Ecosystems What Are Producers Consumers Decomposers Sciencebytes

Ecosystems What Are Producers Consumers Decomposers Sciencebytes 🔥 the must have digital toolkit for mastering organisms & their environment! crafted by experts! 👉📲 get it now: teacherspayteachers produc. Producers are organisms that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. they are the primary source of energy for all other living organisms in an ecosystem. decomposers are organisms that break down dead plant and animal matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. consumers are organisms that obtain their energy by consuming.
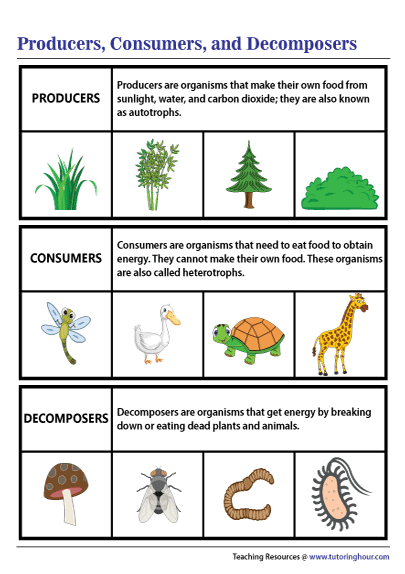
Producers Consumers And Decomposers Diagram Aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. Food chains always start with a producer. this is usually a green plant or algae that completes. to store energy from sunlight as glucose. grass is the producer in the grass → rabbit → fox. Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Today, we're going to delve into the intricate world of ecosystems – those complex webs where life and the environment coexist. we'll explore the roles and r.

Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers Food Chain In Pond Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Today, we're going to delve into the intricate world of ecosystems – those complex webs where life and the environment coexist. we'll explore the roles and r. This tutorial will introduce the main types of biotic (living) factors in ecosystems as producers, consumers, and decomposers. students will learn how producers (e.g., plants) and consumers (e.g., animals) interact in the environment and the role they play in sustaining healthy ecosystems. watch the video to learn more. In an ecosystem, you will find producers, consumers, and decomposers that are all interconnected and depend on each other to survive. a producer is a living organism that creates its own food using sunlight, such as most plants.

Comments are closed.