Diagram Of Perfect Competition Economics Help
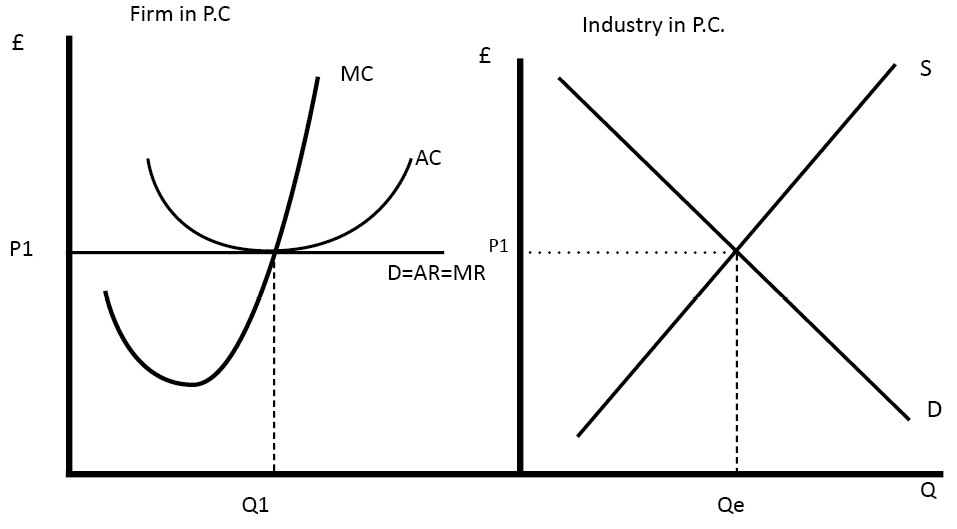
Diagram Of Perfect Competition Economics Help Diagram of perfect competition. the market price is set by the supply and demand of the industry (diagram on right) this sets the market equilibrium price of p1. individual firms (on the left) are price takers. their demand curve is perfectly elastic. a firm maximises profit at q1 where mc = mr. Features of perfect competition. many firms. freedom of entry and exit; this will require low sunk costs. all firms produce an identical or homogeneous product. all firms are price takers, therefore the firm’s demand curve is perfectly elastic. there is perfect information and knowledge. diagram for perfect competition.
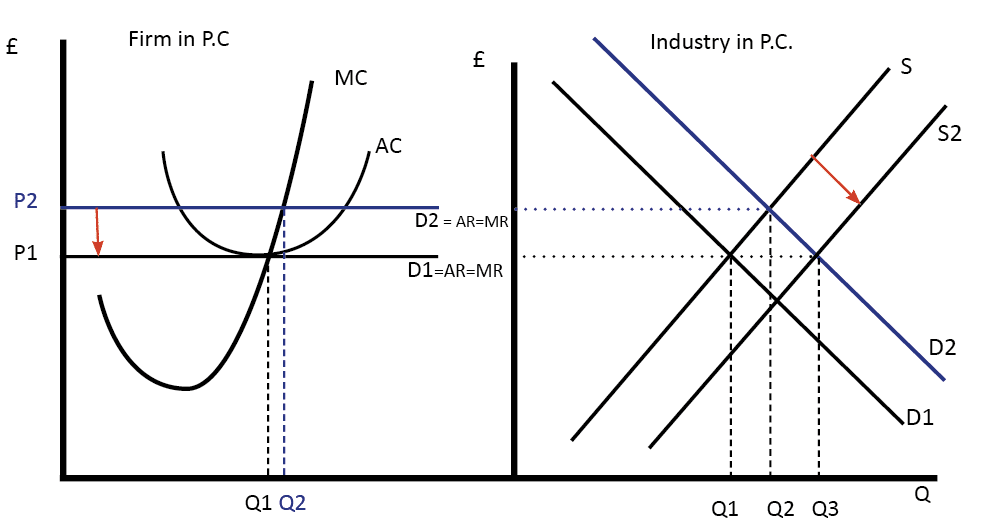
Diagram Of Perfect Competition Economics Help Competition between firms will act as a spur to increase efficiency. in perfect competition, this is likely to occur. 4. resources will not be wasted through advertising because products are homogenous. 5. normal profit means consumers are getting the lowest price. this also leads to greater equality in society. The characteristics of perfect competition imply that each firm has no market power to influence market price and simply takes the market price as it exists. this is why firms within a perfectly competitive market are called “price takers.”. indeed, all firms face individual horizontal demand curves that are perfectly elastic, where the. The perfect competition diagram features various variables: ar: average revenue: the average amount of money the sale of a product generates for the firm. it is the same as the price of the product, and works as the demand line on the diagram. mr: marginal revenue: the extra amount of revenue the sale of one additional product brings. This video provides an introductory overview of the main characteristics and assumptions of perfect competition, along with some examples. perfect competition video 1. activity 2: video the short run, the long run, and relevant diagrams. in perfect competition, there are different outcomes in both the short run and the long run.
