Cross Section Of The Brain Labeled Anatomy Of Inner Brain Human
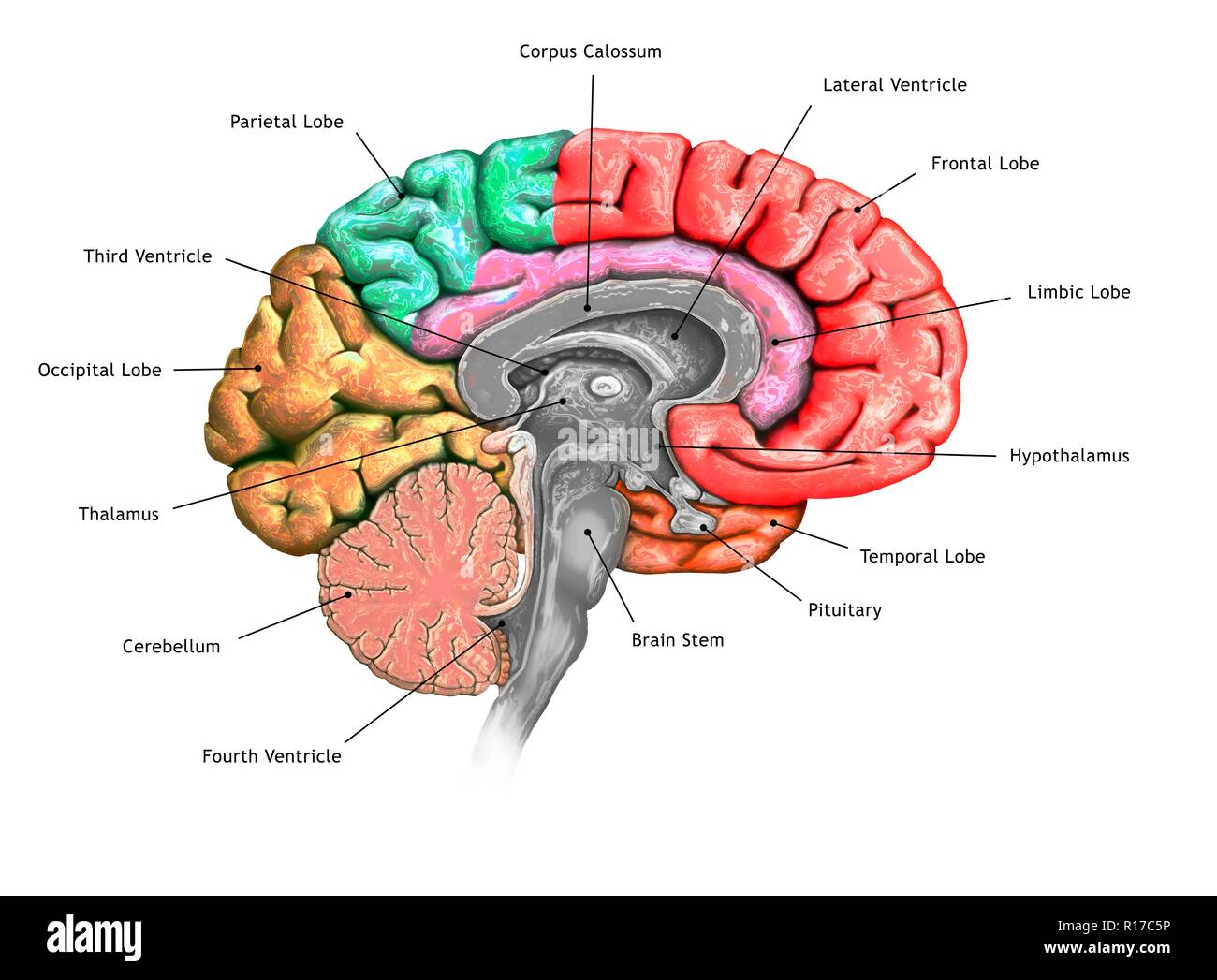
Illustration Of A Cross Section Of The Brain Showing The Various Lobes A midsagittal section of the brain. all four cerebral lobes are visible, as in the cingulate gyrus, which extends through the medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes. the corpus callosum sits beneath the cingulate gyrus. below the cerebrum lies the midbrain, pons, medulla and cerebellum. ‘internal brain regions’ by casey henley is. Labeled brain diagram. first up, have a look at the labeled brain structures on the image below. try to memorize the name and location of each structure, then proceed to test yourself with the blank brain diagram provided below. labeled diagram showing the main parts of the brain. blank brain diagram (free download!).
