Demand Curves What Are They Types And Example
Demand Curves What Are They Types And Example A demand curve is a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded within a specified time frame. demand curves can be used to understand the. Aggregate or market demand curve . the market demand curve describes the quantity demanded by the entire market for a category of goods or services, such as gasoline prices. when the price of oil goes up, all gas stations must raise their prices to cover their costs. oil prices comprise 70% of gas prices; even if the price drops 50%, drivers.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DemandCurve-4197946-Final-64b129da426e4213a0911a47bb9a3bfa.jpg)
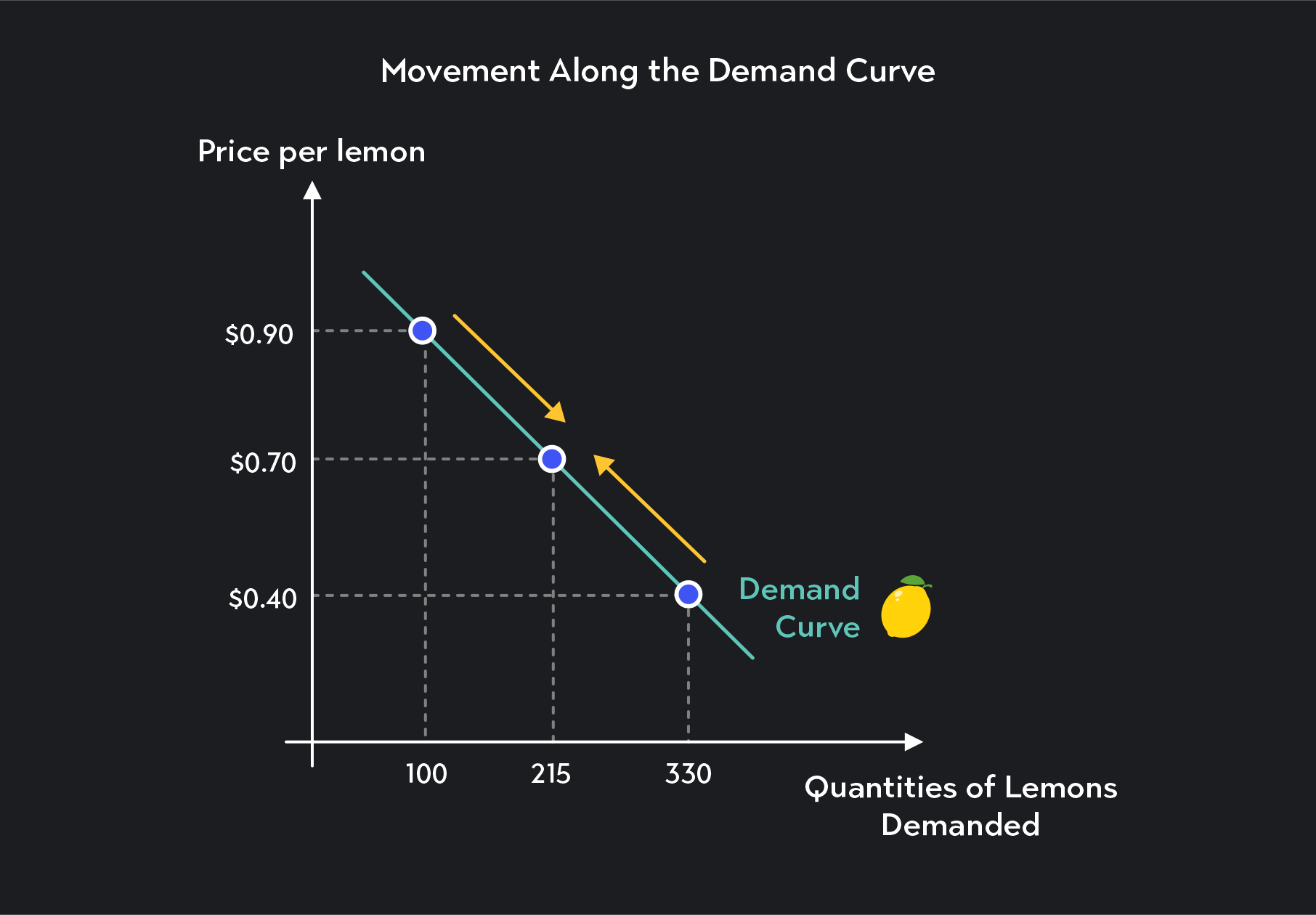
Demand Curves What Are They Types And Example You can read a demand curve in two ways: 1. horizontal read. in a horizontal read of the demand curve, you start with a price, move horizontally to the demand curve, and then down to the x axis to find the associated quantity demanded. at $0.40 per lemon, consumers are willing to buy 330 lemons. 2. Exploring the various types and factors influencing demand curves aids in strategic market analysis, vital for business success. discover more about demand curves and their significance in shaping consumer behavior and pricing strategies. key takeaways. demand curves illustrate the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. Some of the important types of demand curves are listed below: type # 1. negatively sloped straight lines demand curves: it is evident that the value of e at any (p, q) point on a curvilinear demand curve and the value of e at the same (p, q) point on a straight line demand curve—which is a tangent to the former demand curve at the said point—are identical. for example, the value of e at. Here, the curve moves in a downward direction. example: the current price of product a is $8, and the quantity demanded is 100. suppose the price of product a increases from $8 to $10; the quantity demanded decreases from 100 to 80. due to the decline in demand, the manufacturer has decreased the price to $6.
Understanding The Demand Curve And How It Works Outlier Some of the important types of demand curves are listed below: type # 1. negatively sloped straight lines demand curves: it is evident that the value of e at any (p, q) point on a curvilinear demand curve and the value of e at the same (p, q) point on a straight line demand curve—which is a tangent to the former demand curve at the said point—are identical. for example, the value of e at. Here, the curve moves in a downward direction. example: the current price of product a is $8, and the quantity demanded is 100. suppose the price of product a increases from $8 to $10; the quantity demanded decreases from 100 to 80. due to the decline in demand, the manufacturer has decreased the price to $6. The negative slope of the demand curve in figure 3.1 “a demand schedule and a demand curve” suggests a key behavioral relationship of economics. all other things unchanged, the law of demand holds that, for virtually all goods and services, a higher price leads to a reduction in quantity demanded and a lower price leads to an increase in. The demand curve is a line graph utilized in economics, that shows how many units of a good or service will be purchased at various prices. the price is plotted on the vertical (y) axis while the quantity is plotted on the horizontal (x) axis. demand curves are used to determine the relationship between price and quantity, and follow the law of.

Comments are closed.