Dsm 5 Self Rated Level 1 Cross Cutting Symptom Measure Adult

Selected Dsm 5 Assessment Measures Neupsy Key The dsm 5 level 1 cross cutting symptom measure is a self or informant rated measure that assesses mental health domains that are important across psychiatric diagnoses. it is intended to help clinicians identify additional areas of inquiry that may have significant impact on the individual’s treatment and prognosis. Dsm 5 parent guardian rated level 1 cross cutting symptom measure—child age 6–17 (also available in print book) dsm 5 self rated level 1 cross cutting symptom measure—child age 11–17; level 2 cross cutting symptom measures for adults. level 2—depression—adult (promis emotional distress—depression—short form).

Fillable Online Dsm 5 Self Rated Level 1 Cross Cutting Symptom Measure The dsm 5 level 1 cross cutting symptom measure–adult (dsm xc) was developed by the american psychiatric association (apa) as a transdiagnostic measure of current mental health symptomatology. this paper describes utilization of the dsm xc to screen volunteers for participation in mental health research studies as healthy controls. The dsm 5 dimensional cross cutting symptom assessment for adult patients (narrow et al., 2013) is a proposed self or informant rated measure of mental health domains. the proposed measure was developed for a multisite test retest reliability field trial study, designed and coordinated by the dsm 5 research group at the american psychiatric association (apa). the measure used a stratified. Although the recent edition of the dsm (dsm 5; american psychiatric association, 2013a) retains a predominantly categorical diagnostic system, it has integrated a dimensional assessment of cross cutting symptoms, the dsm 5 self rated level 1 cross cutting symptom measure (ccsm; american psychiatric association, 2013b) in section iii (emerging. Sleeping less than usual, but still have a lot of energy? 5. starting lots more projects than usual or doing more risky things than usual? 6. feeling nervous, anxious, frightened, worried, or on edge? 7. feeling panic or being frightened? 8. avoiding situations that make you anxious?.

Selected Dsm 5 Assessment Measures Neupsy Key Although the recent edition of the dsm (dsm 5; american psychiatric association, 2013a) retains a predominantly categorical diagnostic system, it has integrated a dimensional assessment of cross cutting symptoms, the dsm 5 self rated level 1 cross cutting symptom measure (ccsm; american psychiatric association, 2013b) in section iii (emerging. Sleeping less than usual, but still have a lot of energy? 5. starting lots more projects than usual or doing more risky things than usual? 6. feeling nervous, anxious, frightened, worried, or on edge? 7. feeling panic or being frightened? 8. avoiding situations that make you anxious?. Abstract. the dsm 5 self rated level 1 cross cutting symptom measure was developed to aid clinicians with a dimensional assessment of psychopathology; however, this measure resembles a screening tool for several symptomatic domains. the objective of the current study was to examine the basic parameters of sensitivity, specificity, positive and. The dsm 5 tr level 1 cross cutting symptom measure is a self rated measure that assesses mental health domains that are important across psychiatric diagnoses. it is intended to help clinicians identify additional areas of inquiry that may have significant impact on the child’s treatment and prognosis. in addition, the measure may be used to.
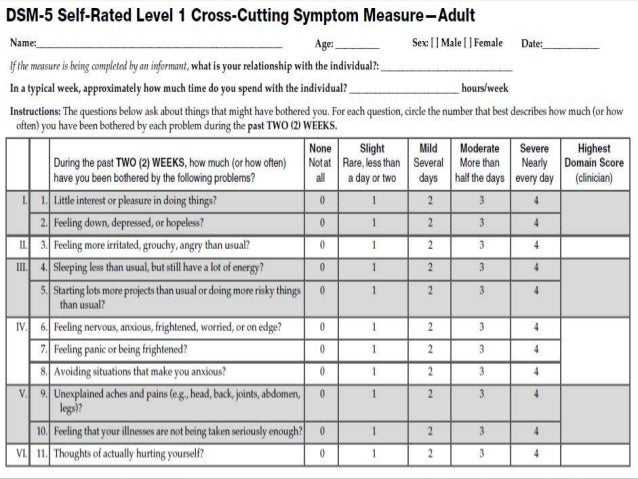
Dsm5 Cross Cutting Symptom Measures Abstract. the dsm 5 self rated level 1 cross cutting symptom measure was developed to aid clinicians with a dimensional assessment of psychopathology; however, this measure resembles a screening tool for several symptomatic domains. the objective of the current study was to examine the basic parameters of sensitivity, specificity, positive and. The dsm 5 tr level 1 cross cutting symptom measure is a self rated measure that assesses mental health domains that are important across psychiatric diagnoses. it is intended to help clinicians identify additional areas of inquiry that may have significant impact on the child’s treatment and prognosis. in addition, the measure may be used to.

Comments are closed.