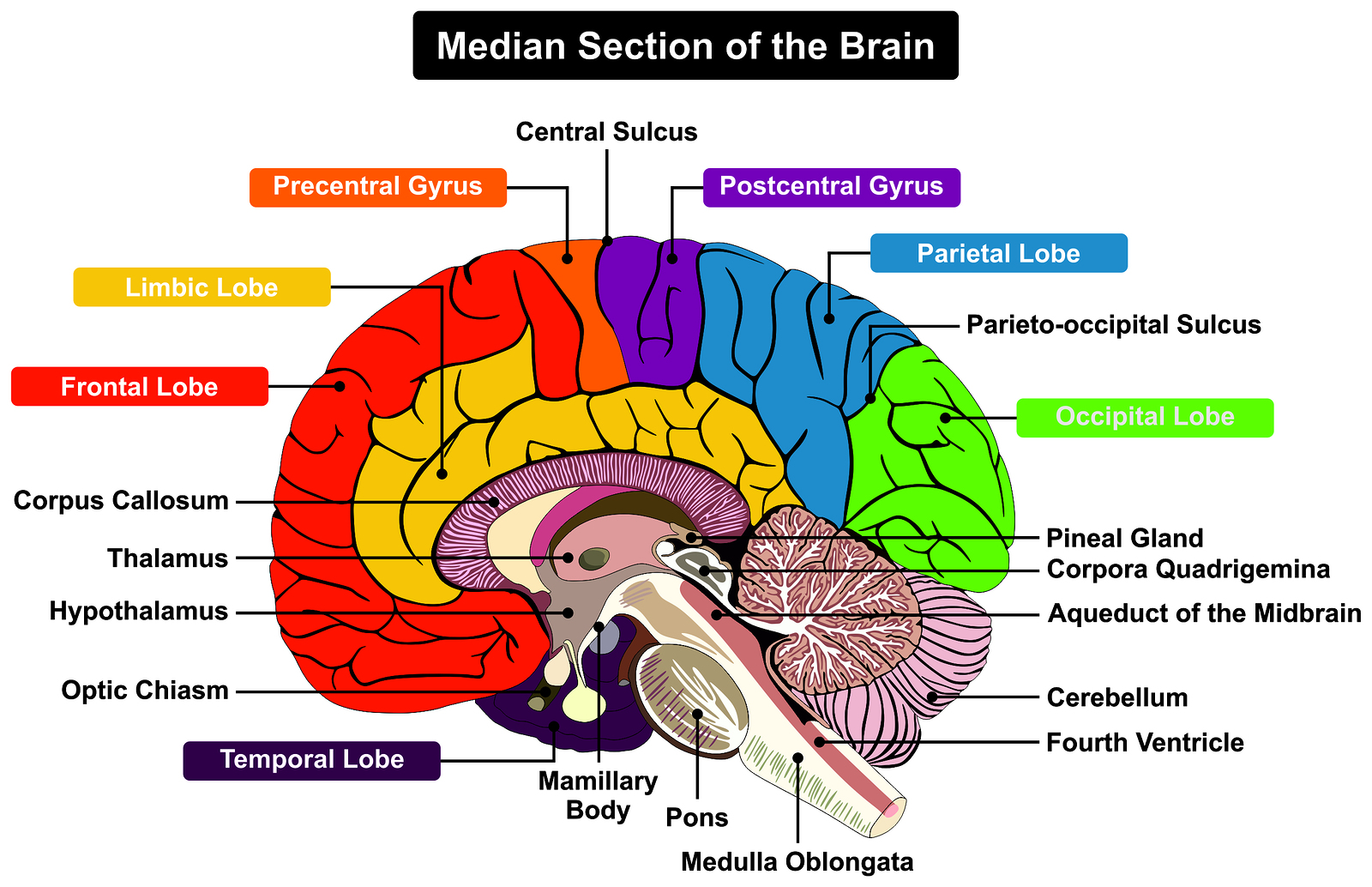
Brain Cross Section Diagram Labeled The three main parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. 1. cerebrum. location: the cerebellum occupies the upper part of the cranial cavity and is the largest part of the human brain. functions: it’s responsible for higher brain functions, including thought, action, emotion, and interpretation of sensory data. Explore the brain's complex functions and composition with innerbody's 3d anatomical model. the brain is one of the most complex and magnificent organs in the human body. our brain gives us awareness of ourselves and of our environment, processing a constant stream of sensory data. it controls our muscle movements, the secretions of our glands. Cross sections are two dimensional, axial views of gross anatomical structures seen in transverse planes. they are obtained by taking imaginary slices perpendicular to the main axis of organs, vessels, nerves, bones, soft tissue, or even the entire human body. cross sections provide the perception of ‘depth’, creating three dimensional. Three anatomical sections of the brain (axial, coronal and sagittal) close this chapter on the brain. figure 9 brain , coronal section : brain , anatomy diagram. numerous illustrations are available on the cerebellum, representation of cerebellar lobes, fissures, sulci and the vermis. figure 10 cerebellum , anterior view : diagram.

