Dna Chromosomes And Cells Science Learning Hub
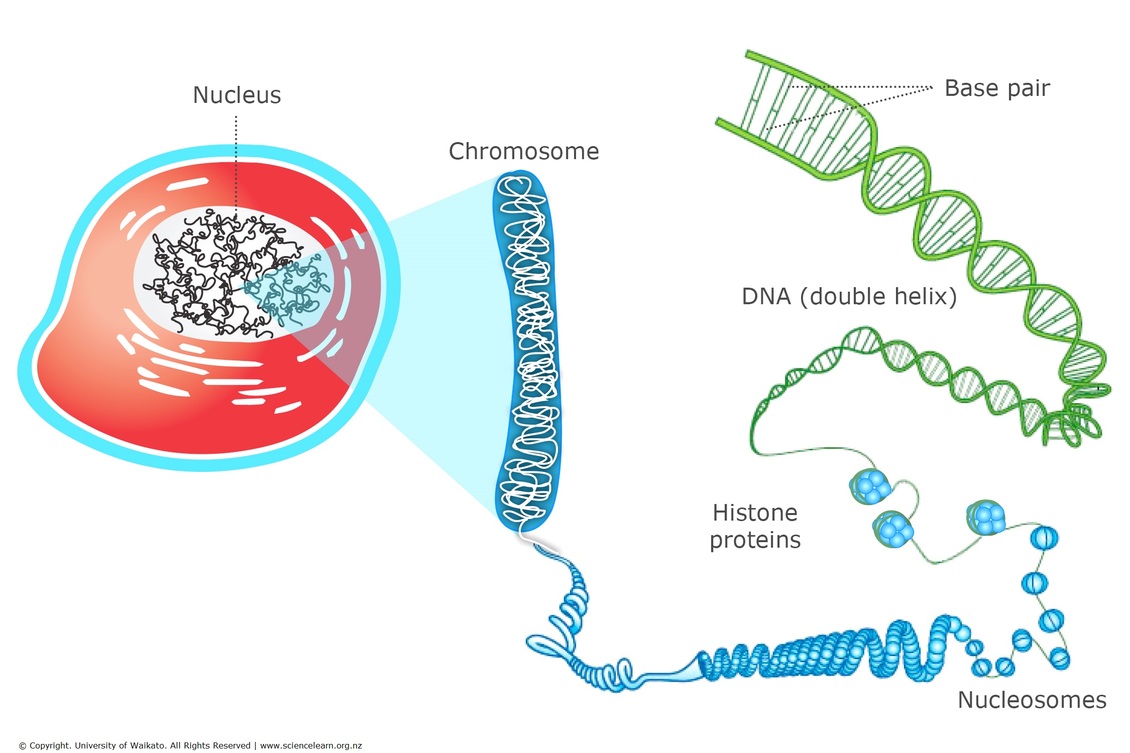
Dna Chromosomes And Cells Science Learning Hub A dna molecule is made up of a s eries of nucleotides arranged in 2 strands that resemble a ladder and twist to form a double helix. nucleotides are made up of a base, a sugar and a phosphate. the 4 bases – adenine (a), guanine (g), cytosine (c) and thymine (t) – pair with each other (a with t and g with c). it is the order or sequence of. Dna, chromosomes and cells. to fit into cells, the dna double helix is wrapped up around histone proteins and then coiled up further into into chromosomes. in eukaryotic cells, chromosomes are found in the nucleus. mitochondria and chloroplasts also contain dna.

Dna Chromosomes And Gene Expression Science Learning Hub If all the dna contained in the chromosomes of one human cell was unwound and the pieces were stretched out in a line end to end, it would be almost 2 metres long. there are approximately 100 trillion cells in the human body, so our bodies contain more than a billion kilometres of dna! the long stringy nature of dna is hard to conceptualise. Dna can also be collected directly from a person using a mouth swab (which collects inner cheek cells). find out more in the articles forensics and dna and crime scene evidence. 2. extract the dna. dna is contained within the nucleus of cells. chemicals are added to break open the cells, extract the dna and isolate it from other cell components. 3. Dna and genomes. dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of living organisms. in humans, dna is found in almost all the cells of the body and provides the instructions they need to grow, function, and respond to their environment. when a cell of the body divides, it will pass on a copy of its dna to each of its daughter cells. The dna double helix (gray) is wrapped around a core particle of histone proteins (colored) to create the nucleosome. nucleosomes are spaced roughly 200 nucleotide pairs apart along the chromosomal dna. (reprinted by permission from k. (more ) life depends on the ability of cells to store, retrieve, and translate the genetic instructions.
