Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help
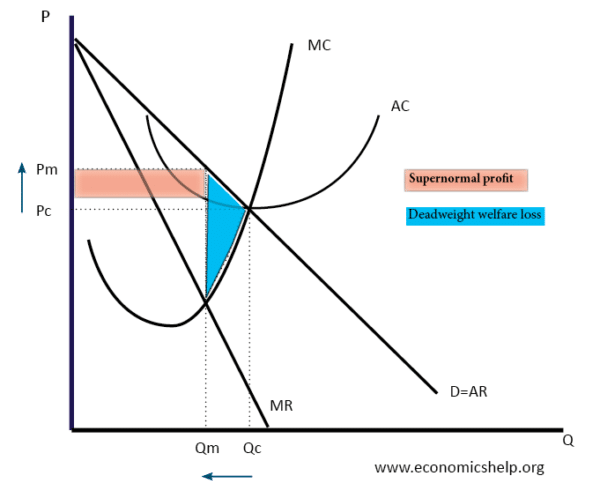
Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help Monopoly graph. a monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where mr = mc. this will be at output qm and price pm. compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output. red area = supernormal profit (ar ac) * q. blue area = deadweight welfare loss (combined loss of producer and consumer surplus. A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e. 100% of market share. in the uk a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share. for example, tesco @30% market share or google 90% of search engine traffic. monopoly diagram. a monopoly maximises profits where mr=mc (at point m).
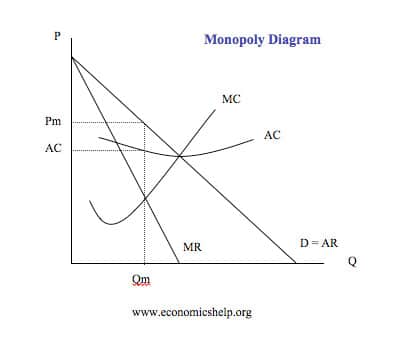
Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help Long run average costs in monopoly. it is assumed monopolies have a degree of economies of scale, which enables them to benefit from lower long run average costs. in a competitive market, firms may produce quantity q2 and have average costs of ac2. a monopoly can produce more and have lower average costs. this enables efficiency of scale. Equation 10.1. q = 10 −p q = 10 − p. this demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in figure 10.4 “demand, elasticity, and total revenue”. total revenue for each quantity equals the quantity times the price at which that quantity is demanded. the monopoly firm’s total revenue curve is given in panel (b). The average revenue, and price will also be the demand curve (darp). if the firm is a single price monopoly, the marginal revenue curve is below demand. note: the cost curves for a monopoly are the same as a perfectly competitive firm and monopolistically competitive firm. the avc and afc are rarely needed in this graph. In this online lesson, we explore the topic of monopoly in detail, covering diagrams, application, and key evaluation points. what you'll study in this online lesson. the characteristics of monopoly. real world examples of monopoly. monopoly diagrams. the economic case for and against monopoly. natural monopoly.

Monopoly Diagram A Level Economics The average revenue, and price will also be the demand curve (darp). if the firm is a single price monopoly, the marginal revenue curve is below demand. note: the cost curves for a monopoly are the same as a perfectly competitive firm and monopolistically competitive firm. the avc and afc are rarely needed in this graph. In this online lesson, we explore the topic of monopoly in detail, covering diagrams, application, and key evaluation points. what you'll study in this online lesson. the characteristics of monopoly. real world examples of monopoly. monopoly diagrams. the economic case for and against monopoly. natural monopoly. Show solution. the correct answer is that the optimal quantity produced for a monopolist is defined at the point where the marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue. it is not the case that the marginal cost is equal to the price. this is accurate in a competitive market, where marginal revenue and price are equivalent, but not in a monopoly. The area of deadweight loss for a monopolist can also be shown in a more simple form, comparing perfect competition with monopoly. alternative diagram. the following diagram assumes that average cost is constant, and equal to marginal cost (atc = mc).under perfect competition, equilibrium price and output is at p and q.
