Drug Study Hfmd Lecture Notes Drug Name Mechanism Of Action
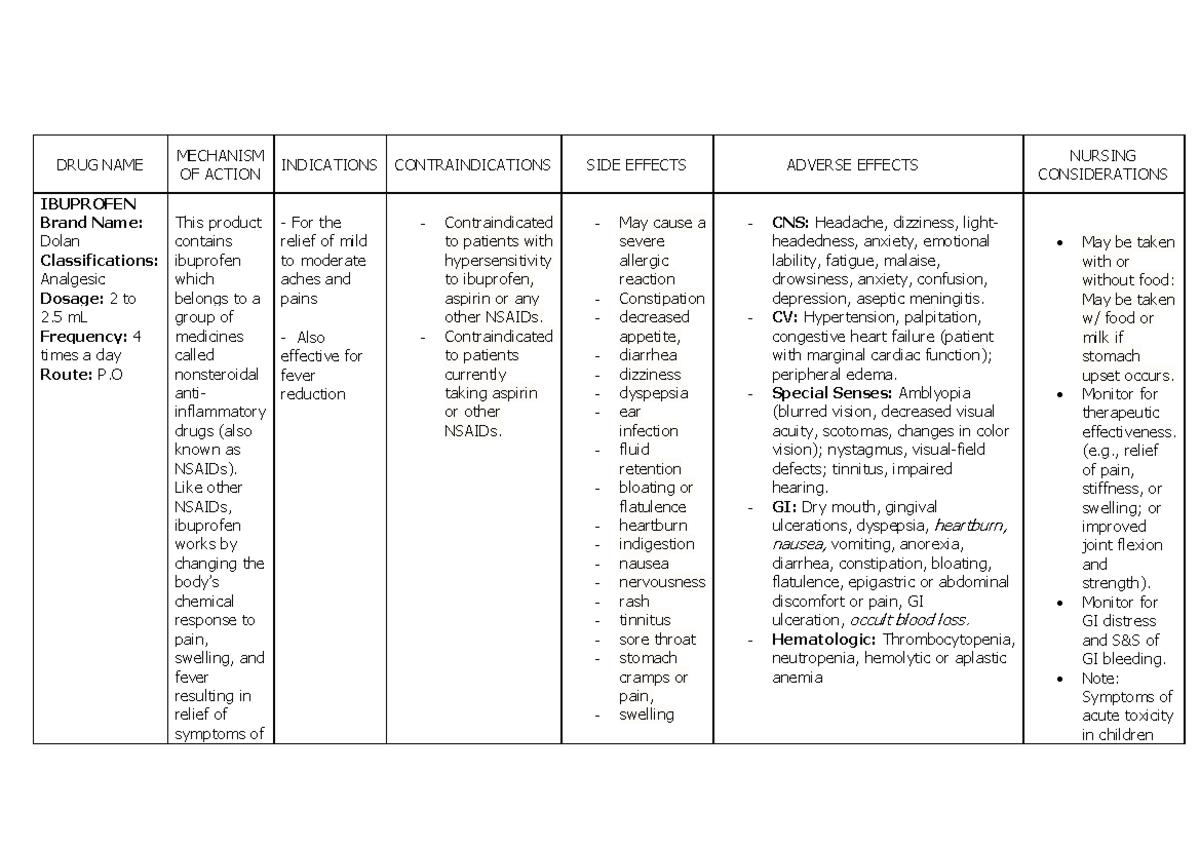
Drug Study Hfmd Lecture Notes Drug Name Mechanism Of Action Drug name mechanism of action indications contraindications side effects adverse effects nursing considerations ibuprofen. brand name: dolan classifications: analgesic dosage: 2 to 2 ml frequency: 4 times a day route: p. this product contains ibuprofen which belongs to a group of medicines called nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs (also. Drug name mechanism of action indications side effects adverse effects contraindicatio ns nursing considerations. generic name: paracet amol brand name: biogesic classification: anti pyretic dosage: 450 mg. route: po tiv. frequency: q6 for 24 hr blocks pain impulses by inhibiting synthesis of prostaglandin.