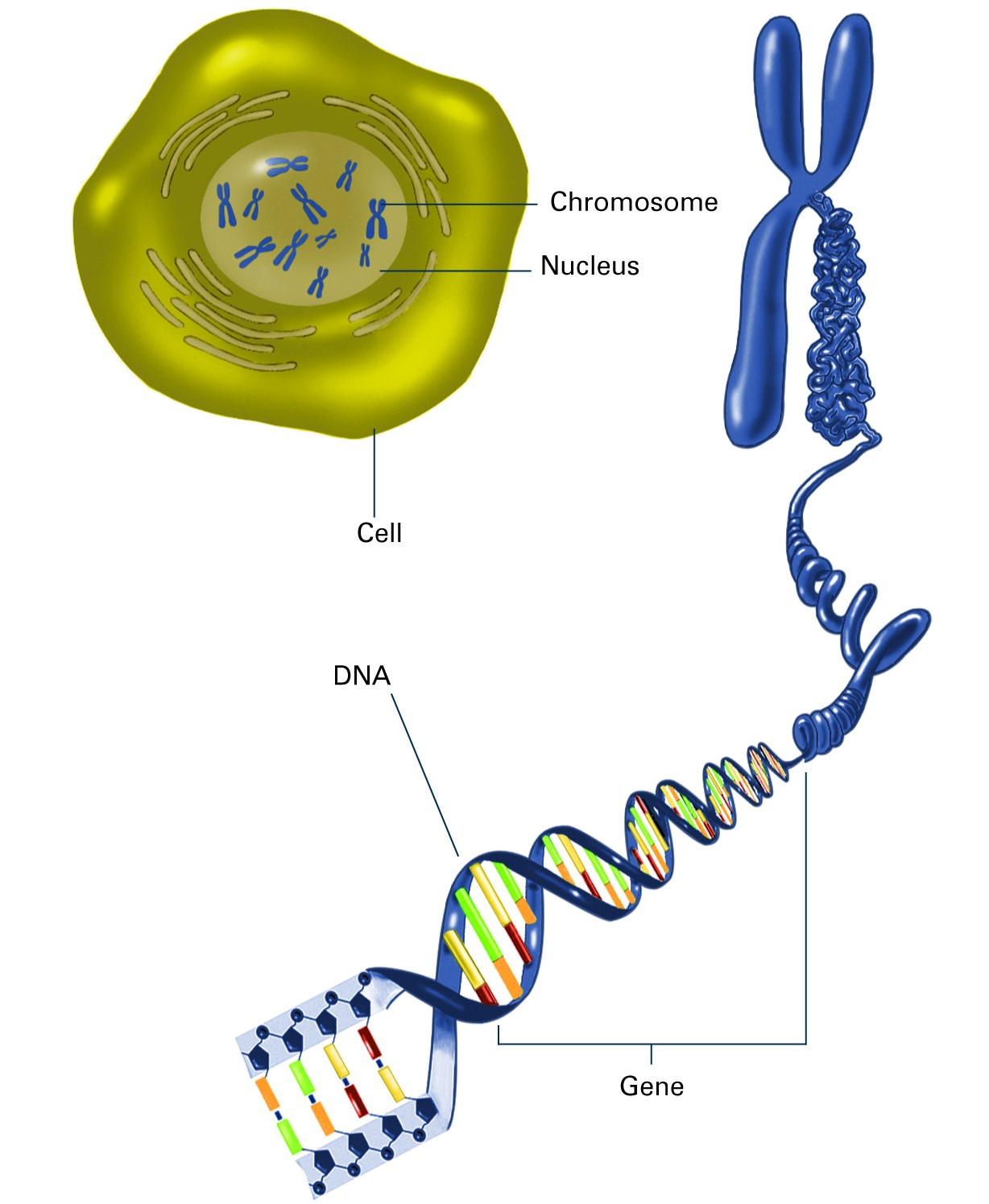
Genetics Dna and genomes. dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of living organisms. in humans, dna is found in almost all the cells of the body and provides the instructions they need to grow, function, and respond to their environment. when a cell of the body divides, it will pass on a copy of its dna to each of its daughter cells. The dna double helix (gray) is wrapped around a core particle of histone proteins (colored) to create the nucleosome. nucleosomes are spaced roughly 200 nucleotide pairs apart along the chromosomal dna. (reprinted by permission from k. (more ) life depends on the ability of cells to store, retrieve, and translate the genetic instructions. The haploid human genome contains approximately 3 billion base pairs of dna packaged into 23 chromosomes. of course, most cells in the body (except for female ova and male sperm) are diploid, with. Dna and genomes. dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of living organisms. in humans, dna is found in almost all the cells of the body and provides the instructions they need to grow, function, and respond to their environment. when a cell of the body divides, it will pass on a copy of its dna to each of its daughter cells.
