Derivative Of Exponential Functions
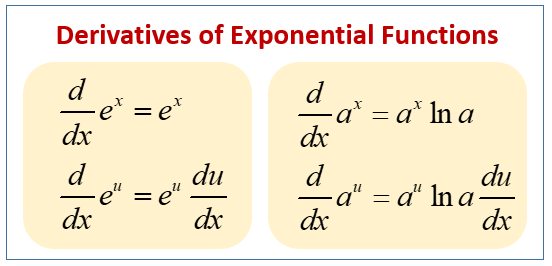
Calculus Exponential Derivatives Examples Solutions Videos Learn how to differentiate exponential functions of the form f(x) = a^x and f(x) = ax using the definition of the derivative and the chain rule. see examples of how to apply the formulas to e^x, 2^x, and e^x(x^2 1). Learn how to compute the derivative of \\ (a^x\\) using the definition of the derivative and the limit \\ (c (a) = \\lim {h \\to 0} \\frac {a^h 1} {h}\\). find out the value of \\ (c (a)\\) that makes the derivative equal to \\ (a^x)\\) and the connection with logarithms.
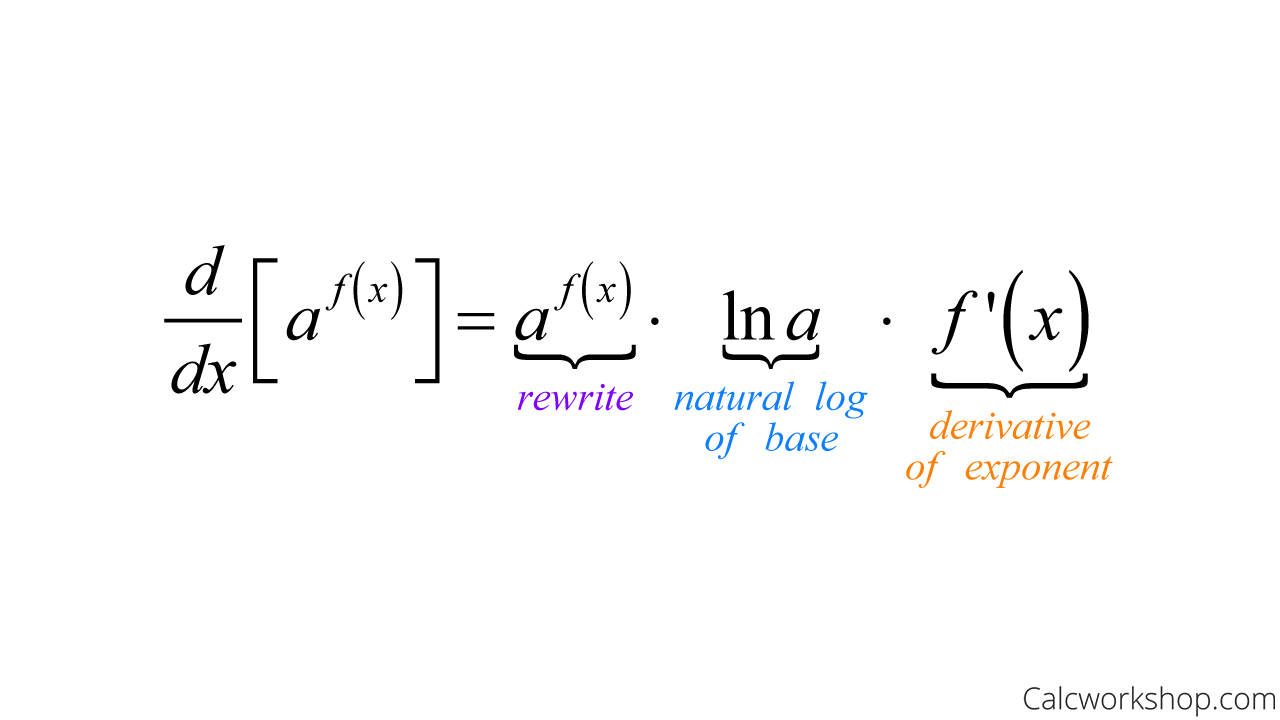
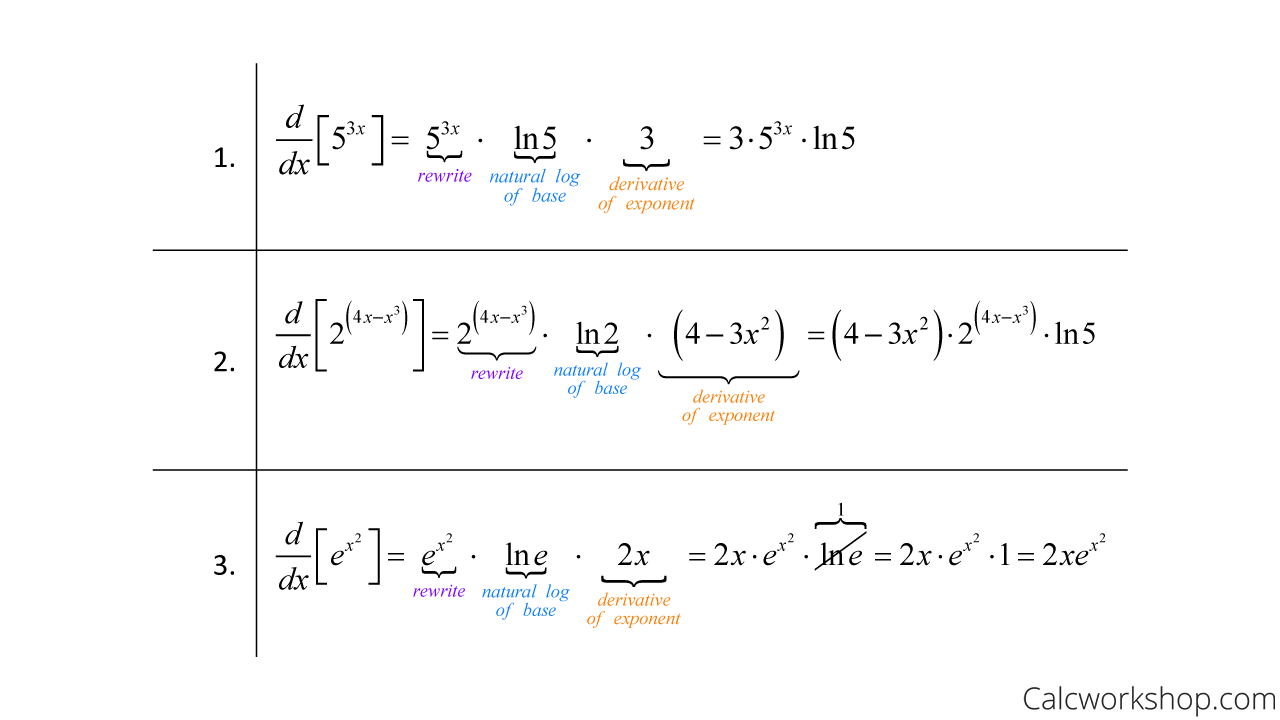
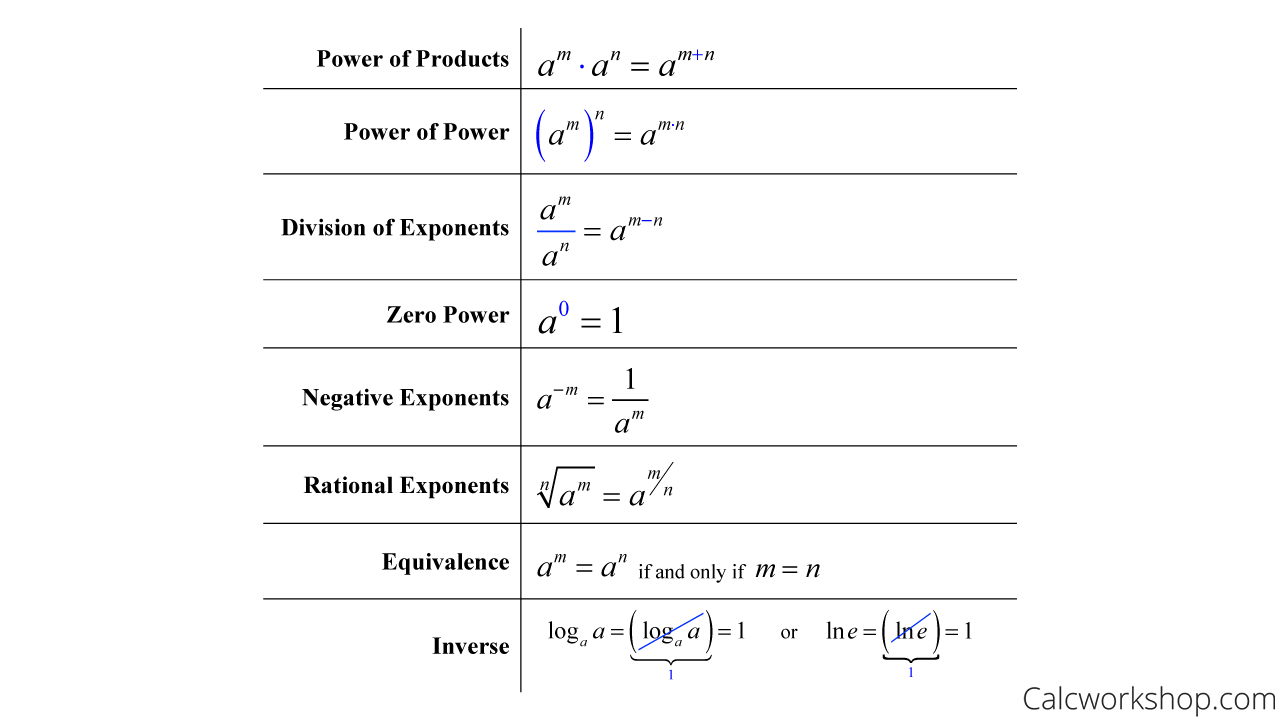
Derivative Of Exponential Function Fully Explained Learn how to find the derivative of exponential function f (x) = a x, a > 0 and f (x) = e x using the first principle of differentiation. see the graph of derivative of exponential function and its properties, and solve problems with faqs. Learn how to differentiate exponential and logarithm functions using definitions, facts and formulas. find the derivatives of natural exponential and logarithm functions, and general exponential and logarithm functions with positive bases. Learn how to find the derivatives of exponential and logarithmic functions using formulas and examples. explore the natural exponential and logarithmic functions, their properties, and their applications. The derivative of an exponential function can be derived using the definition of the derivative. derivatives of exponential functions involve the natural logarithm function, which itself is an important limit in calculus, as well as the initial exponential function. the derivative is the natural logarithm of the base times the original function.
