Ecg For Beginners Ecg Diagnosis Of St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Stemi

Ecg For Beginners Ecg Diagnosis Of St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Learn how to diagnose st elevation myocardial infarction on ecg and how to determine the location of the infarct. Ecg (ekg) in acute stemi (st elevation myocardial infarction) the ecg is the key to diagnosing stemi. ecg criteria for stemi are not used in the presence of left bundle branch block (lbbb) or left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) because these conditions cause secondary st t changes which may mask or simulate ischemic st t changes.
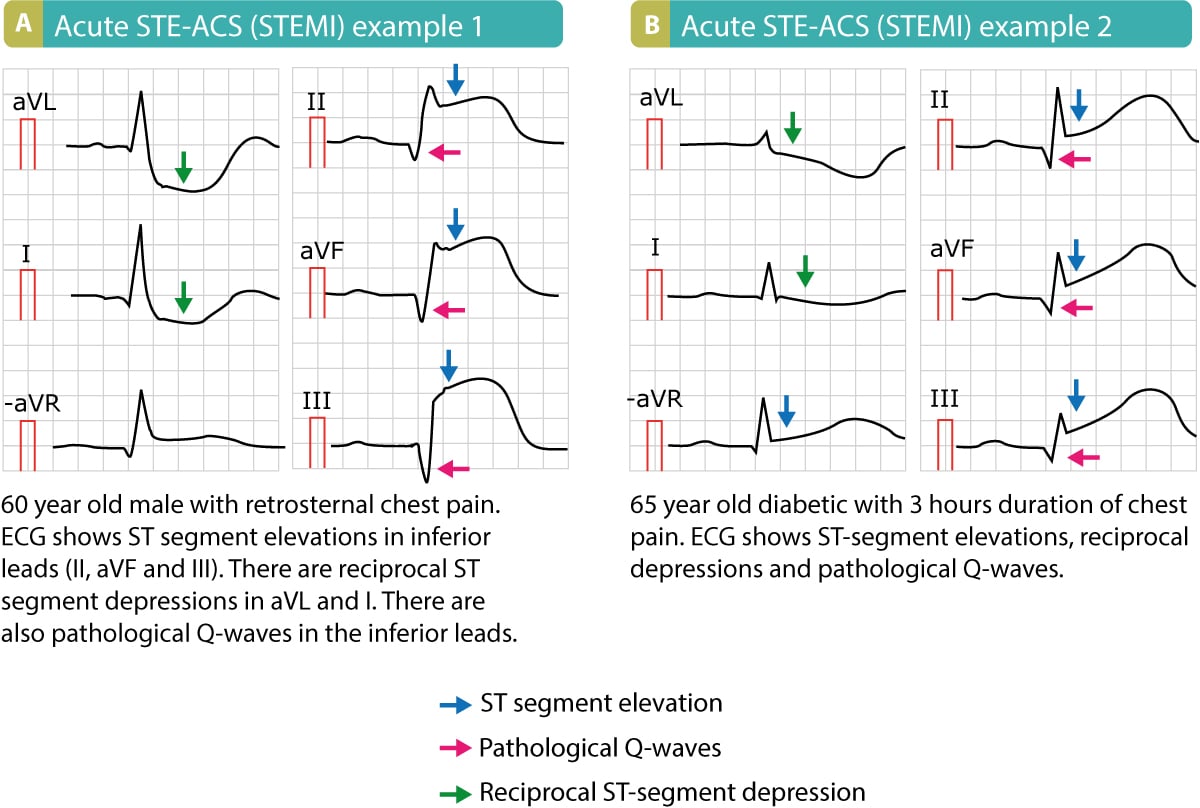
Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis Criteria Ecg An acute st segment elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) arises from the occlusion of 1 or more coronary arteries, causing transmural myocardial ischemia and subsequent myocardial injury or necrosis. risk factors for stemi include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and diabetes, which contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and. In stemi ste acs, on the other hand, reciprocal st segment depressions are typical and there may be t wave inversions in the same leads showing st segment elevation. t wave inversion may, however, occur in perimyocarditis, but only after normalization of the st segment elevations (i.e these two ecg changes do not occur simultaneously). St elevation myocardial infarction (stemi): characterised by transmural myocardial ischaemia causing myocardial injury necrosis; diagnosed by acute anginal chest pain and st elevation on an ecg. aetiology: caused by complete occlusion of one or more coronary arteries, usually due to a thrombus. risk factors: non modifiable (male sex, older age. References. st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) is a clinical syndrome defined by characteristic symptoms of myocardial ischemia in association with persistent electrocardiographic st elevation (ste) and subsequent release of biomarkers of myocardial necrosis. 1 ste is the single best immediately available surrogate marker for detecting.