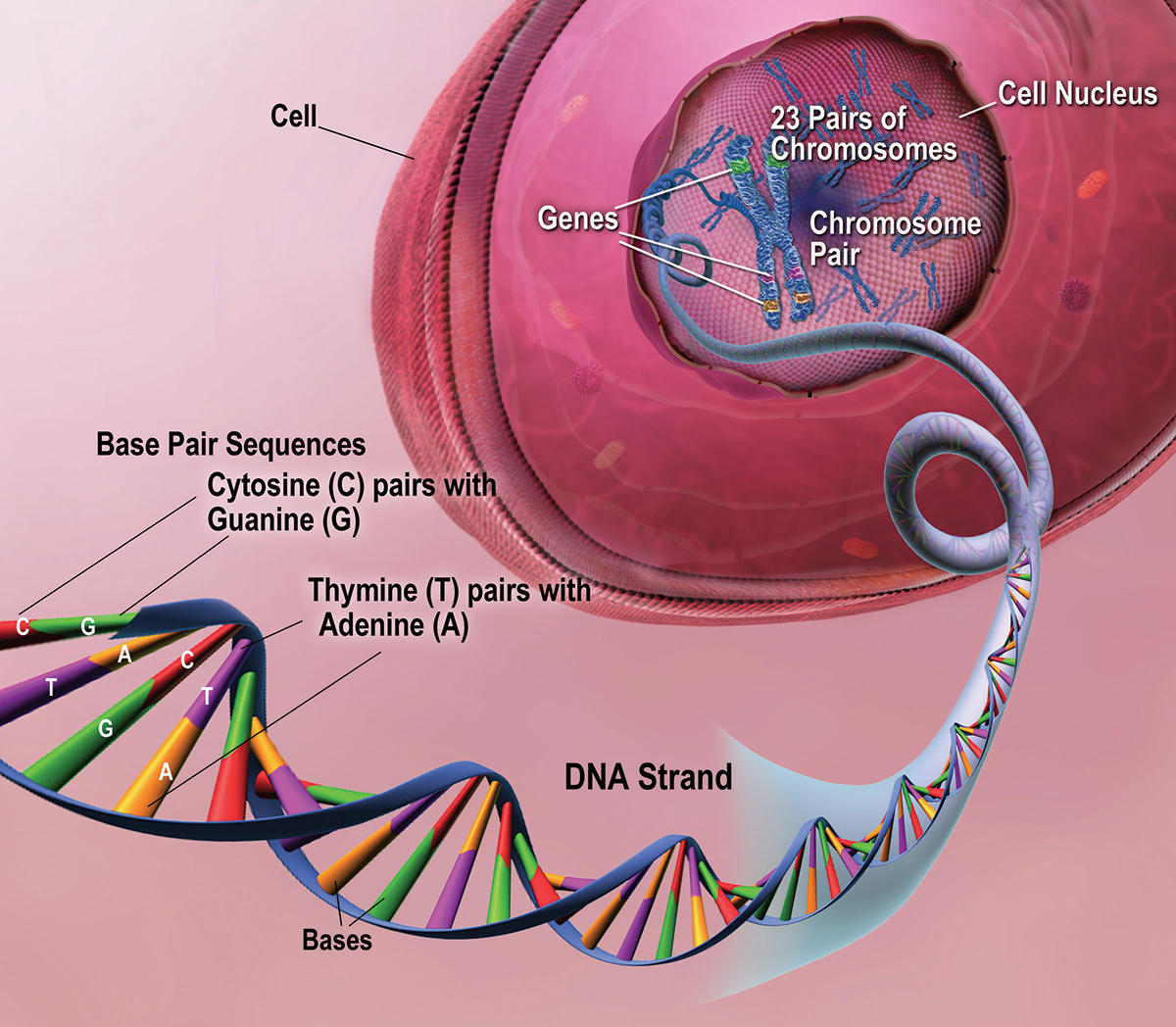
Genes Dna And Chromosomes Explained The haploid human genome contains approximately 3 billion base pairs of dna packaged into 23 chromosomes. of course, most cells in the body (except for female ova and male sperm) are diploid, with. Dna and genomes. dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of living organisms. in humans, dna is found in almost all the cells of the body and provides the instructions they need to grow, function, and respond to their environment. when a cell of the body divides, it will pass on a copy of its dna to each of its daughter cells.

