Deep Brain Stimulation For Medication Resistant Dystonia A Ucsf Case

Deep Brain Stimulation Mu Health Care The following case study describes how the ucsf team successfully treated a young man’s medication resistant dystonia with deep brain stimulation (dbs). progressive symptoms undiagnosed for seven years. a 10 year old boy developed left foot inversion, which made it difficult for him to walk. he subsequently developed a tremor in his right arm. Deep brain stimulation (dbs) is an established treatment for motor disorders like parkinson’s disease, but its mechanisms and effects on neurons and networks are not fully understood, limiting.

Cerebellar Deep Brain Stimulation For Secondary Dystonia A Case Report The ucsf movement disorder and neuromodulation center is the largest center for the surgical treatment of parkinson's disease and other movement disorders in northern california. dr. dr. phillip starr and dr. jill ostrem, the center's co directors, are pioneers in the use of deep brain stimulation (dbs) therapy to treat conditions such as. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus is approved by the food and drug administration for treating dystonia. both targets have shown effectiveness in improving symptoms, but post operative outcomes can vary significantly among patients. Abstract. deep brain stimulation (dbs) is an effective surgical treatment for medication refractory movement disorders, and has been approved by the united states food and drug administration for treatment of dystonia. the success of dbs in the treatment of dystonia depends on our understanding of the anatomy and physiology of this disorder and. And deep brain stimulation trials, as advances in functional stereotactic neurosurgery over the past three decades have markedly widened the scope of dystonia treatment. finally, we will provide an overview of evidence for other interven tions including various rehabilitative paradigms and noninva sive stimulation techniques. * ian o. bledsoe.
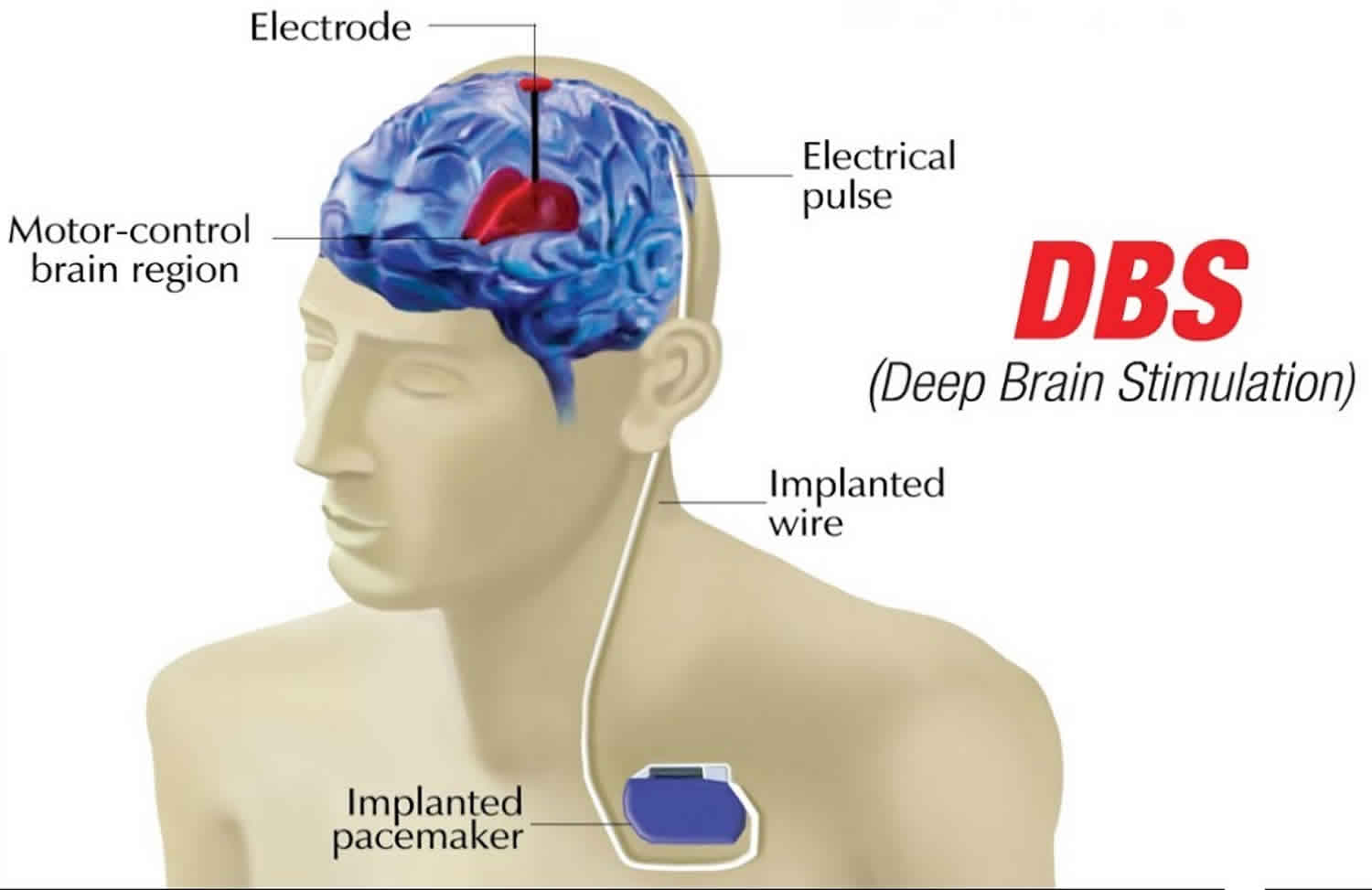
Deep Brain Stimulation Uses Success Rate Side Effects Abstract. deep brain stimulation (dbs) is an effective surgical treatment for medication refractory movement disorders, and has been approved by the united states food and drug administration for treatment of dystonia. the success of dbs in the treatment of dystonia depends on our understanding of the anatomy and physiology of this disorder and. And deep brain stimulation trials, as advances in functional stereotactic neurosurgery over the past three decades have markedly widened the scope of dystonia treatment. finally, we will provide an overview of evidence for other interven tions including various rehabilitative paradigms and noninva sive stimulation techniques. * ian o. bledsoe. This study includes three populations: ten pd patients undergoing deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus (stn), ten pd patients with a globus pallidus (gpi) target and five dystonia patients. all groups will test a variety of strategies for feedback controlled deep brain stimulation, and all patients will undergo a blinded, small. Deep brain stimulation (dbs) has emerged as a promising treatment option for children with medically refractory dystonia. in this review we highlight the relevant literature related to dbs for pediatric dystonia, with emphasis on the background, indications, prognostic factors, challenges, and future directions of pediatric dbs.

