Engine Cooling System History At Donald Winkle Blog

Engine Cooling System History At Donald Winkle Blog In the video, we learn about the general structure and operating principle of one of the subsystems of a car engine the engine cooling system. the video br. An engine cooling system is a set of various parts that allow liquid coolant to flow through the engine block and cylinder head passages to absorb the unnecessary engine heat. as the coolant absorbs heat, its temperature increases. this hot coolant is returned to the radiator through a rubber hose for cooling.
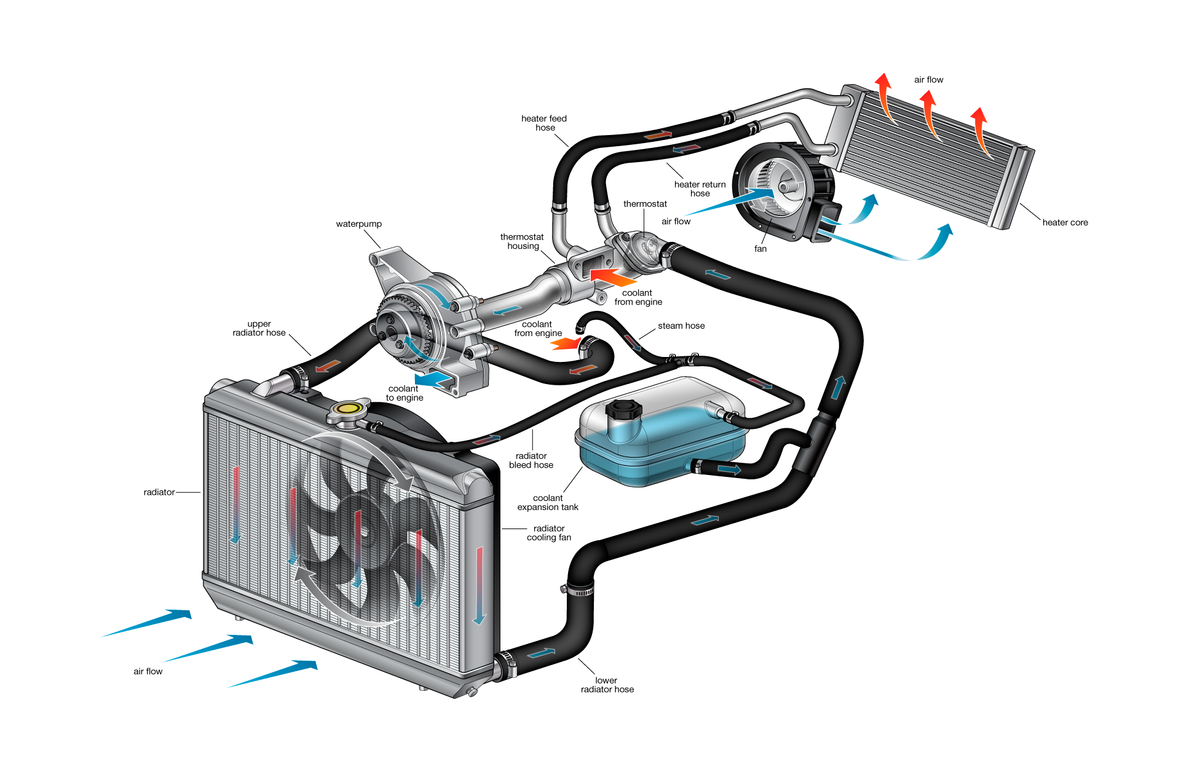
Engine Cooling System History At Donald Winkle Blog The emergence of organic acid technology. the history of automotive cooling systems reflects a continuous quest. engine cooling system history. from . diesel engines 101. how the engine cooling system operates. engine cooling system history coolants play an important role in our past and our future. from the design of. 1] removes extra heat: it is the main function of the engine cooling system to carry away the excess heat generated by the engine. 2] helps to attain optimum temperature faster: the optimum temperature means the temperature at which the engine gives better performance. thus, after starting the engine, it is necessary that the engine should. Internal combustion engine cooling uses either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from an internal combustion engine. for small or special purpose engines, cooling using air from the atmosphere makes for a lightweight and relatively simple system. watercraft can use water directly from the surrounding environment to cool their engines. 1. radiator. radiator is an iron shaped composers used to cool coolant. the working principle of the radiator is to move the temperature from water to free air. in a radiator will be encountered some parts like. upper tank, is a tank to hold hot water or coolant from the engine. lower tank, is a tank to hold coolant that has been cooled and.
