Csf Analysis In Meningitis Algorithm When Lumbar Puncture Is Necessary
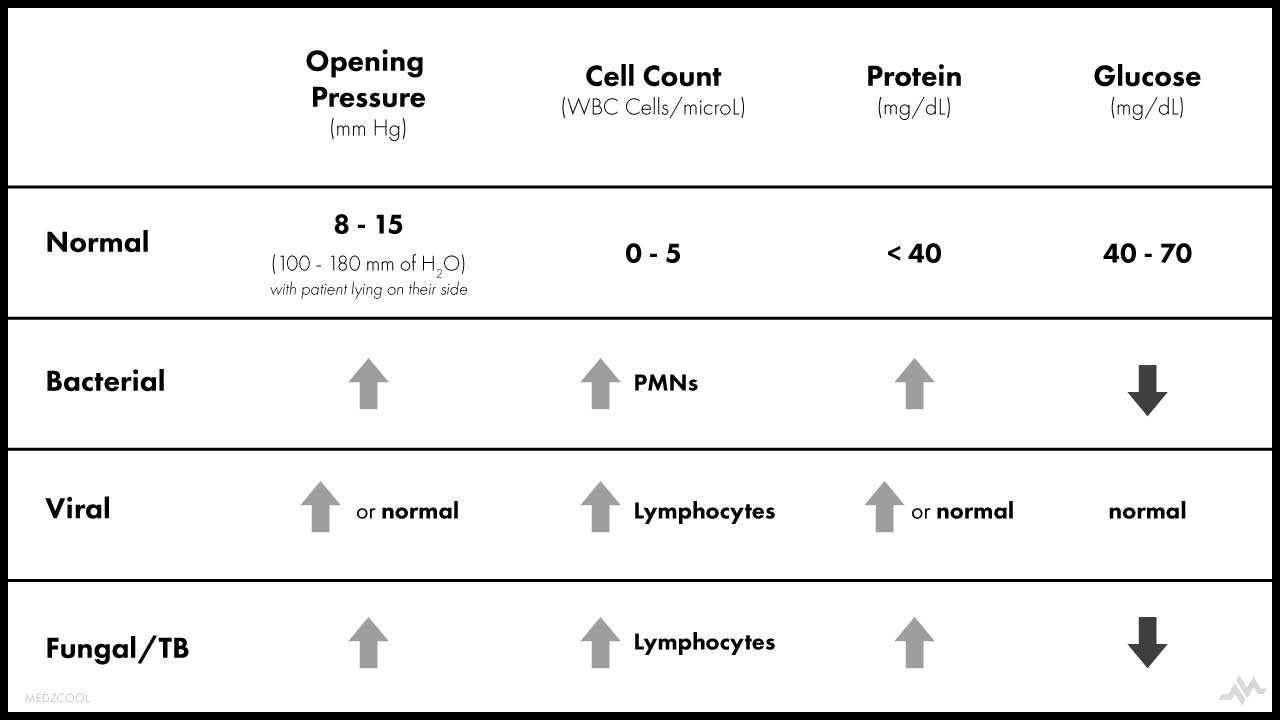
Medline Plus Medical Encyclopedia Csf Analysis In Meningitis Cerebrospinal fluid (csf) analysis is a diagnostic tool for many conditions affecting the central nervous system. the most common indication for lumbar puncture. bacterial meningitis has a 14%. Cerebrospinal fluid (csf) analysis is important for detecting inflammation of the nervous system and the meninges, bleeding in the area of the subarachnoid space that may not be visualized by imaging, and the spread of malignant diseases to the csf.

Csf Analysis In Meningitis Algorithm When Lumbar Puncture Is Necessary Repeat lumbar puncture (primarily used in meningitis; see below). repeat lumbar puncture in meningitis . objectives: (1) the primary objective is to ensure that the csf has been sterilized (this should occur within <24 hours of adequate antibiotic therapy). Cerebrospinal fluid (csf) analysis is a diag and is the most common indication for lumbar puncture. bacterial meningitis has a 14% to 25% mortality rate; therefore, rapid csf evaluation and. The bacterial meningitis score has a sensitivity of 99% to 100% and a specificity of 52% to 62%, and appears to be the most specific tool available currently, although it is not widely used. 25. Rials and methods: this was a retrospective chart review of the results of lps performed in a tertiary care ed from march to october 2003 on patients aged 16 to 50 years suspected of having meningitis. using the electronic record, we recorded presenting symptoms, comorbidities, results of (cerebrospinal fluid) analysis, ed length of stay, and complications. the association between specific.
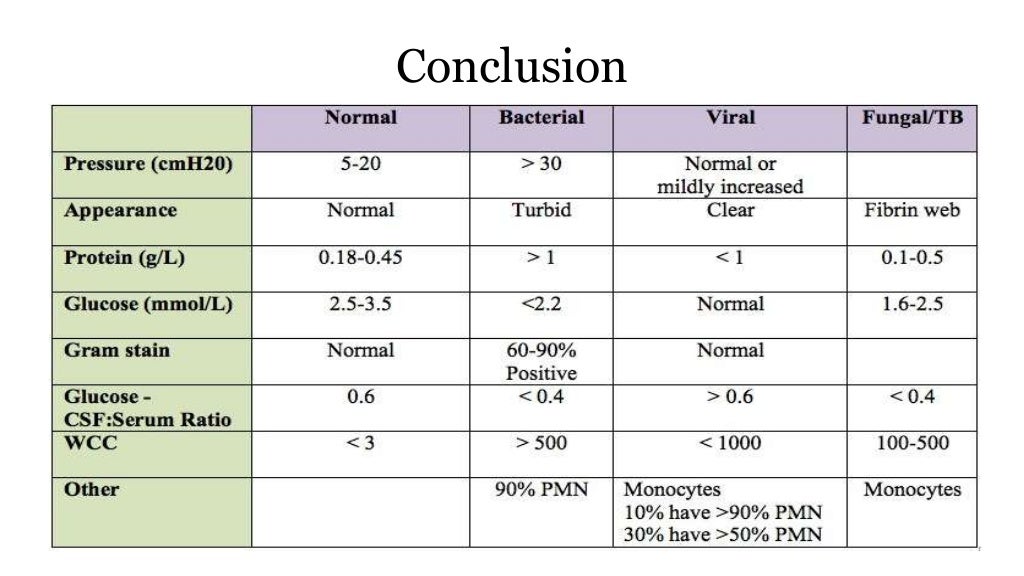
Lumbar Puncture And Csf Analysis The bacterial meningitis score has a sensitivity of 99% to 100% and a specificity of 52% to 62%, and appears to be the most specific tool available currently, although it is not widely used. 25. Rials and methods: this was a retrospective chart review of the results of lps performed in a tertiary care ed from march to october 2003 on patients aged 16 to 50 years suspected of having meningitis. using the electronic record, we recorded presenting symptoms, comorbidities, results of (cerebrospinal fluid) analysis, ed length of stay, and complications. the association between specific. Approach considerations. laboratory examination of the cerebrospinal fluid (csf) usually confirms the presence of meningitis. in the us, a neuroimaging study (either mri or ct scanning) prior to lumbar puncture is mandatory in all patients in whom meningitis is suspected. however, this rule is relaxed in several other countries (see ct scanning. The present article is an abridged translation of the above cited guideline. the guideline has been jointly edited by the dgln and dgn. in view of the importance and developments in csf analysis, the s1 guideline "lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis" was recently prepared by the german society for csf analysis and clinical.

Comments are closed.