Ecg Of St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Stemi Vector Image St elevation myocardial infarction (stemi): characterised by transmural myocardial ischaemia causing myocardial injury necrosis; diagnosed by acute anginal chest pain and st elevation on an ecg. aetiology: caused by complete occlusion of one or more coronary arteries, usually due to a thrombus. risk factors: non modifiable (male sex, older age. References. st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) is a clinical syndrome defined by characteristic symptoms of myocardial ischemia in association with persistent electrocardiographic st elevation (ste) and subsequent release of biomarkers of myocardial necrosis. 1 ste is the single best immediately available surrogate marker for detecting. Division of cardiology, university of texas medical branch, 5.106 john sealy annex, 301 university boulevard, galveston, tx 77555, usa. the ecg is the most useful and feasible diagnostic tool for the initial evaluation, early risk stratification, triage, and guidance of therapy in patients who have chest pain. there is currently a growing trend. St elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) presents with central chest pain that is classically heavy in nature, like a sensation of pressure or squeezing. examination is variable, and findings range from normal to a critically ill patient in cardiogenic shock. a clinical working diagnosis of stemi is made when a patient presents with symptoms.
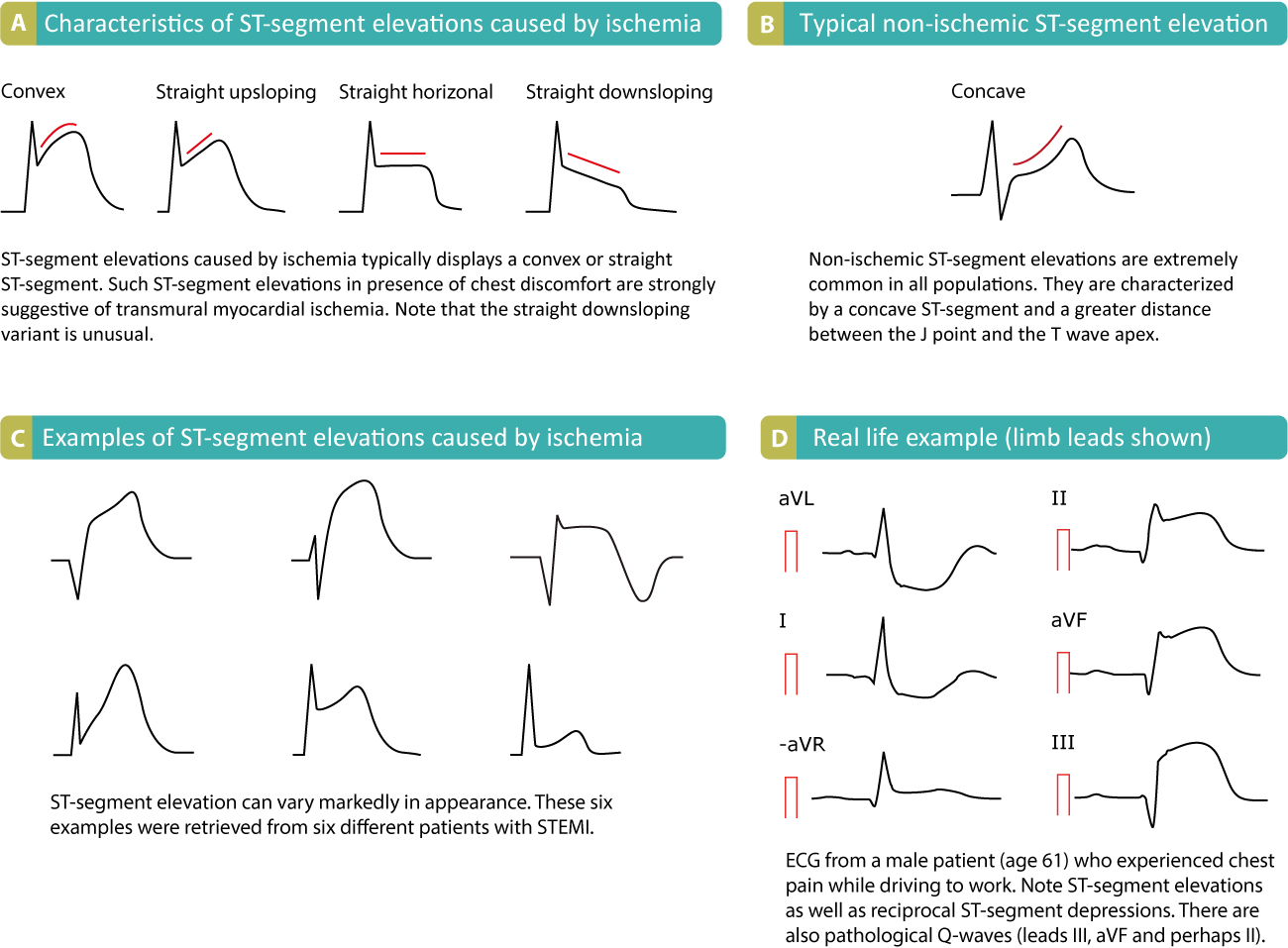
Stemi St Elevation Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis Criteria Ecg Division of cardiology, university of texas medical branch, 5.106 john sealy annex, 301 university boulevard, galveston, tx 77555, usa. the ecg is the most useful and feasible diagnostic tool for the initial evaluation, early risk stratification, triage, and guidance of therapy in patients who have chest pain. there is currently a growing trend. St elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) presents with central chest pain that is classically heavy in nature, like a sensation of pressure or squeezing. examination is variable, and findings range from normal to a critically ill patient in cardiogenic shock. a clinical working diagnosis of stemi is made when a patient presents with symptoms.

Comments are closed.