Dsm 5 And Autism Spectrum Disorders The Changes You Haven T Heard
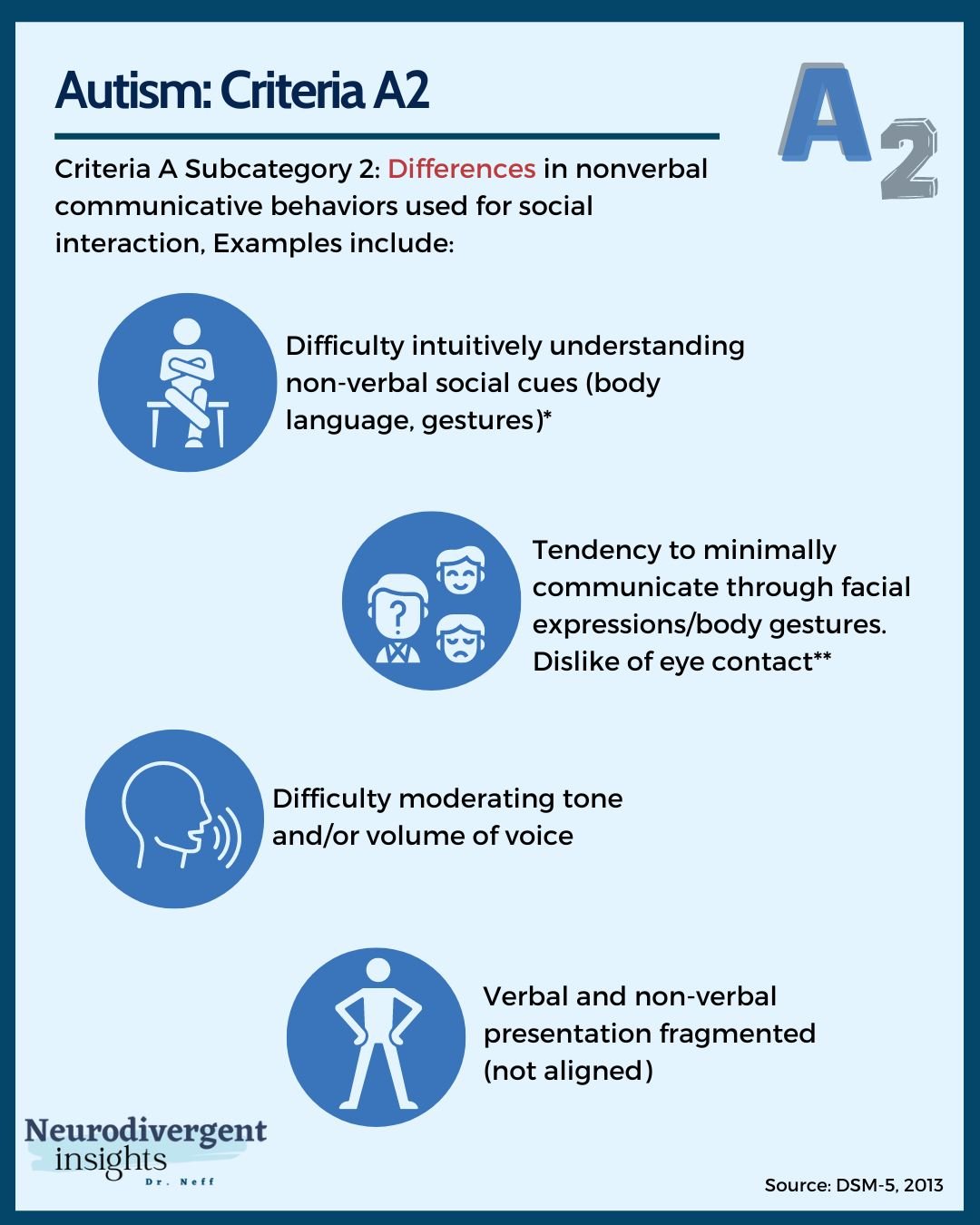
Dsm 5 Criteria For Autism Dsm 5 and autism spectrum disorders: the changes you haven't heard about yet. Article abstract†‹†‹†‹because this piece does not have an abstract, we have provided for your benefit the first 3 sentences of the full text.to the editor: much attention has been drawn to the changes within autism spectrum disorder (asd) criteria in dsm 5. however, in considering the asd revisions, the changes to diagnoses throughout dsm 5 also warrant discussion, because they.
