Dna Structure And Function Of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna

Deoxyribonucleic Acid Or Dna Structure And Function Dna definition. deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. large compressed dna molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the. Dna structure and functions. dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the most complex multicellular humans. dna is a fundamental molecule that holds life’s blueprint. within a eukaryotic cell (plant and animal), they are found inside the.
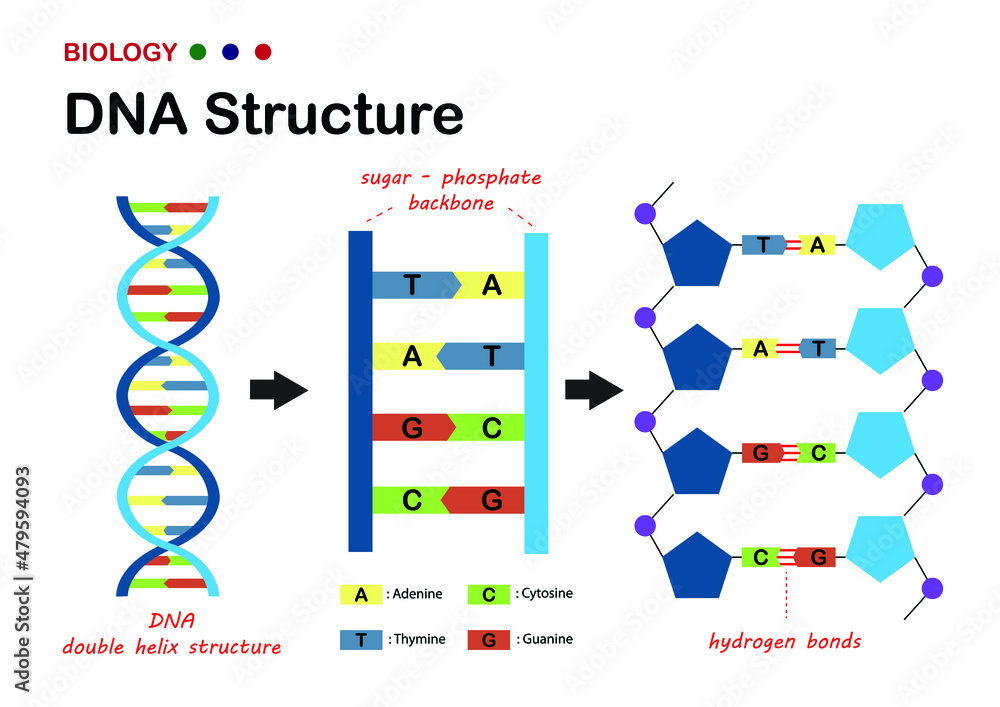
Biological Diagram Show Structure Of Dna Deoxyribonucleic Acid The Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is an organic chemical that contains genetic information and instructions for protein synthesis. it is found in most of every organism. dna is a key part of reproduction in which genetic heredity occurs through the passing down of dna from parent or parents to offspring. Dna nucleotides. the building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides. the three components of a deoxyribonucleotide are a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, a nitrogen containing ring structure that is responsible for complementary base pairing between nucleic acid strands (figure. Encoded within this dna are the directions for traits as diverse as the color of a person's eyes, the scent of a rose, and the way in which bacteria infect a lung cell. dna is found in nearly all. The remarkable structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), from the nucleotide up to the chromosome, plays a crucial role in its biological function. the ability of dna to function as the material through which genetic information is stored and transmitted is a direct result of its elegant structure. in their seminal 1953 paper, watson and crick unveiled two aspects of dna structure: pairing the.