Deep Brain Stimulation Dbs Dystonia Treatment Propel Physiotherapy This study includes three populations: ten pd patients undergoing deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus (stn), ten pd patients with a globus pallidus (gpi) target and five dystonia patients. all groups will test a variety of strategies for feedback controlled deep brain stimulation, and all patients will undergo a blinded, small. Deep brain stimulation (dbs) has emerged as a promising treatment option for children with medically refractory dystonia. in this review we highlight the relevant literature related to dbs for pediatric dystonia, with emphasis on the background, indications, prognostic factors, challenges, and future directions of pediatric dbs.
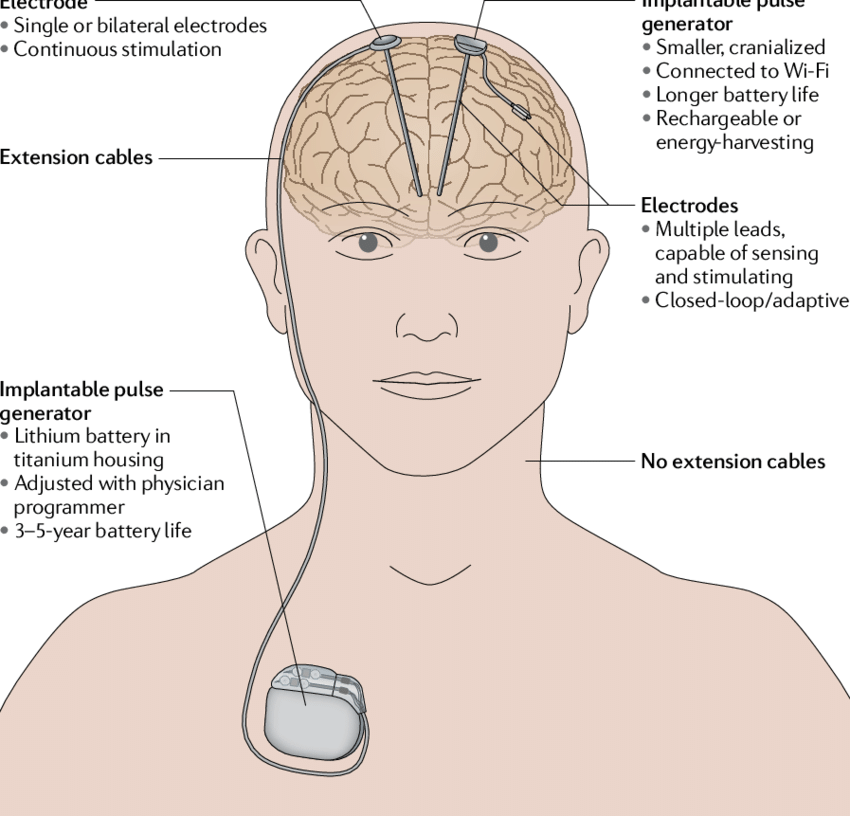
Understanding The Process Of Deep Brain Stimulation Dbs Surgery

Comments are closed.