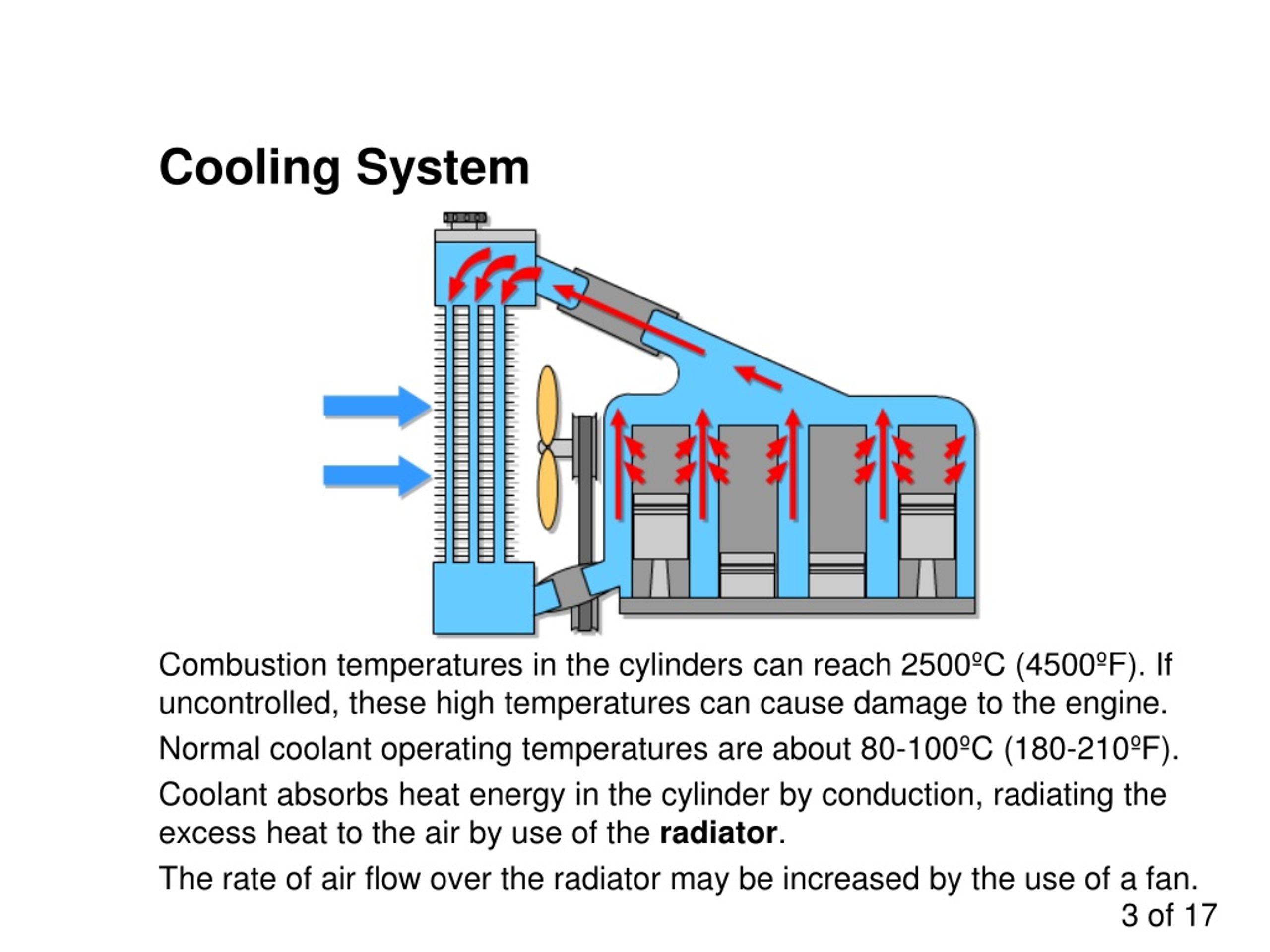
Engine Cooling System History At Donald Winkle Blog Internal combustion engine cooling uses either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from an internal combustion engine. for small or special purpose engines, cooling using air from the atmosphere makes for a lightweight and relatively simple system. watercraft can use water directly from the surrounding environment to cool their engines. 1. radiator. radiator is an iron shaped composers used to cool coolant. the working principle of the radiator is to move the temperature from water to free air. in a radiator will be encountered some parts like. upper tank, is a tank to hold hot water or coolant from the engine. lower tank, is a tank to hold coolant that has been cooled and. When the engine warms up, the wax melts, expands and pushes the valve open, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator. when the engine stops and cools, the valve closes again. water expands when it freezes, and if the water in an engine freezes it can burst the block or radiator. so antifreeze usually ethylene glycol is added to the water. The