Embryology Evolution
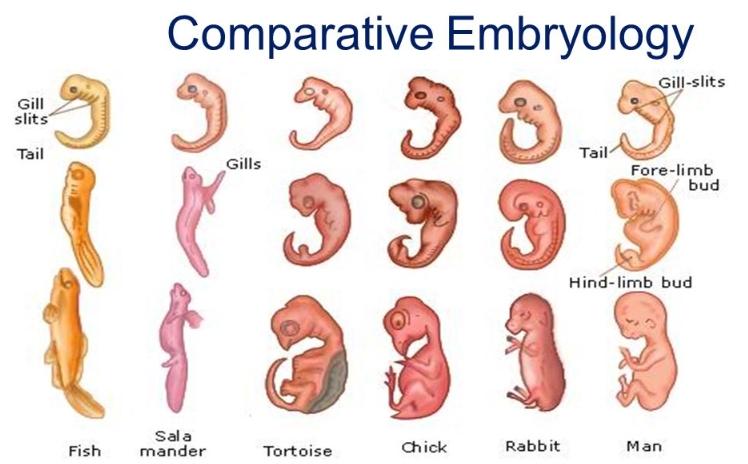
Comparative Embryology Developmental In Biology Freeskill All animals originate in the same way: fusion of egg and sperm give rise to a single cell that develops into a multicellular embryo and later into an adult. the first step of embryonic development. Embryology is the study of embryos and their development. evolution is the study of how organisms change and adapt over time. learn how embryology provides evidence for evolution by showing similarities in early stages of embryonic development across different species.
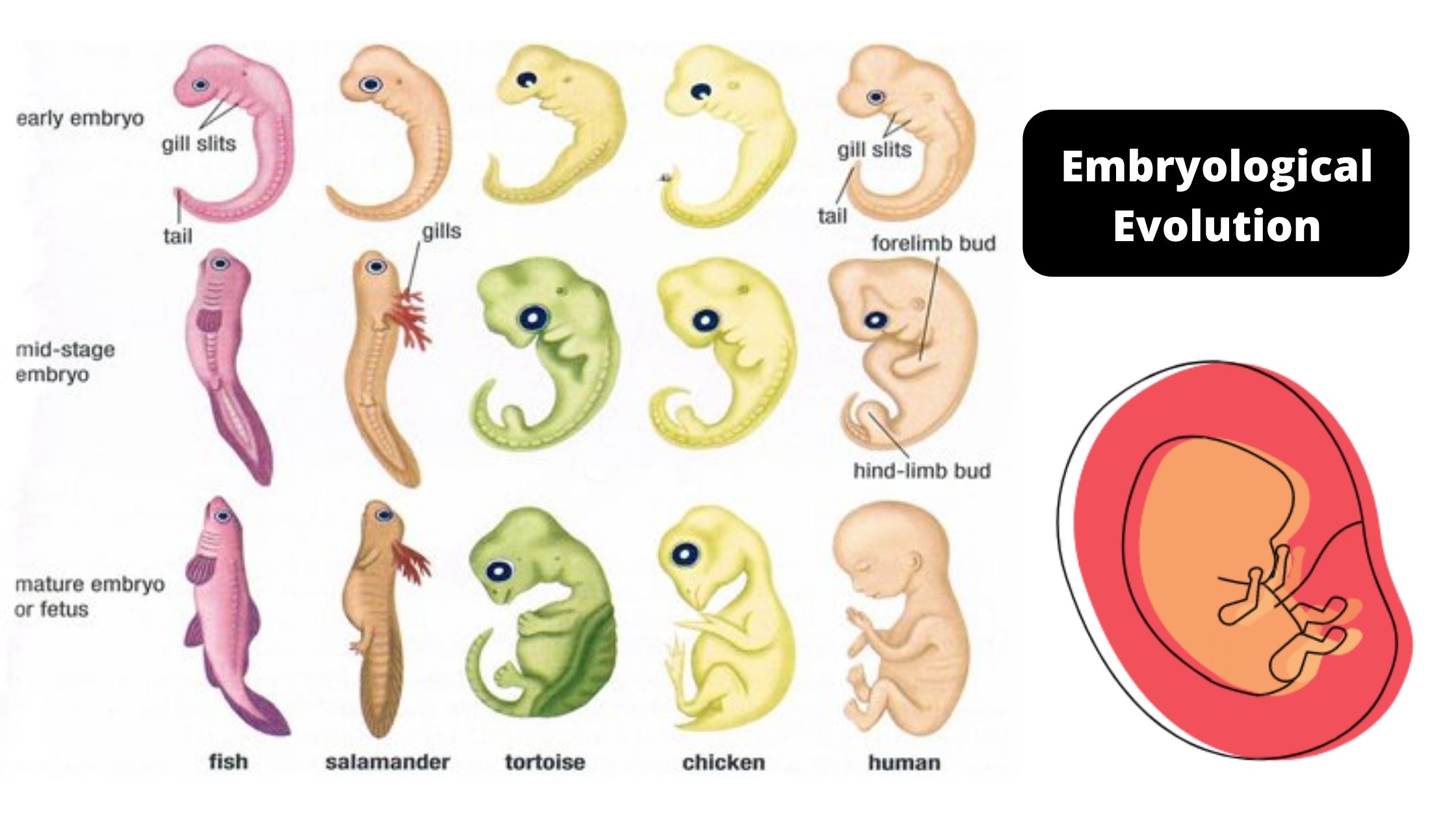
Basic Microbiology Microbiology Note Learn about the history and principles of embryology, the study of the formation and development of an embryo and fetus. explore the discoveries of pioneers such as aristotle, harvey, von baer, roux, spemann, and harrison. Evolutionary embryology. charles darwin's theory of evolution restructured comparative embryology and gave it a new focus. after reading johannes müller's summary of von baer's laws in 1842, darwin saw that embryonic resemblances would be a very strong argument in favor of the genetic connectedness of different animal groups. Anatomy and embryology. another type of evidence for evolution is the presence of structures in organisms that share the same basic form. for example, the bones in the appendages of a human, dog, bird, and whale all share the same overall construction (figure 21.1.2 21.1. 2) resulting from their origin in the appendages of a common ancestor. Learn how developmental features of present day organisms reflect their ancestral origins and support common ancestry. see examples of snake limb buds, baleen whale teeth, and more.
