Elasticity Of Demand Explained
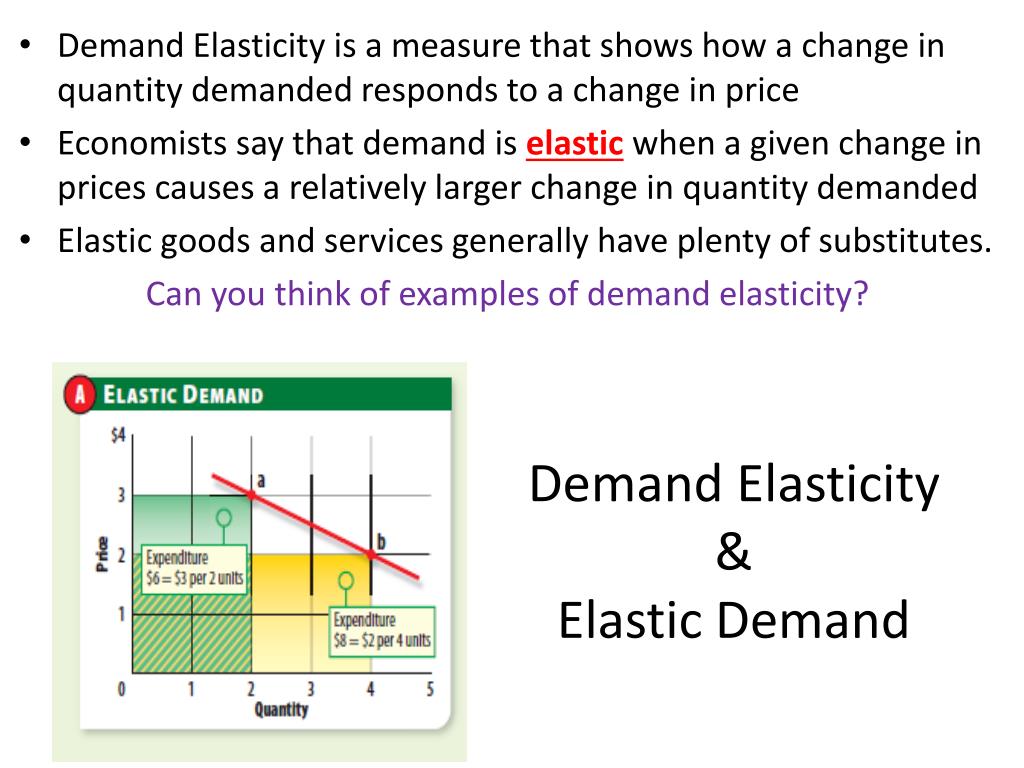
Elasticity Of Demand Explained Price elasticity of demand is a ratio that represents how a change in price affects demand for a product. learn what the different ratios mean for consumer behavior. Again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more. it is read as an absolute value. in this case, a 1% rise in price causes an increase in quantity supplied of 3.5%.

Elasticity Elasticity Of Demand Definition Economics Formula A good's price elasticity of demand ( , ped) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. when the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good (law of demand), but it falls more for some than for others. the price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent. Understanding elasticity. 26 february 2017 by tejvan pettinger. elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. price elasticity of demand (ped) – measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. price elasticity of supply (pes. The price elasticity of demand (ped) is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price. it can be calculated from the following formula: % change in quantity demanded % change in price (6.1.3) (6.1.3) % change in quantity demanded % change in price. when ped is greater than one, demand is elastic. Learn how to calculate and interpret ped, which measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price. find out the factors that affect elasticity and the implications for revenue, price discrimination and tax incidence.