Brain Structure Differentiation Introduction To Neuroscience Cross sections are two dimensional, axial views of gross anatomical structures seen in transverse planes. they are obtained by taking imaginary slices perpendicular to the main axis of organs, vessels, nerves, bones, soft tissue, or even the entire human body. cross sections provide the perception of ‘depth’, creating three dimensional. Three anatomical sections of the brain (axial, coronal and sagittal) close this chapter on the brain. figure 9 brain , coronal section : brain , anatomy diagram. numerous illustrations are available on the cerebellum, representation of cerebellar lobes, fissures, sulci and the vermis. figure 10 cerebellum , anterior view : diagram. Gray and white matter are two different regions of the central nervous system. in the brain, gray matter refers to the darker, outer portion, while white matter describes the lighter, inner section underneath. in the spinal cord, this order is reversed: the white matter is on the outside, and the gray matter sits within. New york: elsevier churchill livingstone. fig 22.1: lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere indicating the major gyri and sulci, fig. 22.2: sagittal section of the brain, with the brain stem removed, showing the medial aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere, fig. 22.3: left lateral aspect of the brain, and fig: 22.4: the medial surface.
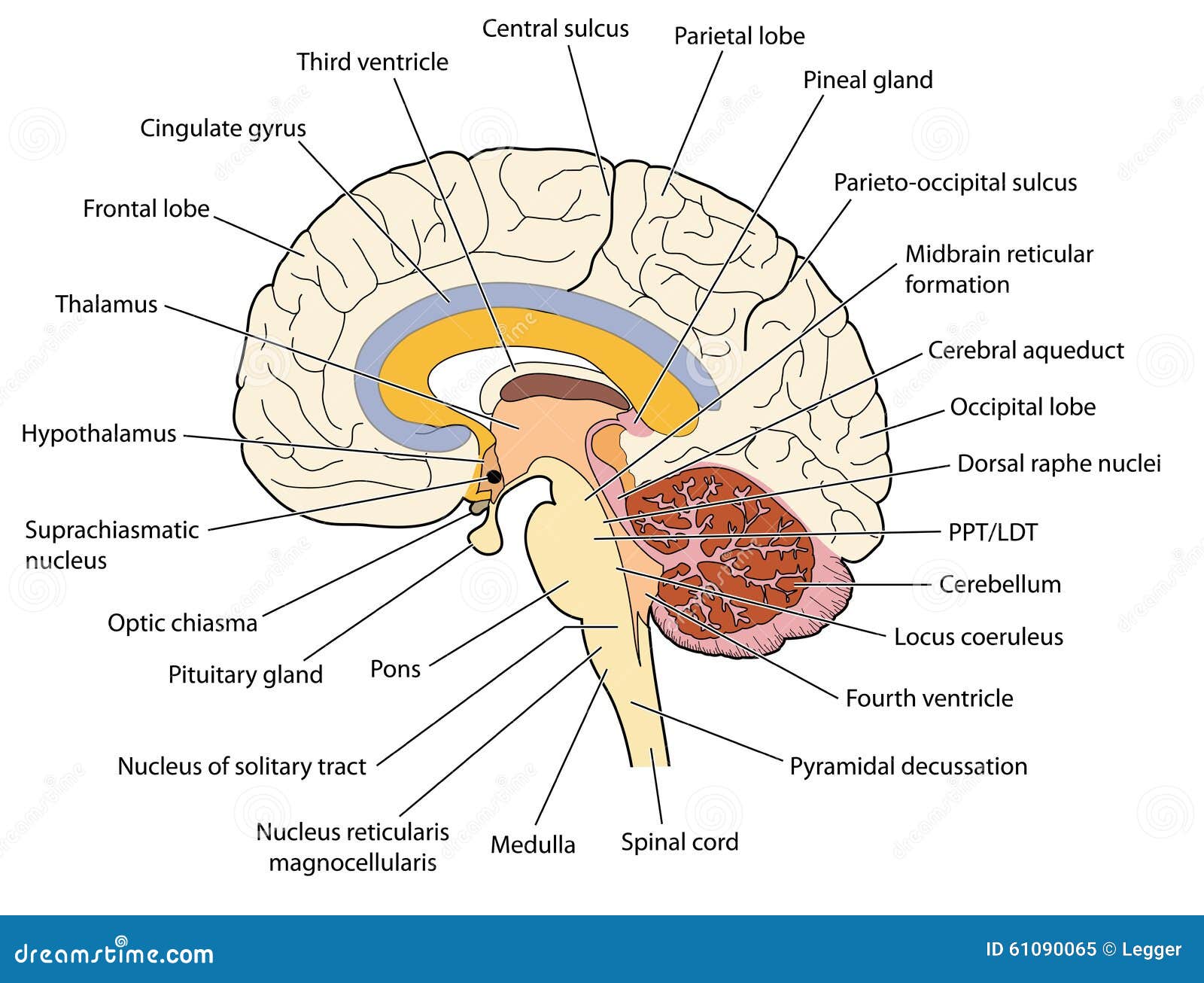
Cross Section Through The Brain Stock Vector Image 61090065 Gray and white matter are two different regions of the central nervous system. in the brain, gray matter refers to the darker, outer portion, while white matter describes the lighter, inner section underneath. in the spinal cord, this order is reversed: the white matter is on the outside, and the gray matter sits within. New york: elsevier churchill livingstone. fig 22.1: lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere indicating the major gyri and sulci, fig. 22.2: sagittal section of the brain, with the brain stem removed, showing the medial aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere, fig. 22.3: left lateral aspect of the brain, and fig: 22.4: the medial surface.