basics remain the same. the cooling system is filled with a 50 50 mixture of ethylene glycol and water. this fluid is referred to as antifreeze or coolant. it is the media used by the cooling system to remove engine heat and disperse it. antifreeze is kept under pressure in the cooling system as the heat expands the fluid, up to 15 psi.
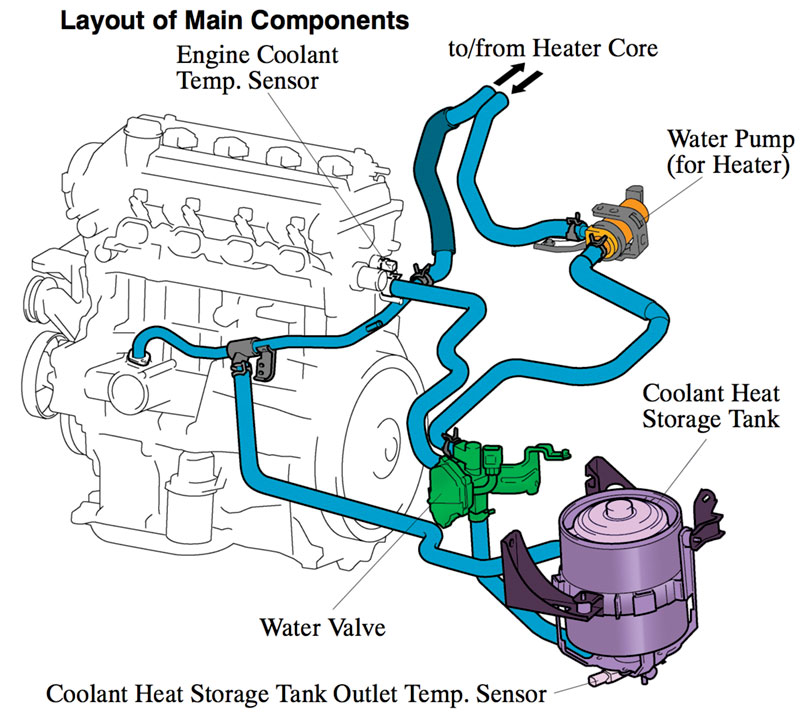
Engine Cooling System History At Donald Winkle Blog When the engine warms up, the wax melts, expands and pushes the valve open, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator. when the engine stops and cools, the valve closes again. water expands when it freezes, and if the water in an engine freezes it can burst the block or radiator. so antifreeze usually ethylene glycol is added to the water. The basics remain the same. the cooling system is filled with a 50 50 mixture of ethylene glycol and water. this fluid is referred to as antifreeze or coolant. it is the media used by the cooling system to remove engine heat and disperse it. antifreeze is kept under pressure in the cooling system as the heat expands the fluid, up to 15 psi.

Comments are closed.