Digital Literacy Upsc At Ollie Wright Blog
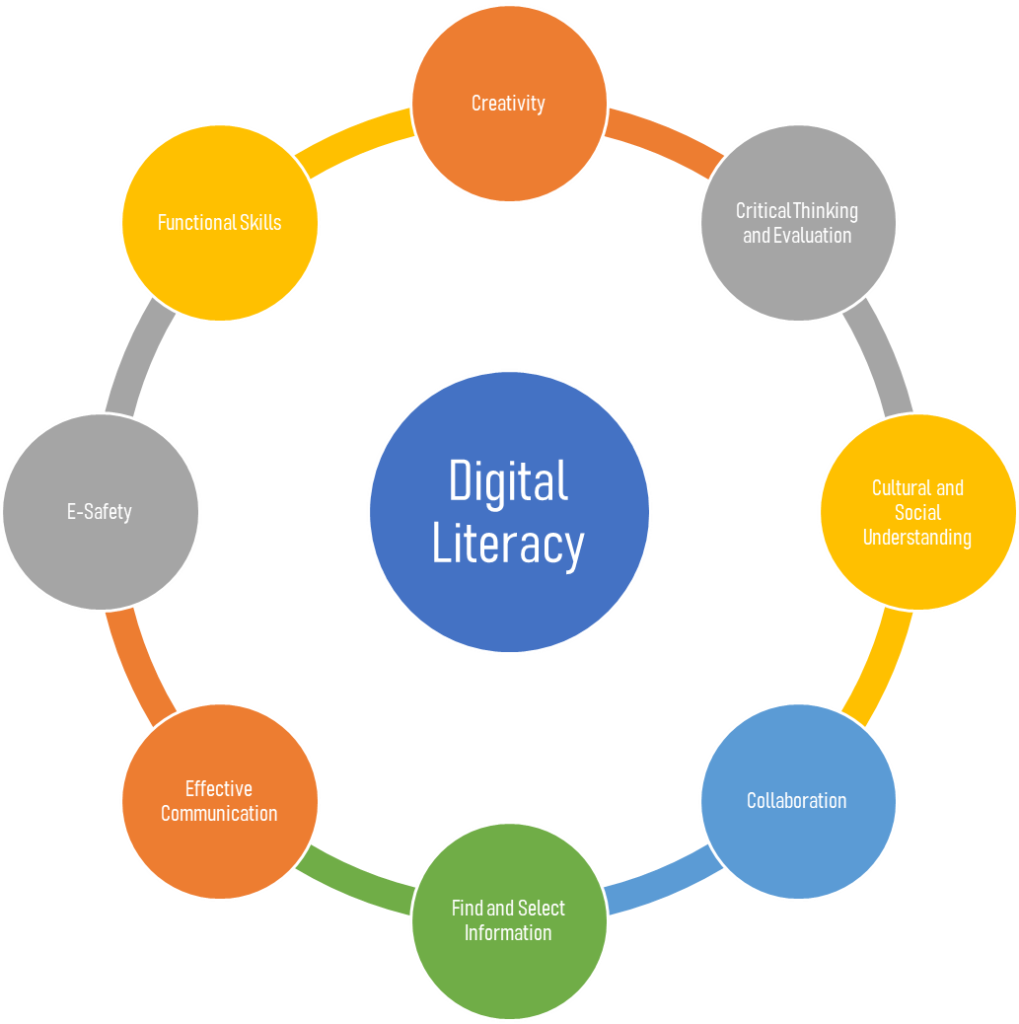
Digital Literacy Upsc At Ollie Wright Blog The digital divide emanating from information poverty, lack of infrastructure, and lack of digital literacy leads to social and economic backwardness. the digital divide can be seen throughout the socio economic spectrum of india i.e. between rural and urban india, rich and poor, india’s demographic profile (old and young, male and female). To maximize india’s demographic and digital dividends, india must focus on enhancing digital literacy and accessibility. as smartphone usage in rural areas rose to 74.8% in 2022, leveraging this for educational resources and skills development is crucial. continued support for youth aspirations will drive economic participation and growth.
