Economics Chapter 5 Section 3 Shifts In The Supply Curve
Shifts In The Supply Curve Ilearnthis In supply because the good has become more expensive to produce. marginal cost. a rise in the cost of an input will translate directly into a higher. cut production and lower the marginal cost into it equals the lower price (supply curve shifts left) if a firm has no control over the price the only solution is to technology. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like any change in the cost of an input used to produce a good (e.g labor, machinery) will affect, a rise in the cost of an input will cause, a supplier sets output at the most profitable level, where marginal revenue (price) is equal to marginal cost marginal cost includes the cost of the inputs that go into production, so a rise in.

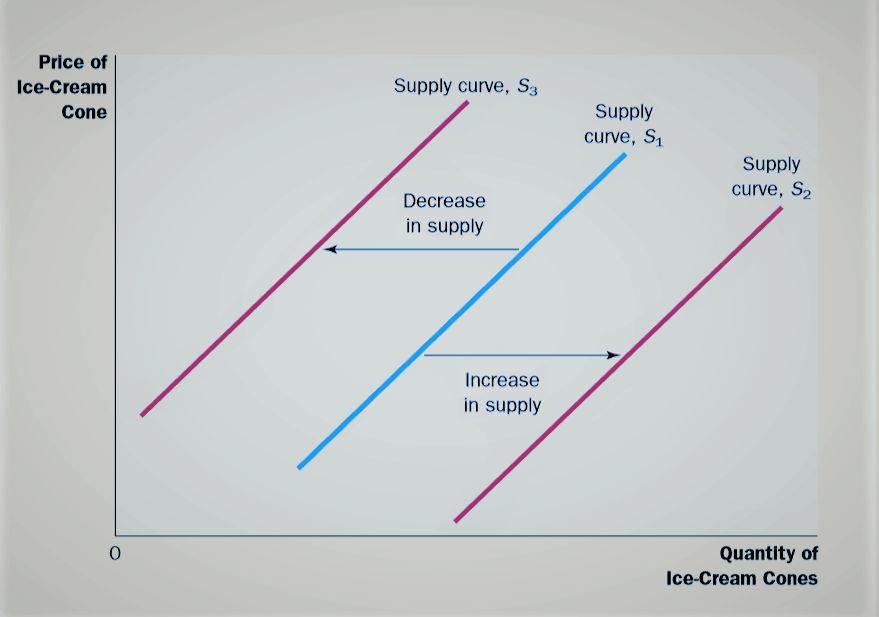
Factors Affecting Supply Economics Help 13. when one company enters the market with a successful idea, the may increase as other producers may enter the market and increase the supply of the good or service. when this happens, the supply curve shifts to the right. Figure 3.10 shifts in supply: a car example decreased supply means that at every given price, the quantity supplied is lower, so that the supply curve shifts to the left, from s 0 to s 1. increased supply means that at every given price, the quantity supplied is higher, so that the supply curve shifts to the right, from s 0 to s 2. 5.3 elasticity and pricing. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: analyze how price elasticities impact revenue. evaluate how elasticity can cause shifts in demand and supply. predict how the long run and short run impacts of elasticity affect equilibrium. Economics: chapter 5. the document discusses supply, including the law of supply, how profits influence production levels and market entry, supply schedules and graphs, elasticity of supply in the short and long run, costs of production including fixed, variable, and marginal costs, and how firms determine output levels.

Movement And Shift In Supply Curve 5.3 elasticity and pricing. learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: analyze how price elasticities impact revenue. evaluate how elasticity can cause shifts in demand and supply. predict how the long run and short run impacts of elasticity affect equilibrium. Economics: chapter 5. the document discusses supply, including the law of supply, how profits influence production levels and market entry, supply schedules and graphs, elasticity of supply in the short and long run, costs of production including fixed, variable, and marginal costs, and how firms determine output levels. The shift is generally in terms of the quantity when the supply curve is elastic. figure 6.7 impact of elasticity of the supply curve on the impact of a shift in the demand curve. the shift is generally in terms of the price when the supply curve is inelastic. a shift in the supply curve has a different effect on the equilibrium. The shift of supply to the right, from s 0 to s 2, means that at all prices, the quantity supplied has increased. in this example, at a price of $20,000, the quantity supplied increases from 18 million on the original supply curve (s 0) to 19.8 million on the supply curve s 2, which is labeled m.

Comments are closed.