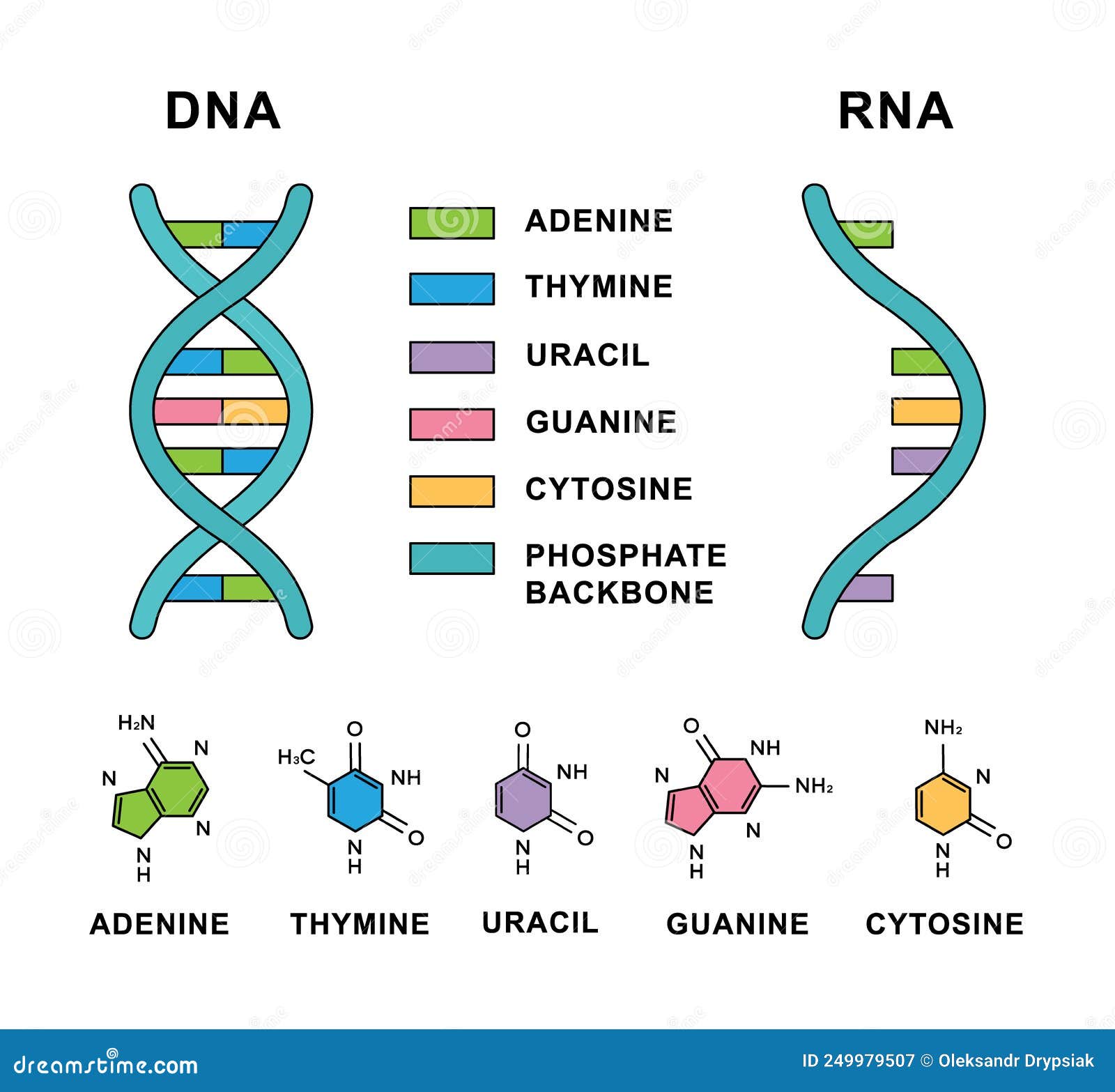
Deoxyribonucleic Acid And Ribonucleic Acid With Nucleobases Formulas Encoded within this dna are the directions for traits as diverse as the color of a person's eyes, the scent of a rose, and the way in which bacteria infect a lung cell. dna is found in nearly all. The remarkable structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), from the nucleotide up to the chromosome, plays a crucial role in its biological function. the ability of dna to function as the material through which genetic information is stored and transmitted is a direct result of its elegant structure. in their seminal 1953 paper, watson and crick unveiled two aspects of dna structure: pairing the. The importance of dna became clear in 1953 thanks to the work of james watson*, francis crick, maurice wilkins and rosalind franklin. by studying x ray diffraction patterns and building models, the scientists figured out the double helix structure of dna a structure that enables it to carry biological information from one generation to the next. The structure and function of dna. biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting dna as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. dna was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. early in the 1950s, dna was first examined by x ray diffraction.

Comments are closed.