Cell Chromosomes And Dna Sciencelearn Hub Dna Activities Medical
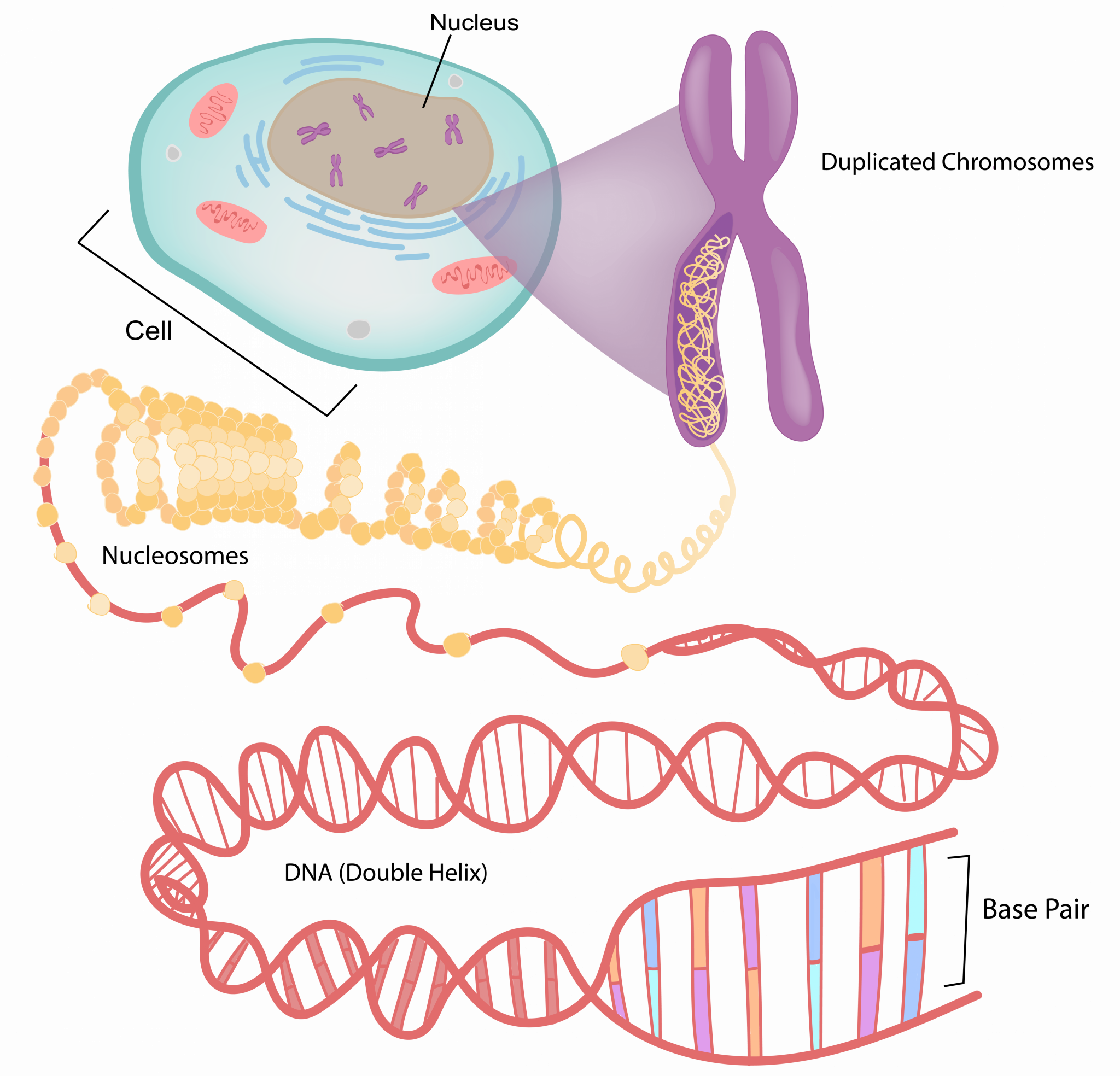
5 2 The Genetic Basis Of Gene Expression The Evolution And Biology Of Sex

Comments are closed.