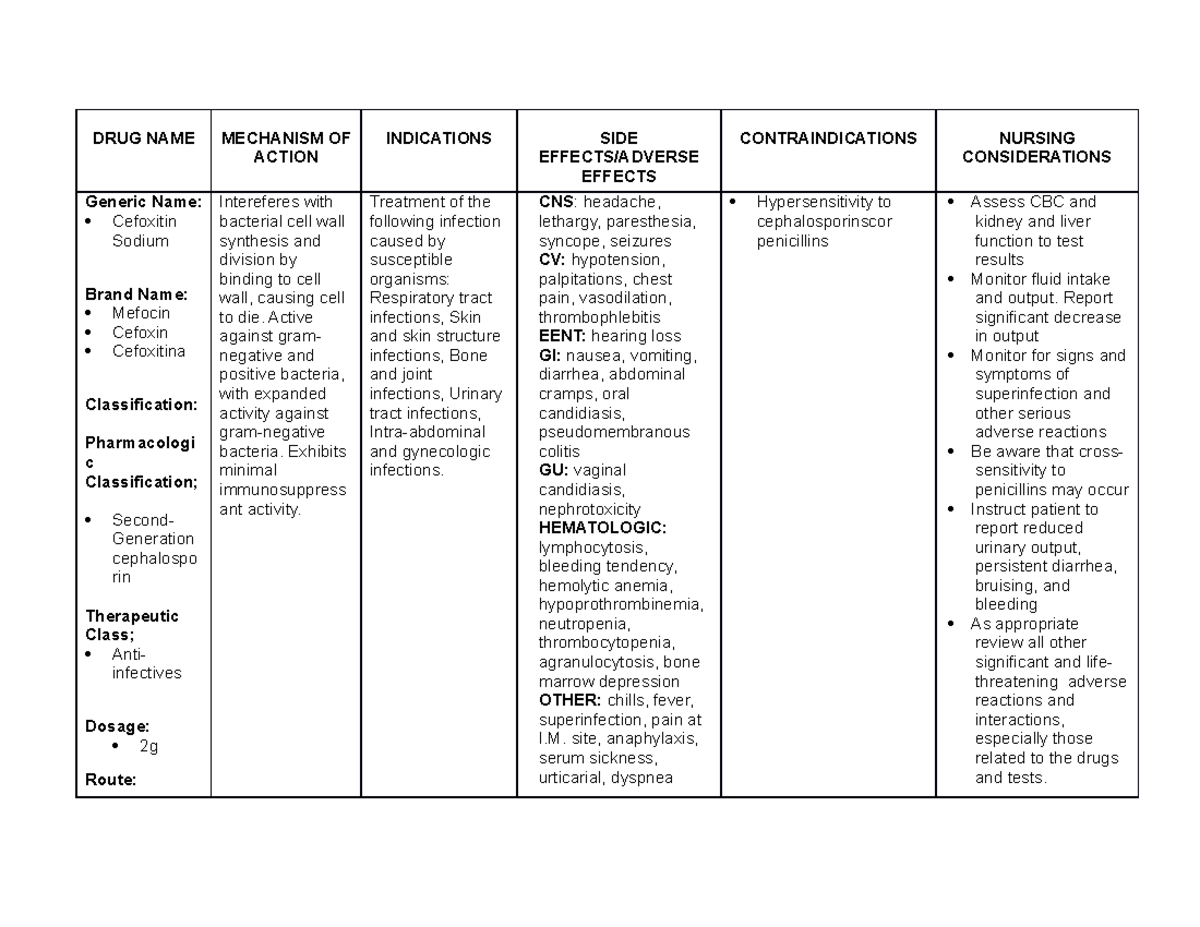
Drug Study Lecture Notes 1 Drug Name Mechanism Of Action Lecture notes. 100% (9) 7. celecoxib drug study; drugstudy for pediatric pnuemonia; preview text. drug name mechanism of action indication contraindication. Topics covered in 20.201. mechanisms of action of drugs and drug classes. role of drug structure and drug transport proteins in uptake and distribution. kinetics of drug behavior in the human body. metabolism: ~ chemical alterations of drugs ~ generation of toxic metabolites ~ metabolic activation of drugs. Affinity: a measure of how tightly a drug binds to the receptor. if the drug does not bind well, then the action of the drug will be shorter and the chance of binding will also be less. this can be measured numerically by using the dissociation constant k d. the k d is the concentration of drug when 50% of receptors are occupied. thus, the. Mechanism of drug action. 1) the document discusses the mechanism of drug action, including principles of drug action like stimulation, depression, irritation, and replacement. it also discusses drug action via discrete functional proteins like enzymes, ion channels, transporters, and receptors. 2) the majority of drugs act through interaction.