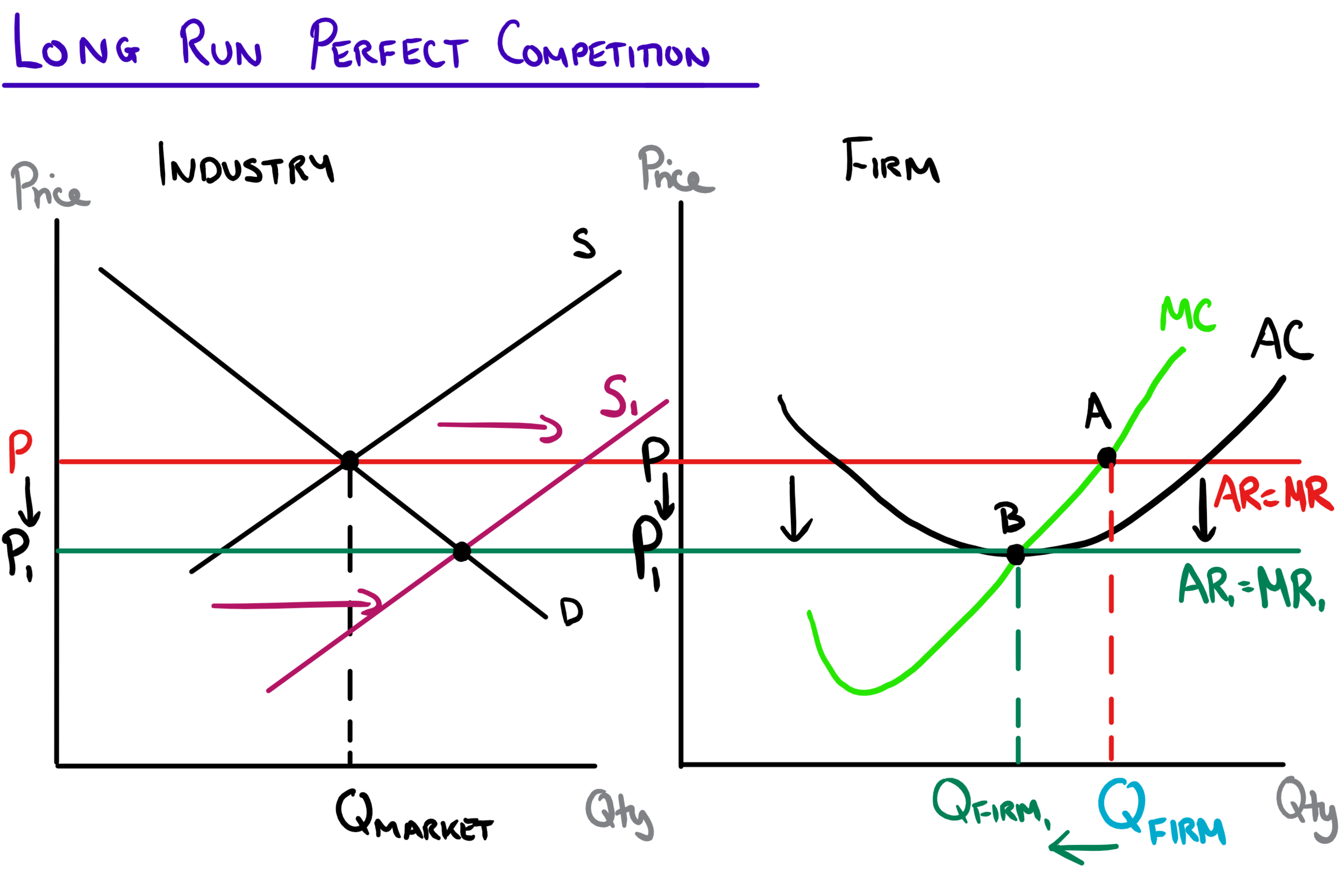
Perfect Competition Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Tutoring The perfect competition diagram features various variables: ar: average revenue: the average amount of money the sale of a product generates for the firm. it is the same as the price of the product, and works as the demand line on the diagram. mr: marginal revenue: the extra amount of revenue the sale of one additional product brings. This video provides an introductory overview of the main characteristics and assumptions of perfect competition, along with some examples. perfect competition video 1. activity 2: video the short run, the long run, and relevant diagrams. in perfect competition, there are different outcomes in both the short run and the long run. This aqa economics study note covers perfect competition. in the bustling marketplace of economic models, perfect competition holds a coveted spot. it represents a utopian world of efficient resource allocation, where firms are mere players following the rules, leading to an optimal outcome for consumers and society. let's dive into this model, unpacking its features, implications, and. Perfect competition is a theoretical market structure. it does provide a useful benchmark for evaluating efficiency for real world market structures, e.g. monopolies and oligopolies. perfectly competitive markets has an efficient allocation of resources where resources are allocated to their most valued uses.