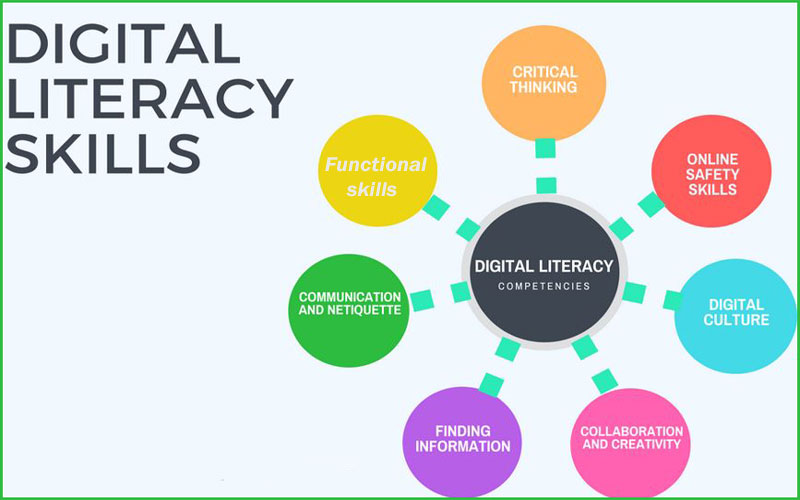
Digital Literacy Upsc At Ollie Wright Blog The digital india mission, a flagship initiative of the indian government, seeks to transform the nation into a digitally empowered society and knowledge driven economy. india's dedication to bridging the digital divide and enhancing digital literacy is evident through a series of impactful endeavours. recognizing the vulnerability of rural. Nine pillars of digital india initiative: broadband highways: focus on building extensive high speed broadband networks nationwide to boost connectivity and digital empowerment. universal access to mobile connectivity: extend mobile coverage to remote areas, enabling all citizens to engage with mobile services and participate in the digital. Measuring digital literacy has become crucial since the pandemic. the right to free and compulsory education (2009) guarantees elementary schooling to all children in the age group of 6 14 years. by 2018, the percentage of 6 14 years out of school children had come down to 2.8 per cent. the government had also launched the rashtriya madhyamik. For secondary schools, the proportion of 15 16 year olds, declined from 9.9% in 2020 to 7.5% in 2022. the penetration of smartphones in rural india: in 2018, only 36% of rural households had a smartphone but during 2020 21, with the economy and the education system transitioning to a virtual mode, having access to a digital device almost became.

Digital Literacy Creating Our Own Narratives Appropriating The Measuring digital literacy has become crucial since the pandemic. the right to free and compulsory education (2009) guarantees elementary schooling to all children in the age group of 6 14 years. by 2018, the percentage of 6 14 years out of school children had come down to 2.8 per cent. the government had also launched the rashtriya madhyamik. For secondary schools, the proportion of 15 16 year olds, declined from 9.9% in 2020 to 7.5% in 2022. the penetration of smartphones in rural india: in 2018, only 36% of rural households had a smartphone but during 2020 21, with the economy and the education system transitioning to a virtual mode, having access to a digital device almost became. However, this requires a focus on digital literacy. aser 2022: spotlight on rural youth: the annual status of education report (aser) 2022 focuses on rural youth aged 14 to 18. understanding their choices, educational pursuits, work aspirations, and digital engagement provides insights for targeted support and policymaking. edtech and digital. In our fast paced world, literacy is a vital tool for personal growth and societal progress. from 1820's 12% global literacy to today's 87% (2022), its importance is evident. developed nations boast a 99% literacy rate. in 2018, brazil reached 93%, china 97%, and india 74% (uis 2018a, 2018b). literacy opens doors, enabling access to information and active societal engagement. this blog.

Comments are closed.