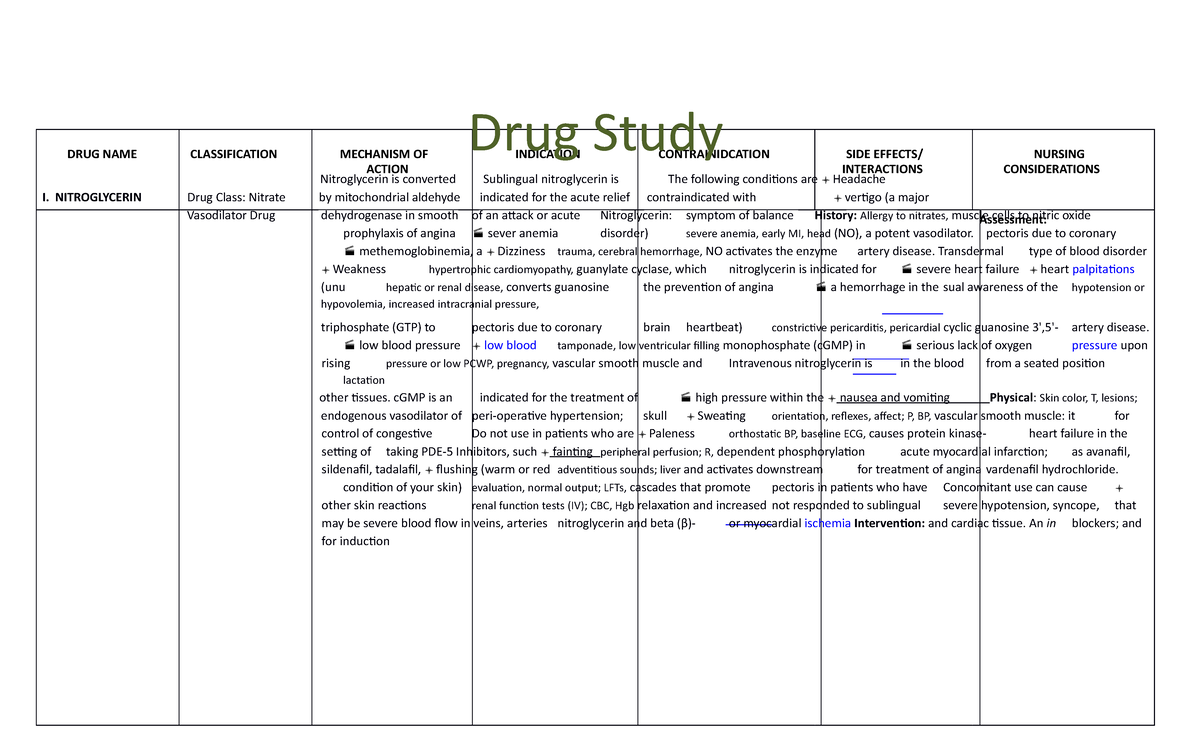
Drug Study On Agents Lecture Notes Drug Name Classification Affinity: a measure of how tightly a drug binds to the receptor. if the drug does not bind well, then the action of the drug will be shorter and the chance of binding will also be less. this can be measured numerically by using the dissociation constant k d. the k d is the concentration of drug when 50% of receptors are occupied. thus, the. Mechanism of drug action. 1) the document discusses the mechanism of drug action, including principles of drug action like stimulation, depression, irritation, and replacement. it also discusses drug action via discrete functional proteins like enzymes, ion channels, transporters, and receptors. 2) the majority of drugs act through interaction. Cellular mechanisms of drug action contd… 3. mechanisms associated with neurohumoural transmission •a number of drugs interfere with the synthesis, release, effects or re uptake of neurotransmitters. once again enzyme and or receptor mediated effects may be responsible. •for example, reserpine blocks the transport system of. Introduction. drug discovery has evolved from the identification of active substances in traditional medicines to the direct search for new medicines using high throughput screening campaigns, fragment based screening, virtual screening, and other approaches (leveridge et al., 2018). however, under debate are questions regarding the importance.

Comments are closed.