Explaining Price Elasticity Of Demand Tutor2u Economics The price elasticity of demand (ped) is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price. it can be calculated from the following formula: % change in quantity demanded % change in price (6.1.3) (6.1.3) % change in quantity demanded % change in price. when ped is greater than one, demand is elastic. Learn how to calculate and interpret ped, which measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price. find out the factors that affect elasticity and the implications for revenue, price discrimination and tax incidence. Explain the concept of price elasticity of demand and its calculation. explain what it means for demand to be price inelastic, unit price elastic, price elastic, perfectly price inelastic, and perfectly price elastic. explain how and why the value of the price elasticity of demand changes along a linear demand curve. Elasticity is a term used in economics to describe responsiveness in one variable to changes in another. typically, elasticity is used to describe how much demand for a product changes as its.
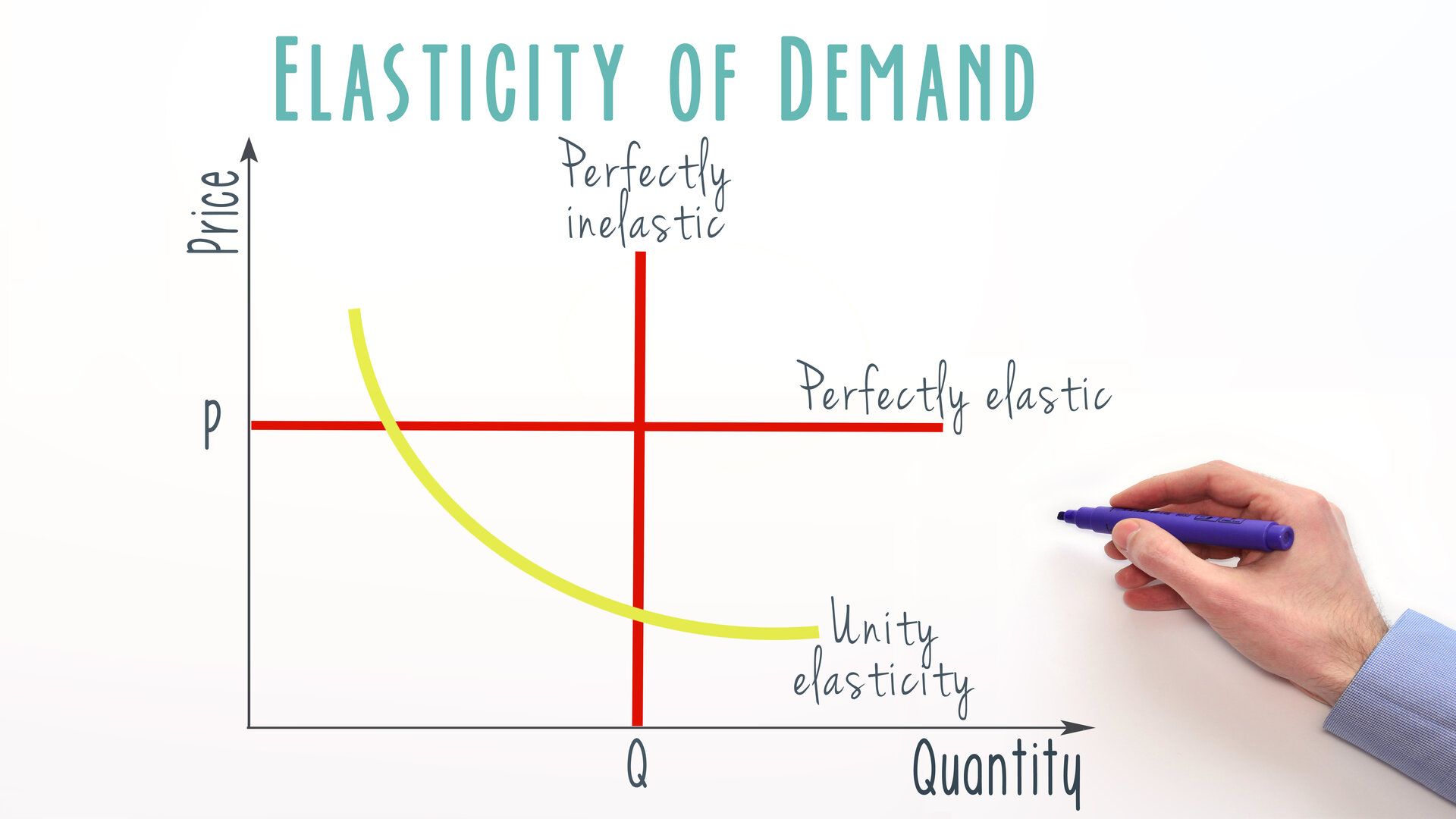
What Is Price Elasticity Of Demand Formula Examples Explain the concept of price elasticity of demand and its calculation. explain what it means for demand to be price inelastic, unit price elastic, price elastic, perfectly price inelastic, and perfectly price elastic. explain how and why the value of the price elasticity of demand changes along a linear demand curve. Elasticity is a term used in economics to describe responsiveness in one variable to changes in another. typically, elasticity is used to describe how much demand for a product changes as its.

Comments are closed.