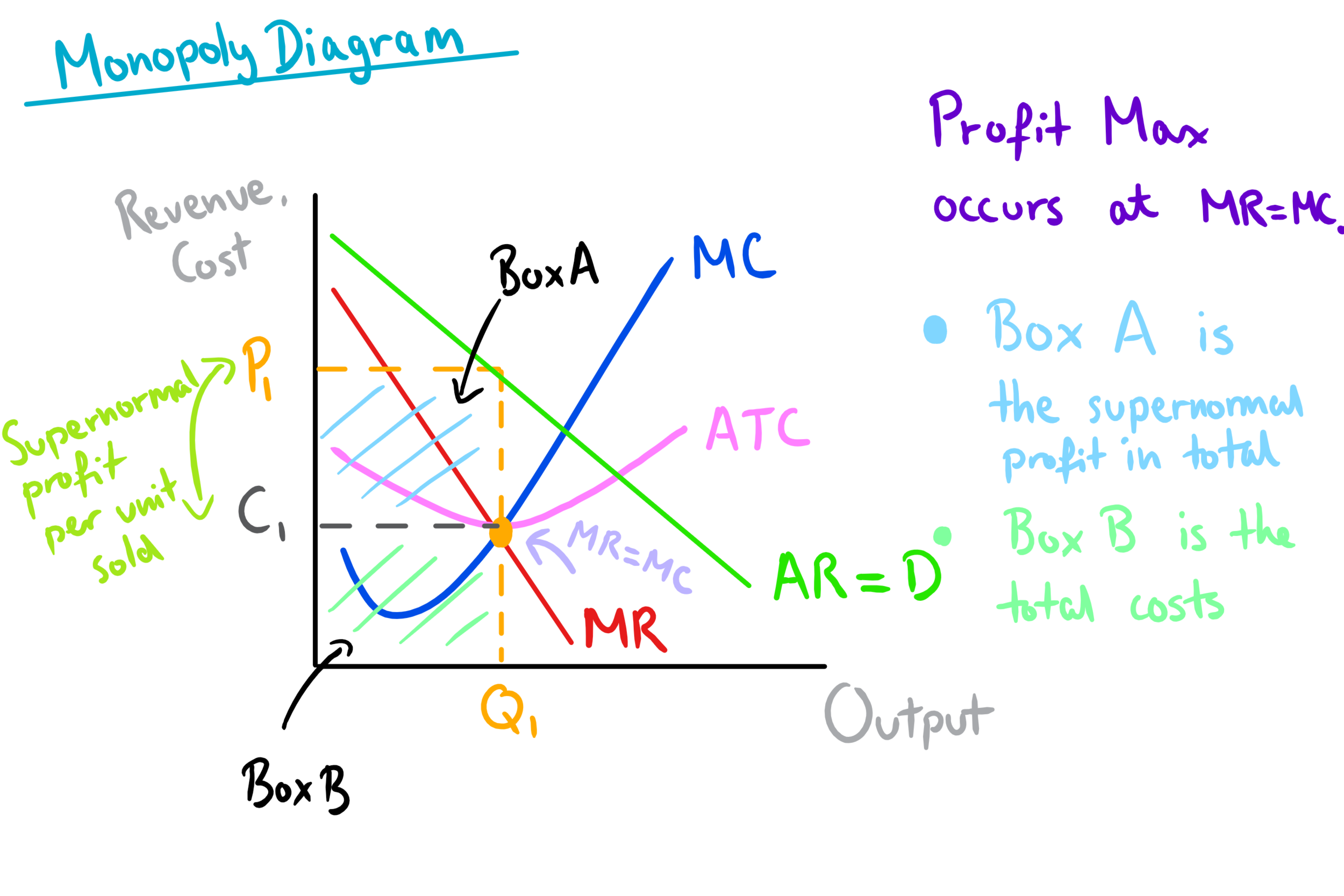
Monopolies Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Tutoring Exam Prep Show solution. the correct answer is that the optimal quantity produced for a monopolist is defined at the point where the marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue. it is not the case that the marginal cost is equal to the price. this is accurate in a competitive market, where marginal revenue and price are equivalent, but not in a monopoly. The area of deadweight loss for a monopolist can also be shown in a more simple form, comparing perfect competition with monopoly. alternative diagram. the following diagram assumes that average cost is constant, and equal to marginal cost (atc = mc).under perfect competition, equilibrium price and output is at p and q.