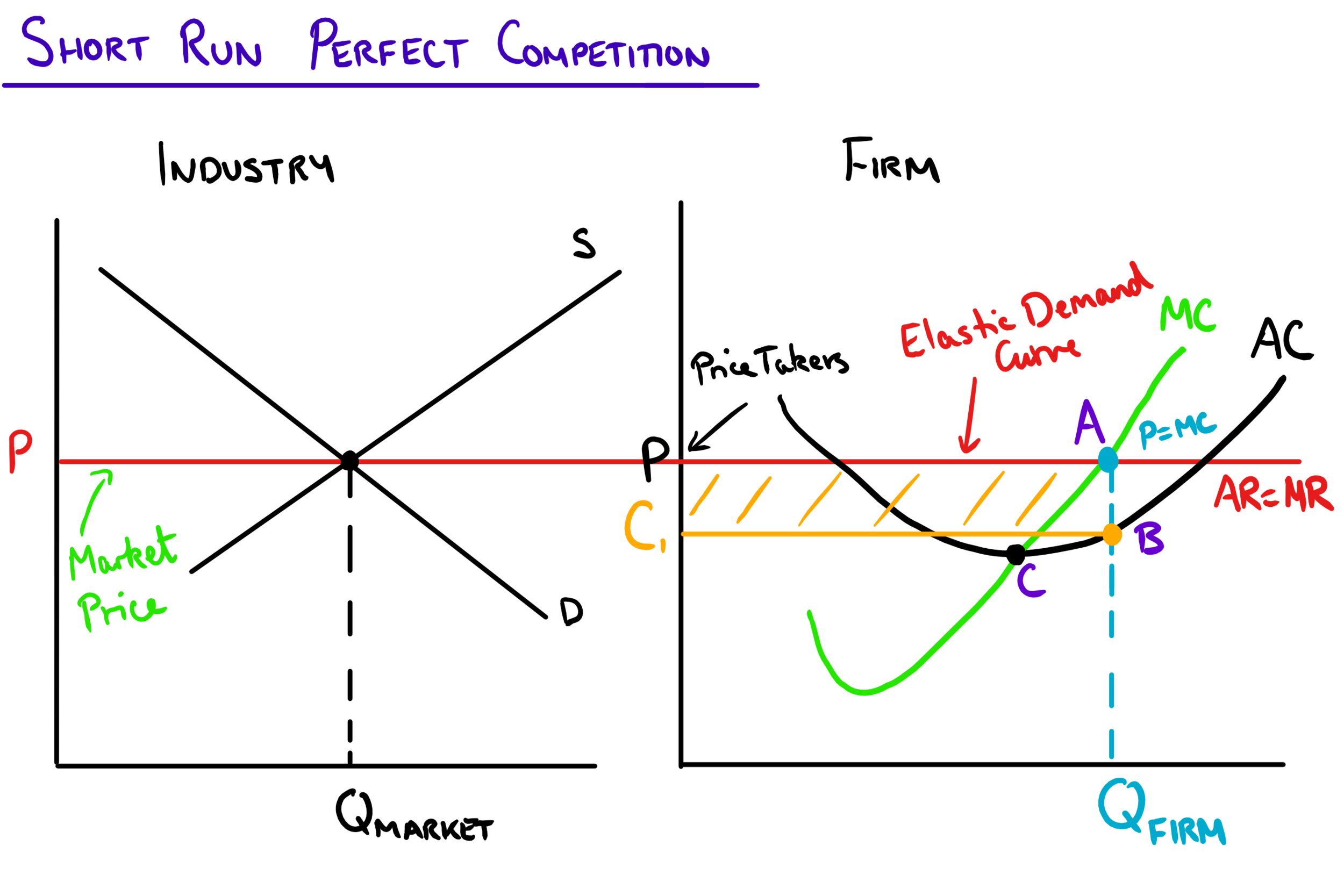
Perfect Competition Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Tutoring This aqa economics study note covers perfect competition. in the bustling marketplace of economic models, perfect competition holds a coveted spot. it represents a utopian world of efficient resource allocation, where firms are mere players following the rules, leading to an optimal outcome for consumers and society. let's dive into this model, unpacking its features, implications, and. Perfect competition is a theoretical market structure. it does provide a useful benchmark for evaluating efficiency for real world market structures, e.g. monopolies and oligopolies. perfectly competitive markets has an efficient allocation of resources where resources are allocated to their most valued uses.

Comments are closed.