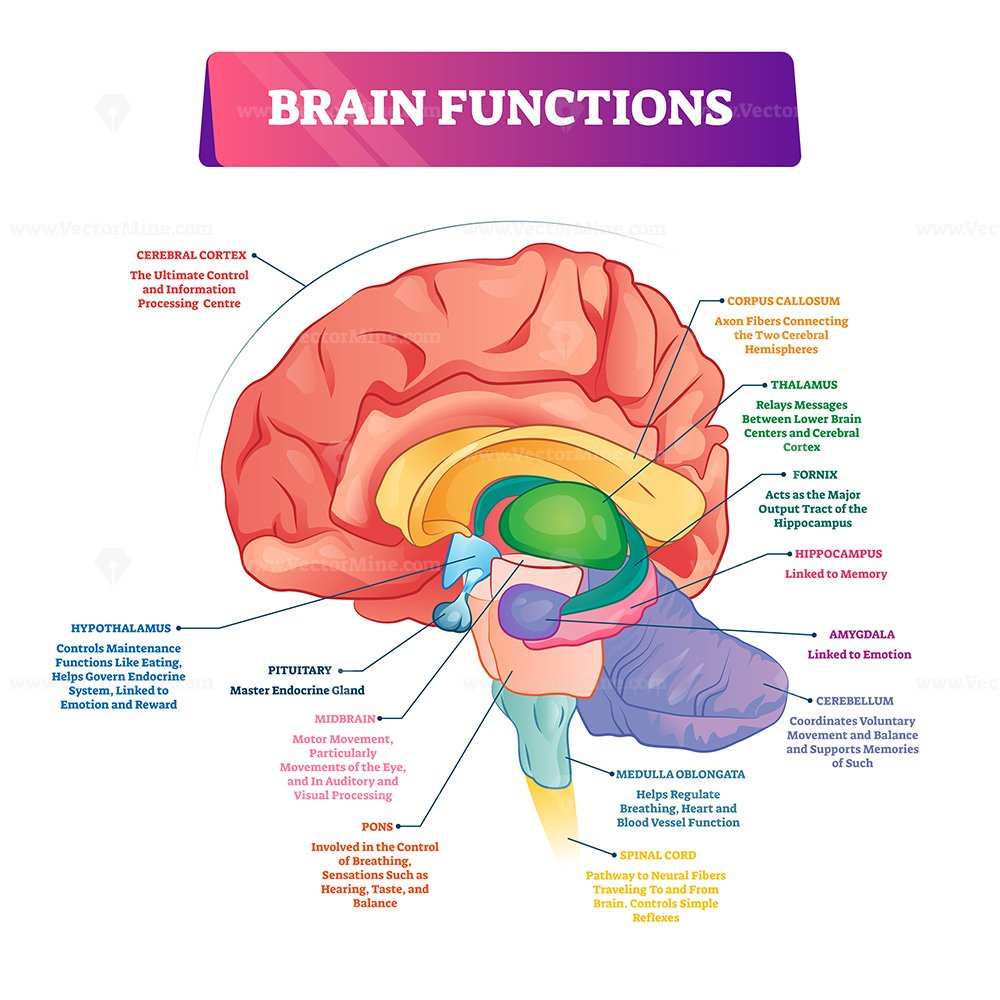
Brain Sections And Organ Part Functions In Labeled Anatomical Outline

Comments are closed.