Diagram Of Actin And Myosin

Diagram Of Actin And Myosin Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) and actin forms thinner filaments (7nm in diameter). actin and myosin filaments work together to generate force. this force produces the muscle cell contractions that facilitate the movement of the muscles and. In figure 12.7.11 12.7. 11, you can see that a sarcomere is constructed so that the stationary myosin fibers are located centrally, with two parallel sets of actin fibers interspersed between the myosin fibers, to the left and the right of the center. note that the actin fibers do not cross the center line, and that at the center, the myosin.
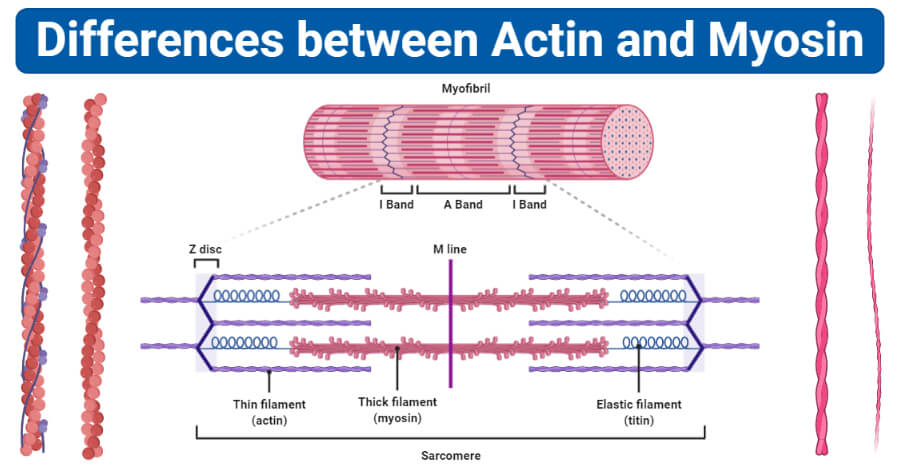
Actin And Myosin Filaments Diagram Actin filaments, usually in association with myosin, are responsible for many types of cell movements. myosin is the prototype of a molecular motor —a protein that converts chemical energy in the form of atp to mechanical energy, thus generating force and movement. the most striking variety of such movement is muscle contraction, which has. As the myosin s1 segment binds and releases actin, it forms what are called cross bridges, which extend from the thick myosin filaments to the thin actin filaments. the contraction of myosin's s1. These are longer (4 5 µm in length) and thicker (0.01 µm in diameter). nature. actin proteins are globular proteins. myosin proteins are motor proteins. molecular weight. the molecular weight of the actin proteins is relatively less. the molecular weight of myosin proteins is relatively more. abundance in muscle cells. Summary. myosin is a critical protein in muscle contraction and various cellular processes. its structure, comprising two heavy chains and four light chains, is essential for its function. the synthesis of myosin involves transcription, translation, and post translational modifications. myosin is classified into different types based on its.

Actin And Myosin Biology Dictionary These are longer (4 5 µm in length) and thicker (0.01 µm in diameter). nature. actin proteins are globular proteins. myosin proteins are motor proteins. molecular weight. the molecular weight of the actin proteins is relatively less. the molecular weight of myosin proteins is relatively more. abundance in muscle cells. Summary. myosin is a critical protein in muscle contraction and various cellular processes. its structure, comprising two heavy chains and four light chains, is essential for its function. the synthesis of myosin involves transcription, translation, and post translational modifications. myosin is classified into different types based on its. The main functions of actin filaments include: forming a dynamic cytoskeleton to provide structural support to cells. supporting and allowing cell motility. supporting muscle contractions as actin filaments slide alongside myosin filaments. in muscle, actin molecules twist together to form a 'thin filament' which interdigitate with thick. Actin. highly conserved 375 aa, 43 kd protein. the most abundant protein in non muscle cells : 1 5%. roles: cell shape, polarization, locomotion, division; vesicle traffic. monomer = g actin.

Comments are closed.