Dry And Secondary Drowning What You Need To Know
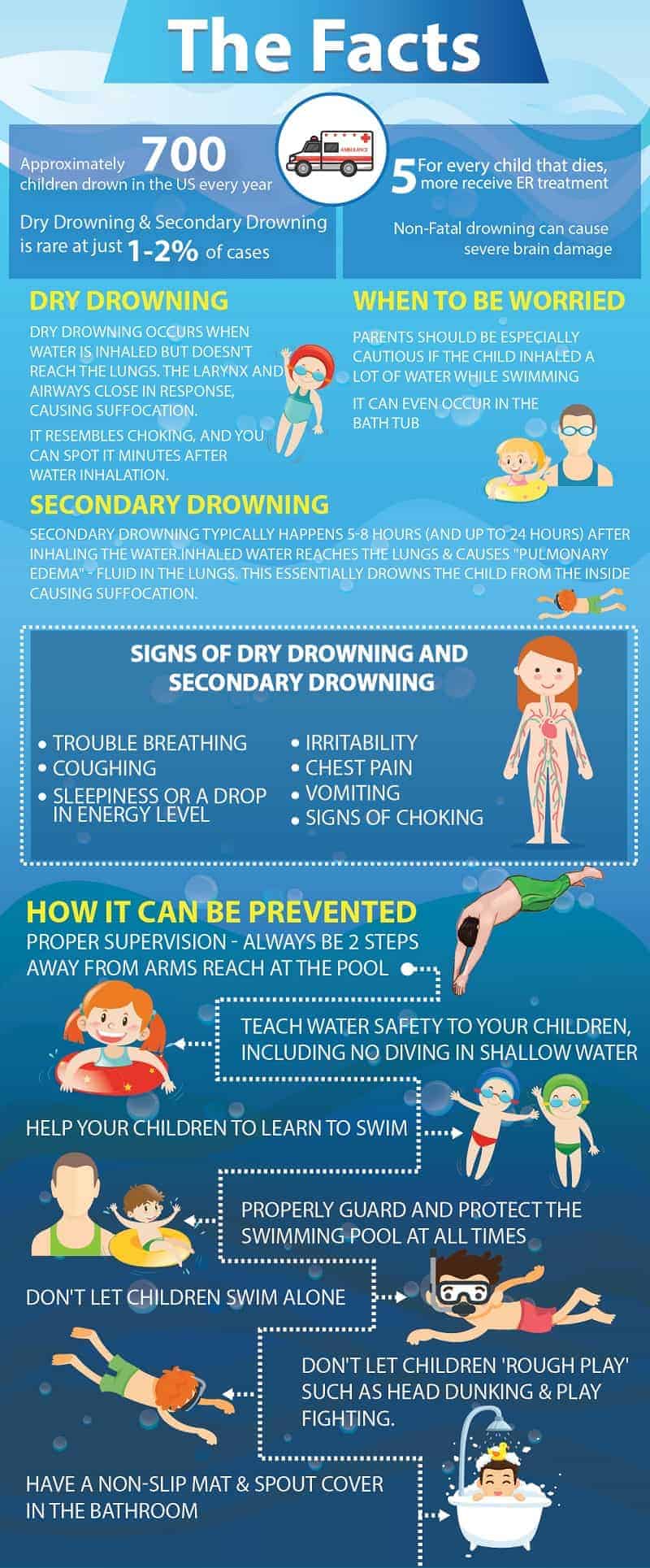
Dry Drowning Secondary Drowning What You Need To Know To Keep Your Symptoms. drowning complications can include: coughing. chest pain. trouble breathing. feeling extremely tired. your child may also have changes in behavior such as such as irritability or a drop. Dry drowning is an airway closure from choking on water without getting fluid in your lungs. drowning is defined as a respiratory impairment — that is, being unable to breathe — because you.

Dry Drowning Secondary Drowning What You Need To Know To Keep Your Symptoms to watch for after a water incident include: difficulty breathing or speaking. irritability or unusual behavior. coughing. chest pain. low energy or sleepiness after a water incident. if. Dry drowning symptoms typically involve laryngospasm, a reflex contraction of the vocal cords that prevents water from entering the lungs but can also prevent adequate air intake through the windpipe. laryngospasm can occur minutes to hours after initially breathing in water and could be life threatening without proper medical attention. Drowning remains a leading cause of unintentional death for people of all ages – especially for children under 14, according to the centers for disease control and prevention. on average, there are 3,500 fatalities annually from drowning – or about ten people a day who die from drowning, says dr. boniface. “drowning occurs when you can. The reason: drowning is the leading cause of injury and death in kids ages 1 to 4 years old. and you may have heard of "dry drowning" and "secondary drowning," which have come to refer to complications that crop up after a drowning scare, with the claim being that they can develop sometimes several hours or even days later, and often in children.

Dry Drowning Secondary Drowning What You Need To Know To Keep Kids Safe Drowning remains a leading cause of unintentional death for people of all ages – especially for children under 14, according to the centers for disease control and prevention. on average, there are 3,500 fatalities annually from drowning – or about ten people a day who die from drowning, says dr. boniface. “drowning occurs when you can. The reason: drowning is the leading cause of injury and death in kids ages 1 to 4 years old. and you may have heard of "dry drowning" and "secondary drowning," which have come to refer to complications that crop up after a drowning scare, with the claim being that they can develop sometimes several hours or even days later, and often in children. 0:02. 0:47. the terms “dry drowning” and “secondary drowning” have cropped up in the media in recent years. while “dry drowning” and “secondary drowning” have been used to describe. You need to get the person to the emergency room if you suspect secondary drowning. it’s crucial to seek medical care since secondary drowning can be fatal. depending on how severe it is, it can be treated with oxygen, antibiotics or diuretics, which can help eliminate fluid in the lungs. in more severe cases, you could need a breathing.

Dry Drowning Secondary Drowning What You Need To Know To Keep Your Kids 0:02. 0:47. the terms “dry drowning” and “secondary drowning” have cropped up in the media in recent years. while “dry drowning” and “secondary drowning” have been used to describe. You need to get the person to the emergency room if you suspect secondary drowning. it’s crucial to seek medical care since secondary drowning can be fatal. depending on how severe it is, it can be treated with oxygen, antibiotics or diuretics, which can help eliminate fluid in the lungs. in more severe cases, you could need a breathing.

Comments are closed.