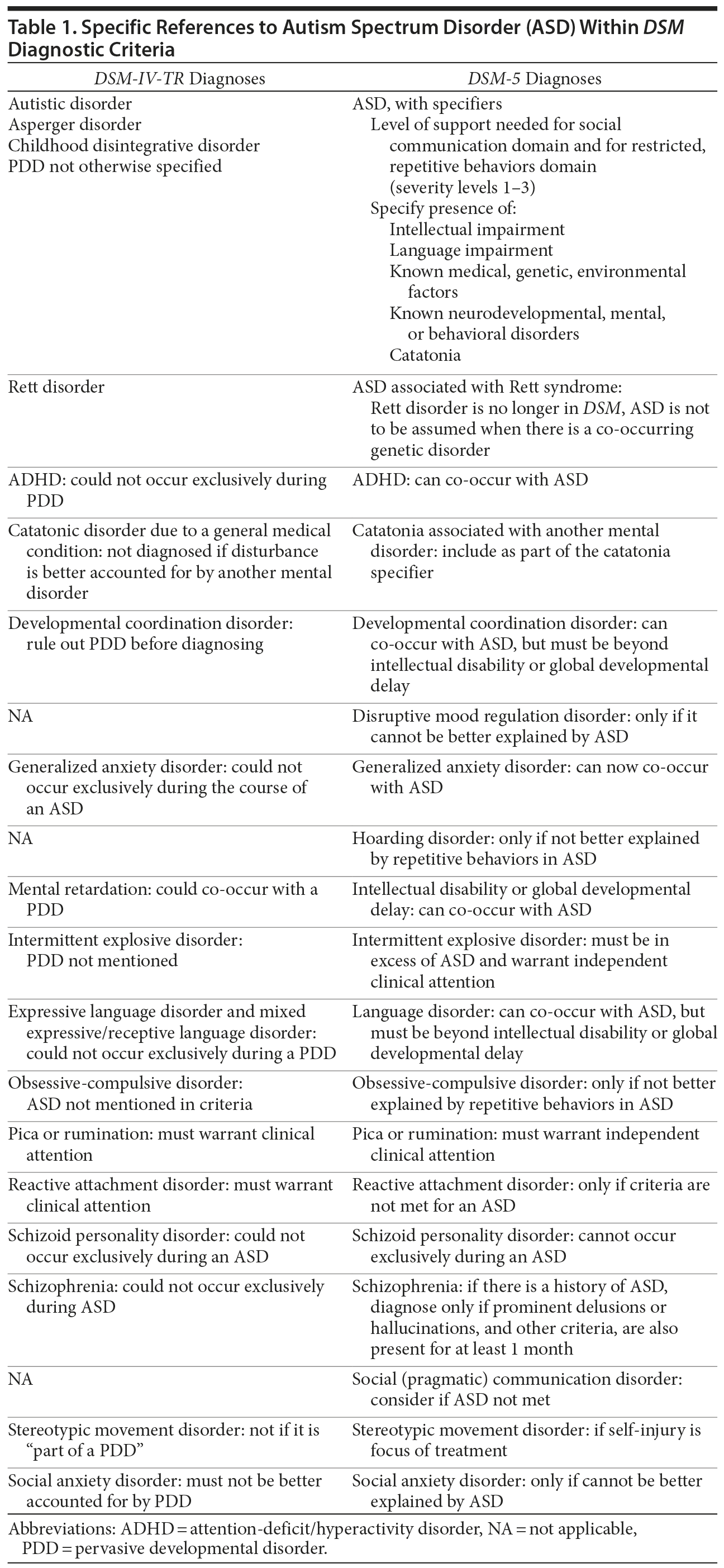
Dsm 5 And Autism Spectrum Disorders The Changes You Haven T Heard The dsm 5 removes the restriction of cooccurring disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder and adhd, in patients with asd (miller, 2014). due to the frequent cooccurring conditions between. Six major changes included: 1. four previously separate categories of autism consolidated into one umbrella diagnosis of “autism spectrum disorder.”. the previous categories were: autistic disorder. asperger syndrome. childhood disintegrative disorder. pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (pdd nos) 2. As asd is now considered part of a spectrum, the dsm 5 also includes three levels of support needs to differentiate patients under the diagnostic umbrella. levels can be assigned for each symptom and break down into “mild” (requiring support), “moderate” (requiring substantial support) and “severe” (requiring very substantial support). We conducted a 5 year follow up systematic review and meta analysis to determine change in frequency of autism spectrum disorder (asd) diagnosis since diagnostic and statistical manual 5 (dsm 5) publication and explore the impact of social communication disorder (scd). for 33 included studies, use o ….