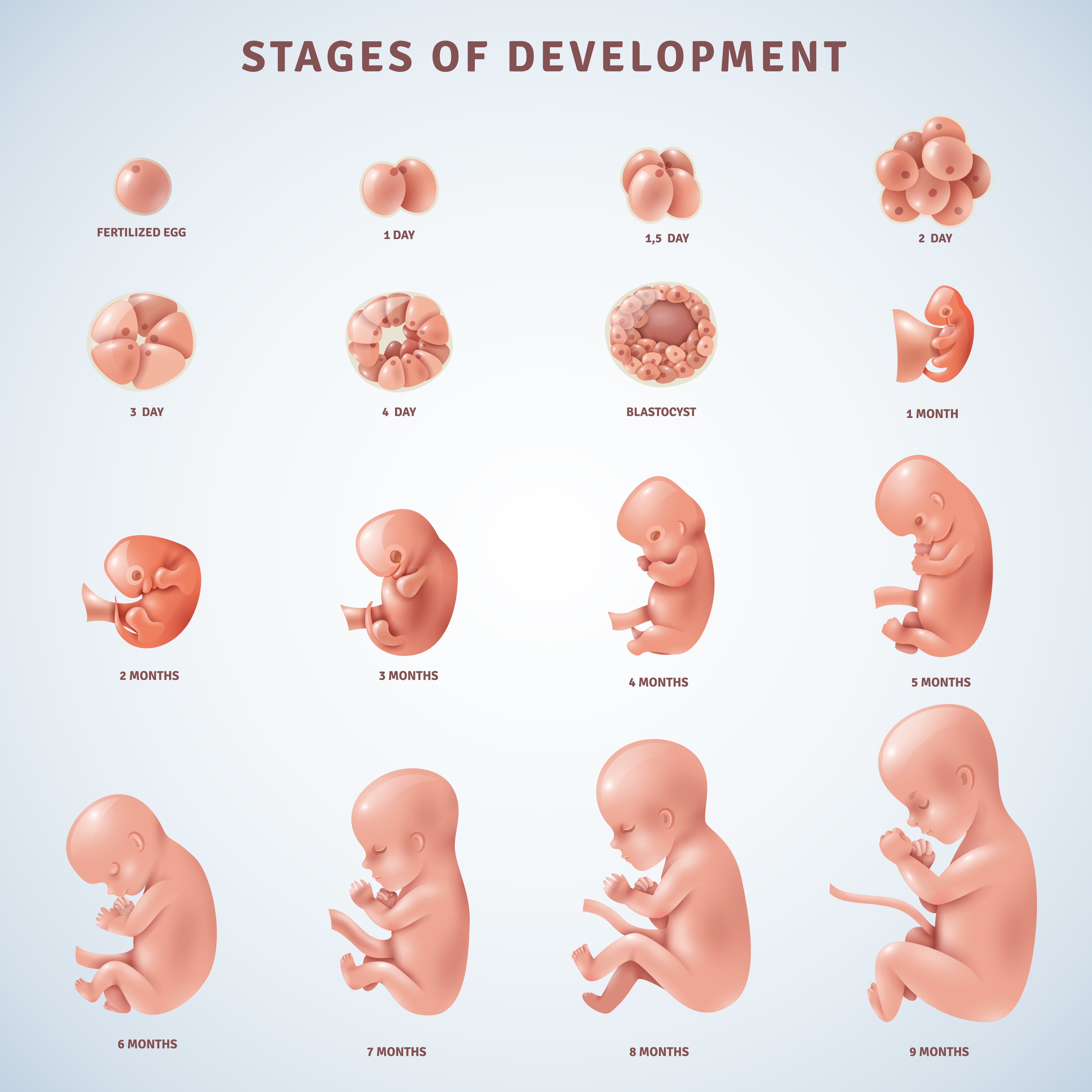
Stages Human Embryonic Development 475937 Vector Art At Vecteezy Anatomy and embryology. another type of evidence for evolution is the presence of structures in organisms that share the same basic form. for example, the bones in the appendages of a human, dog, bird, and whale all share the same overall construction (figure 21.1.2 21.1. 2) resulting from their origin in the appendages of a common ancestor. Learn how developmental features of present day organisms reflect their ancestral origins and support common ancestry. see examples of snake limb buds, baleen whale teeth, and more. Evolutionary developmental biology (evo–devo) is that part of biology concerned with how changes in embryonic development during single generations relate to the evolutionary changes that occur between generations. charles darwin argued for the importance of development (embryology) in understanding evolution. after the discovery in 1900 of mendel’s research on genetics, however, any. Evidence of evolution: embryology. evidence of evolution: embryology. apply: embryology and evolution. science > middle school biology > evolution >.

Comments are closed.