Monopoly Edexcel Economics Revision
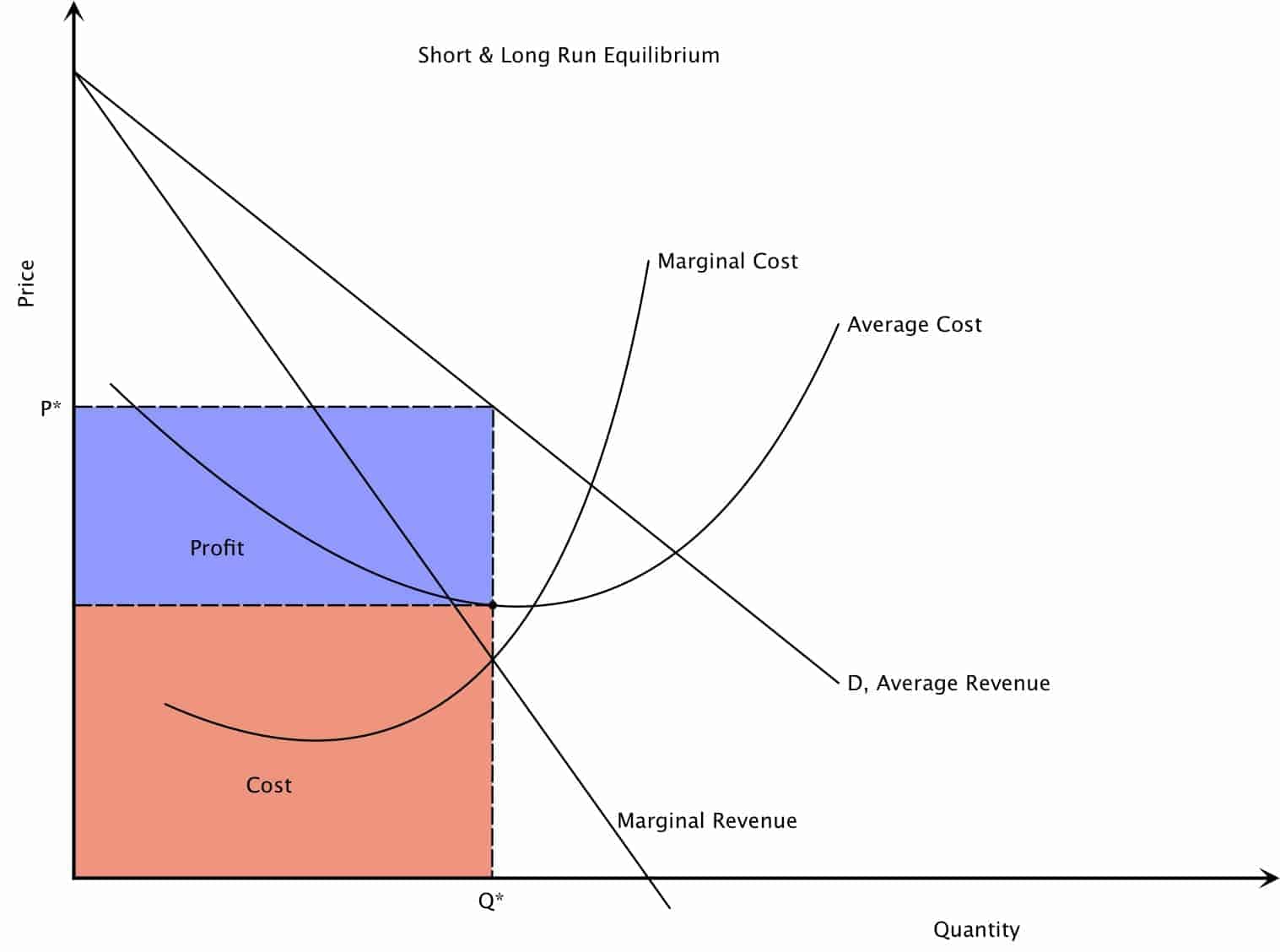
Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist

Comments are closed.