Drop 173 Number Of Teeth Visible In Maxila Mandible And Buccal Corridor

Maxilla And Mandible Anatomy Buccal corridors can be defined as that space between the facial surface of the last visible posterior teeth and the corners of the lips when the patient is smiling.9 buccal corridors can be influenced by the anteroposterior position of the maxilla, arch form, maxillary width, and facial pattern.10–15 however, there is little to no supporting. Educational project of the graduate program in dentistry at puc minas.didactic, technical scientific videos, aimed at dental students and professionals, prod.

Mandible And Maxilla Anatomy In the non extraction group, the buccal corridor decreased significantly (p< 0.01). the narrowing of the buccal corridor in the non extraction group can be explained by the widening of the dental arch at the level of the first molars and second premolars in the maxilla. Buccal corridor space has been thought of primarily in terms of maxillary width, but there is also evidence that they are heavily influenced by the antero posterior position of maxilla. the present study was undertaken with an aim of evaluating and comparing the dental and skeletal factors related to buccal corridor space in individuals having. The recent article by drs dustin roden johnson, ronald gallerano, and jeryl english (the effects of buccal corridor spaces and arch form on smile esthetics. am j orthod dentofacial orthop 2005;127;343 50) provides useful information regarding concepts of smile esthetics in relation to the width of arch form and the presence or absence of buccal corridor spaces, as evaluated by orthodontists. The total smile area; bcl:tsa, ratio between the buccal corridor area in relation to the last visible maxillary teeth and the total smile area. meyer, woods, and manton 301.

Permanent Teeth A Maxillary Teeth Buccal Labial View B Mandibular The recent article by drs dustin roden johnson, ronald gallerano, and jeryl english (the effects of buccal corridor spaces and arch form on smile esthetics. am j orthod dentofacial orthop 2005;127;343 50) provides useful information regarding concepts of smile esthetics in relation to the width of arch form and the presence or absence of buccal corridor spaces, as evaluated by orthodontists. The total smile area; bcl:tsa, ratio between the buccal corridor area in relation to the last visible maxillary teeth and the total smile area. meyer, woods, and manton 301. The maxillary posterior dentitions for all subjects were digitally altered to produce a range of smile fullness: narrow (28% buccal corridor), medium narrow (22% buccal corridor), medium (15%. Photographs of samples were evaluated for buccal corridor width in relation to canines and the last visible tooth. the mean intermolar width decreased 0.83 mm in the extraction group and increased.

Buccal Corridor Castlemill Dental The maxillary posterior dentitions for all subjects were digitally altered to produce a range of smile fullness: narrow (28% buccal corridor), medium narrow (22% buccal corridor), medium (15%. Photographs of samples were evaluated for buccal corridor width in relation to canines and the last visible tooth. the mean intermolar width decreased 0.83 mm in the extraction group and increased.

Adult Transverse Diagnosis And Treatment A Case Based Review
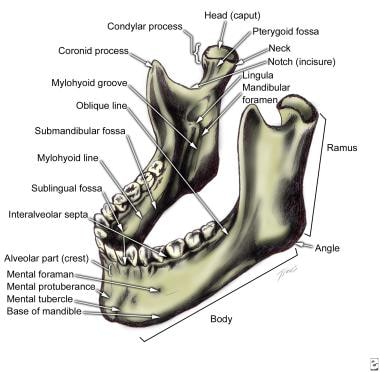
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla

Comments are closed.