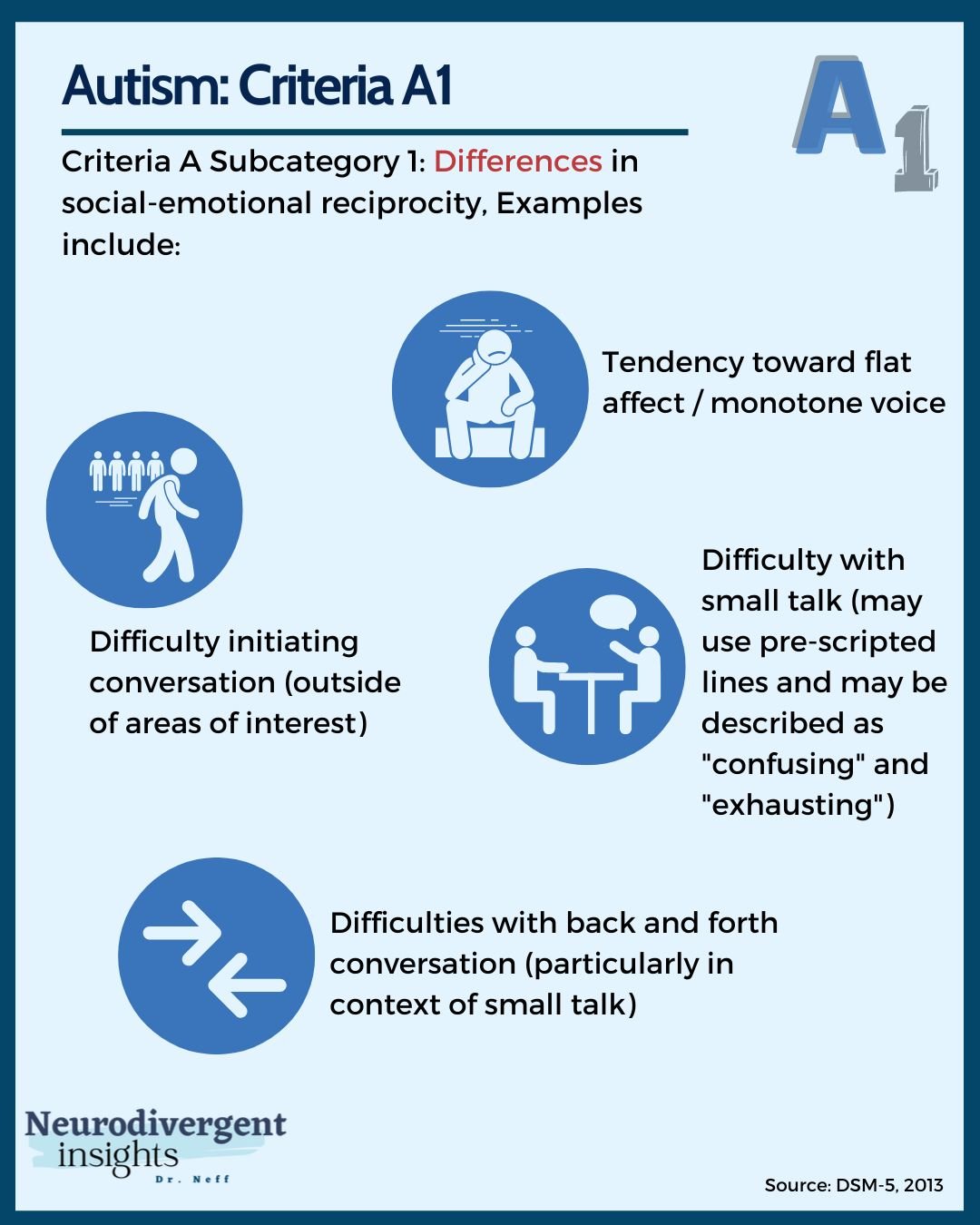
Dsm 5 Criteria For Autism As asd is now considered part of a spectrum, the dsm 5 also includes three levels of support needs to differentiate patients under the diagnostic umbrella. levels can be assigned for each symptom and break down into “mild” (requiring support), “moderate” (requiring substantial support) and “severe” (requiring very substantial support). We conducted a 5 year follow up systematic review and meta analysis to determine change in frequency of autism spectrum disorder (asd) diagnosis since diagnostic and statistical manual 5 (dsm 5) publication and explore the impact of social communication disorder (scd). for 33 included studies, use o …. Editorial: dsm 5 and autism spectrum disorders – two decades of perspectives from the jcpp. the newest revision of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (dsm), the dsm 5, will be published in less than a year and anticipation is high. the changes to the pervasive developmental disorders (pdd) criteria are likely to be. Autism in dsm 5. dsm 5 has been conceived as both conservative and progressive; it attempts to keep important diagnostic traditions intact while it introduces clinically important paradigmatic shifts. rejecting a categorical understanding of autism (with its all or nothing approach to diagnosis) and replacing it with a dimensional model is a.

Dsm 5 Changes In The Diagnosis Of Autism Spectrum Disorders Youtube Editorial: dsm 5 and autism spectrum disorders – two decades of perspectives from the jcpp. the newest revision of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (dsm), the dsm 5, will be published in less than a year and anticipation is high. the changes to the pervasive developmental disorders (pdd) criteria are likely to be. Autism in dsm 5. dsm 5 has been conceived as both conservative and progressive; it attempts to keep important diagnostic traditions intact while it introduces clinically important paradigmatic shifts. rejecting a categorical understanding of autism (with its all or nothing approach to diagnosis) and replacing it with a dimensional model is a.

Comments are closed.