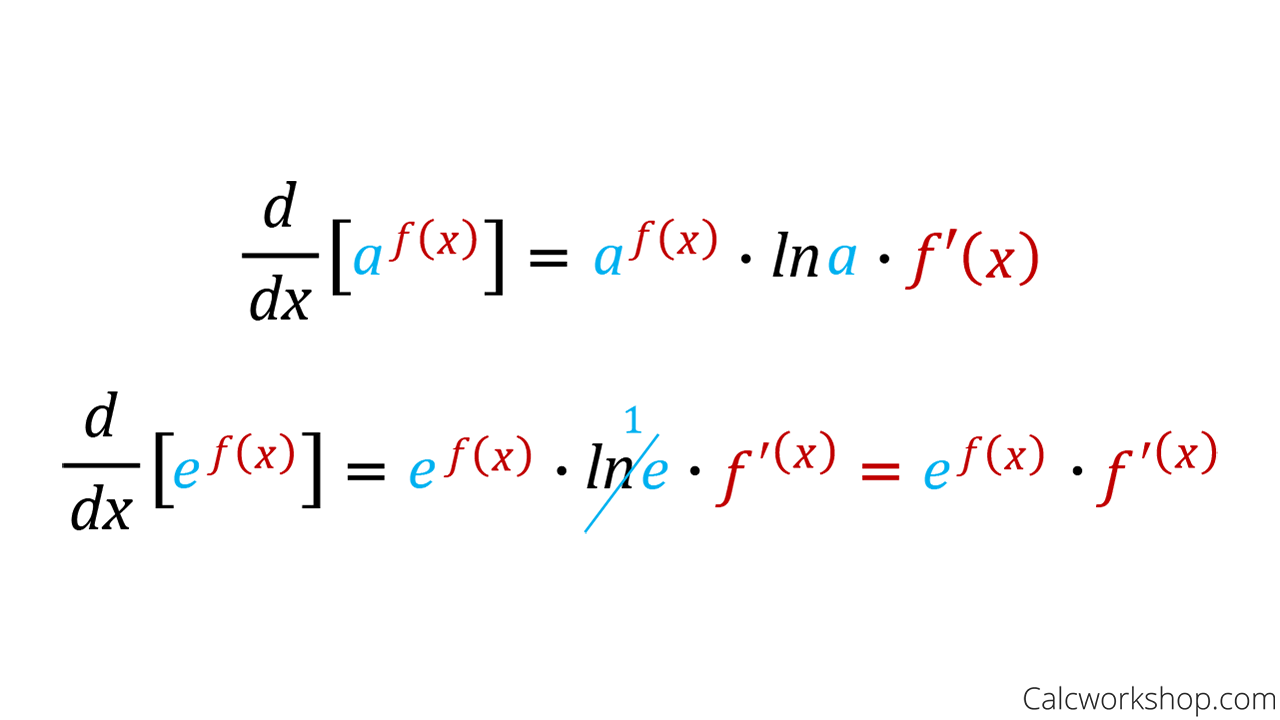
Derivative Of Exponential Function Learn how to find the derivatives of exponential and logarithmic functions using formulas and examples. explore the natural exponential and logarithmic functions, their properties, and their applications. The derivative of an exponential function can be derived using the definition of the derivative. derivatives of exponential functions involve the natural logarithm function, which itself is an important limit in calculus, as well as the initial exponential function. the derivative is the natural logarithm of the base times the original function. The function e(x) = ex is called the natural exponential function. its inverse, l(x) = logex = lnx is called the natural logarithmic function. figure 3.33 the graph of e(x) = ex is between y = 2x and y = 3x. for a better estimate of e, we may construct a table of estimates of b ′ (0) for functions of the form b(x) = bx. The derivative of the function ex is ex. the value of base e is obtained from the limit in equation (10.2.1). this can be written in either of two equivalent forms. the base of the natural exponential function is the real number defined as follows: e = lim h → 0(1 h)1 h = lim n → ∞(1 1 n)n. mastered material check.

Derivatives Of Exponential Functions Youtube The function e(x) = ex is called the natural exponential function. its inverse, l(x) = logex = lnx is called the natural logarithmic function. figure 3.33 the graph of e(x) = ex is between y = 2x and y = 3x. for a better estimate of e, we may construct a table of estimates of b ′ (0) for functions of the form b(x) = bx. The derivative of the function ex is ex. the value of base e is obtained from the limit in equation (10.2.1). this can be written in either of two equivalent forms. the base of the natural exponential function is the real number defined as follows: e = lim h → 0(1 h)1 h = lim n → ∞(1 1 n)n. mastered material check.
Derivative Of Exponential Function Fully Explained
Derivative Of Exponential Function Fully Explained

Comments are closed.