Dsm 5 And Autism 2013

Dsm 5 Asd Guidelines Feb2013 Pdf Nonverbal Communication In 2013, the apa released the fifth edition of dsm (dsm 5). it stated that an autism diagnosis requires persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by the following: deficits in social emotional reciprocity, in nonverbal communicative behaviors used for social interaction, and in. Dsm 5 diagnostic criteria autism speaks is pleased to provide the full text of the diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder (asd) and the related diagnosis of social communication disorder (scd), as they appear in the fifth edition of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (dsm 5). as of may 2013,.
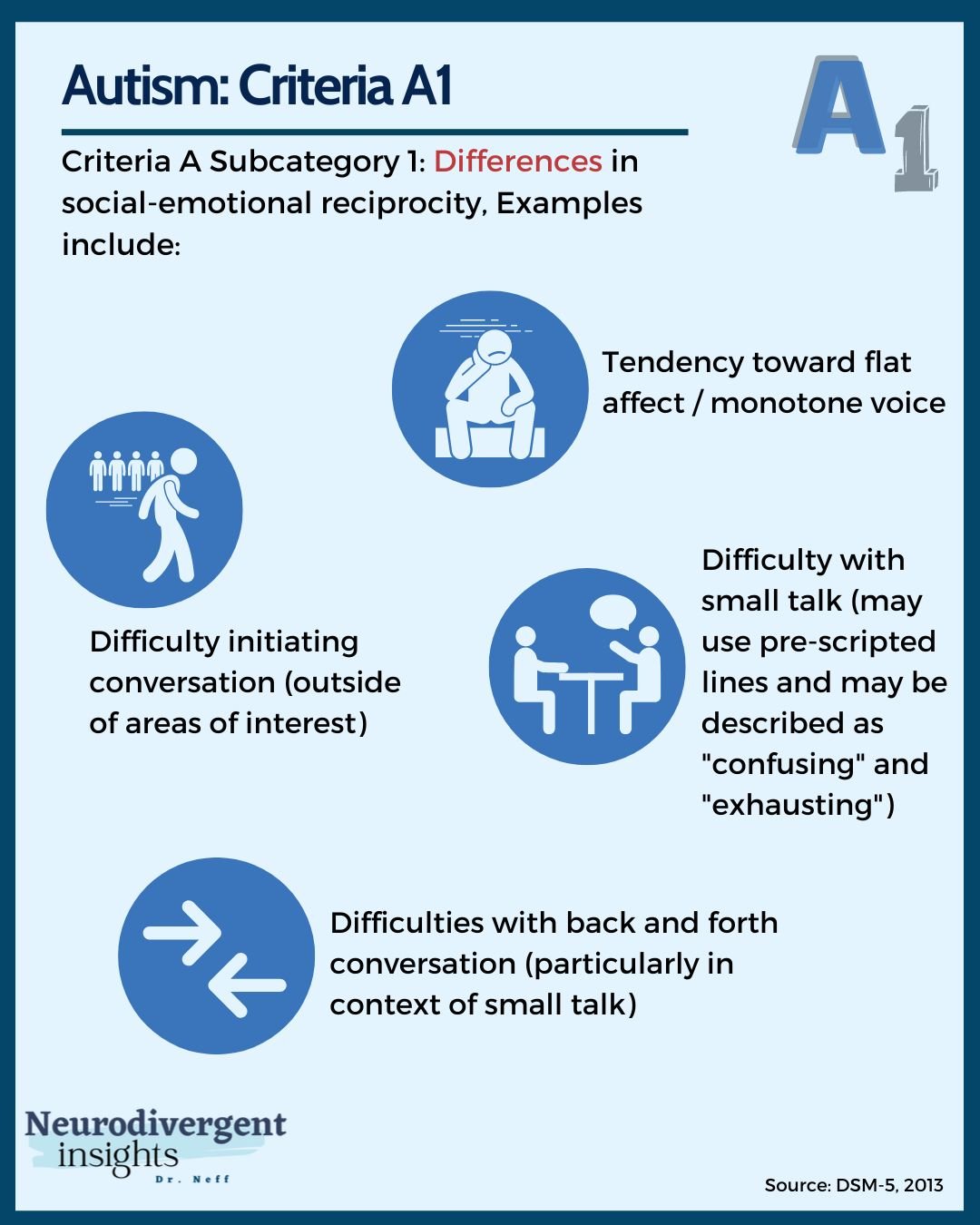
Dsm 5 Criteria For Autism Six major changes included: 1. four previously separate categories of autism consolidated into one umbrella diagnosis of “autism spectrum disorder.”. the previous categories were: autistic disorder. asperger syndrome. childhood disintegrative disorder. pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (pdd nos) 2. The fifth edition of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (dsm 5), released by the american psychiatric association (apa) in 2013, redefined the criteria for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (asd). an autism diagnosis requires persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts. It reads as follows: autism spectrum disorder. diagnostic criteria 299.00 (f84.0) deficits in social emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions. Ired criteria may change. anges possible . dsm‐5 crit. ife. by 3 of 3 symptoms:a1. deficits in social‐emotional reciprocity; ranging from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversation through reduced sharing of interests, emotions, and affect and response to total lack of initi.
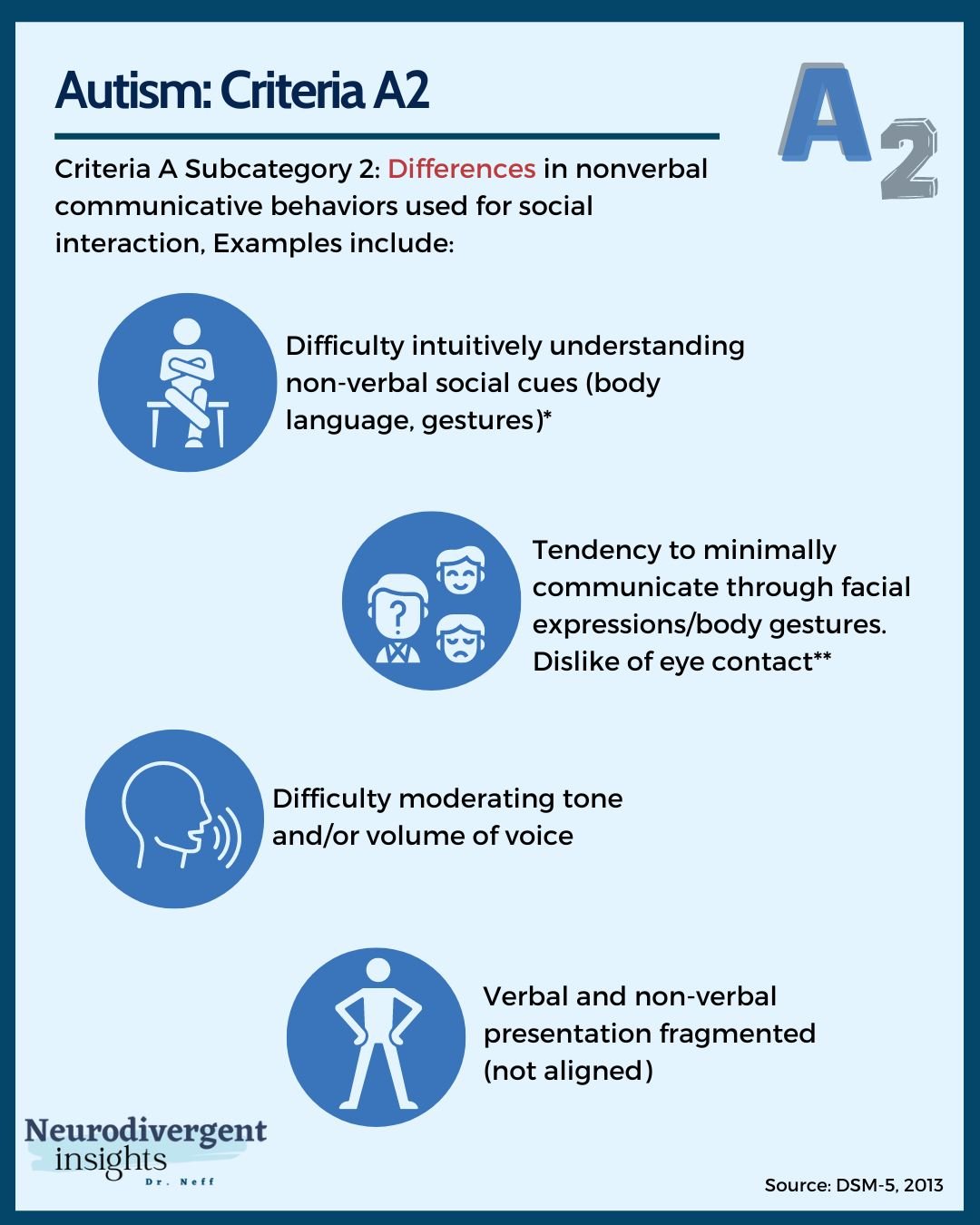
