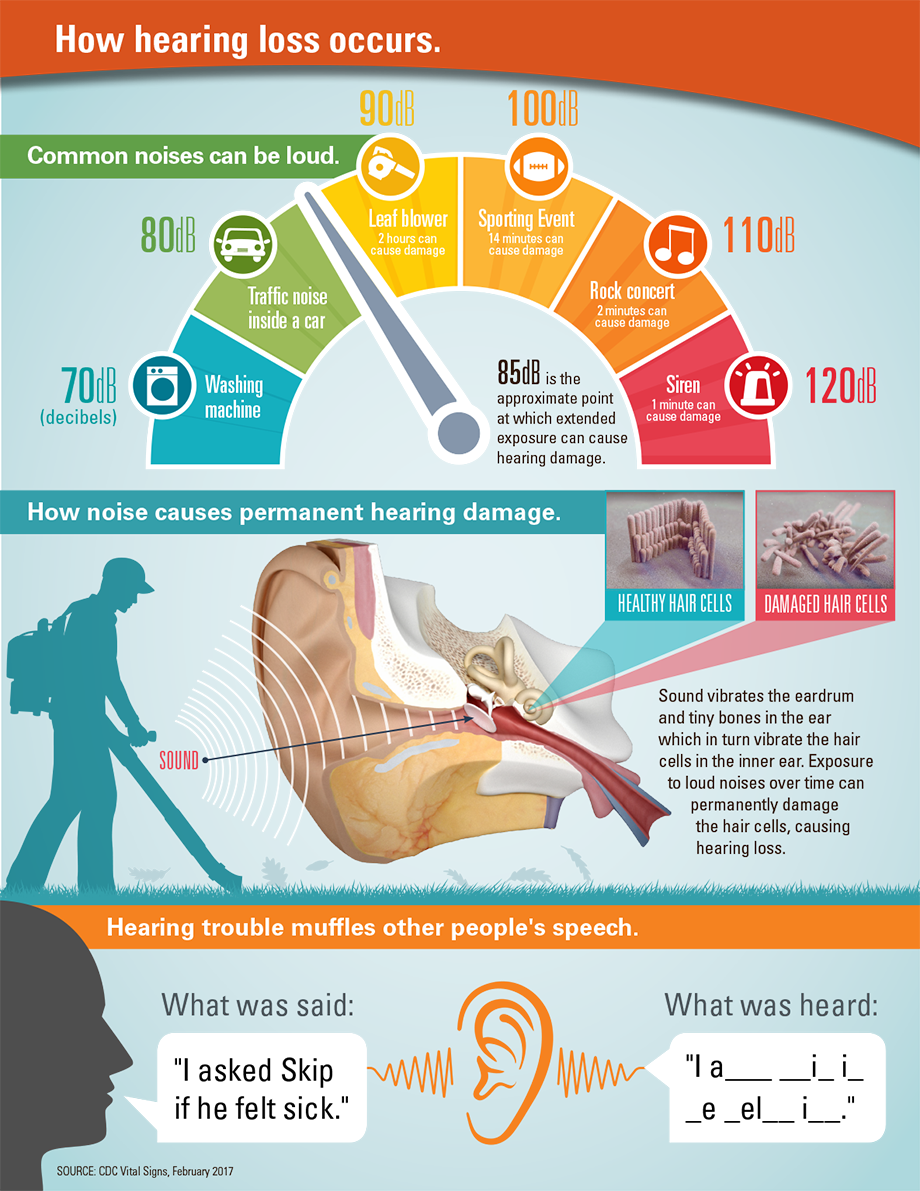
Noise Induced Hearing Loss Nihl Hearing Loss From Loud Noise Some of the most common symptoms of nihl include: a feeling of fullness or pressure in your ear. inability to hear high pitched sounds, like birds singing. muffled or distorted speech. symptoms can last minutes, hours or days after noise exposure ends. your hearing may return to normal, but you still have damage. The sight and hearing association distributes “know noise,” a curriculum for third to sixth grade students on prevention of noise induced hearing loss. sight and hearing association. 674. Hearing loss and tinnitus can occur in one or both ears. sometimes exposure to impulse or continuous loud noise causes a temporary hearing loss that disappears 16 to 48 hours later. recent research suggests, however, that although the loss of hearing seems to disappear, there may be residual long term damage to your hearing. A. morgan selleck, md, hamid r. djalilian, md, and isaac d. erbele, md, hearing committee members. approximately 23 million americans aged 20 and older suffer from noise induced hearing loss (nihl). 1 nihl is the most significant preventable cause of hearing loss in the united states. 2 nihl has traditionally been defined as occurring at 3, 4.

Understanding Noise Induced Hearing Loss Nihl Earsolutions Hearing loss and tinnitus can occur in one or both ears. sometimes exposure to impulse or continuous loud noise causes a temporary hearing loss that disappears 16 to 48 hours later. recent research suggests, however, that although the loss of hearing seems to disappear, there may be residual long term damage to your hearing. A. morgan selleck, md, hamid r. djalilian, md, and isaac d. erbele, md, hearing committee members. approximately 23 million americans aged 20 and older suffer from noise induced hearing loss (nihl). 1 nihl is the most significant preventable cause of hearing loss in the united states. 2 nihl has traditionally been defined as occurring at 3, 4. Noise induced hearing loss. approximately 40 million american adults may have hearing loss resulting from noise exposure. 1 noise induced hearing loss is caused by damage to the hair cells found in the inner ear. hair cells are small sensory cells that convert the sounds we hear (sound energy) into electrical signals that travel to the brain. The decibel scale for noise induced hearing loss is as follows: 110–150 decibels: permanent hearing loss may occur. it can result from fireworks, gunshots, jet planes, sirens, jackhammers, chain saws, personal music players at full volume, or music concerts. 90–110 decibels: gradual hearing loss is experienced over a period of time.
Noise Induced Hearing Loss Pacific Northwest Audiology Noise induced hearing loss. approximately 40 million american adults may have hearing loss resulting from noise exposure. 1 noise induced hearing loss is caused by damage to the hair cells found in the inner ear. hair cells are small sensory cells that convert the sounds we hear (sound energy) into electrical signals that travel to the brain. The decibel scale for noise induced hearing loss is as follows: 110–150 decibels: permanent hearing loss may occur. it can result from fireworks, gunshots, jet planes, sirens, jackhammers, chain saws, personal music players at full volume, or music concerts. 90–110 decibels: gradual hearing loss is experienced over a period of time.

Comments are closed.