Dsm 5 Criteria For Autism It reads as follows: autism spectrum disorder. diagnostic criteria 299.00 (f84.0) deficits in social emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversation; to reduced sharing of interests, emotions, or affect; to failure to initiate or respond to social interactions. Ired criteria may change. anges possible . dsm‐5 crit. ife. by 3 of 3 symptoms:a1. deficits in social‐emotional reciprocity; ranging from abnormal social approach and failure of normal back and forth conversation through reduced sharing of interests, emotions, and affect and response to total lack of initi. However, it can take a significant amount of time for each revision to be completed. for example, the dsm iv was published in 1984 and revised in 2000. it wasn’t until 2013 that the current version of the dsm, the dsm 5, was published. the dsm 5 made some major changes to the diagnosis of autism from earlier versions. most notably, it removed. More accurate dsm 5 diagnosis. while dsm does not outline recommended treatment and services for mental disorders, determining an accurate diagnosis is a first step for a clinician in defining a treatment plan for a patient. the neurodevelopmental work group, led by susan swedo, md, senior investigator at the national . institute of mental.

Increases In The Prevalence Of Autism Disorder Exploring Biological However, it can take a significant amount of time for each revision to be completed. for example, the dsm iv was published in 1984 and revised in 2000. it wasn’t until 2013 that the current version of the dsm, the dsm 5, was published. the dsm 5 made some major changes to the diagnosis of autism from earlier versions. most notably, it removed. More accurate dsm 5 diagnosis. while dsm does not outline recommended treatment and services for mental disorders, determining an accurate diagnosis is a first step for a clinician in defining a treatment plan for a patient. the neurodevelopmental work group, led by susan swedo, md, senior investigator at the national . institute of mental.

Comments are closed.