Court Hierarchy Chart
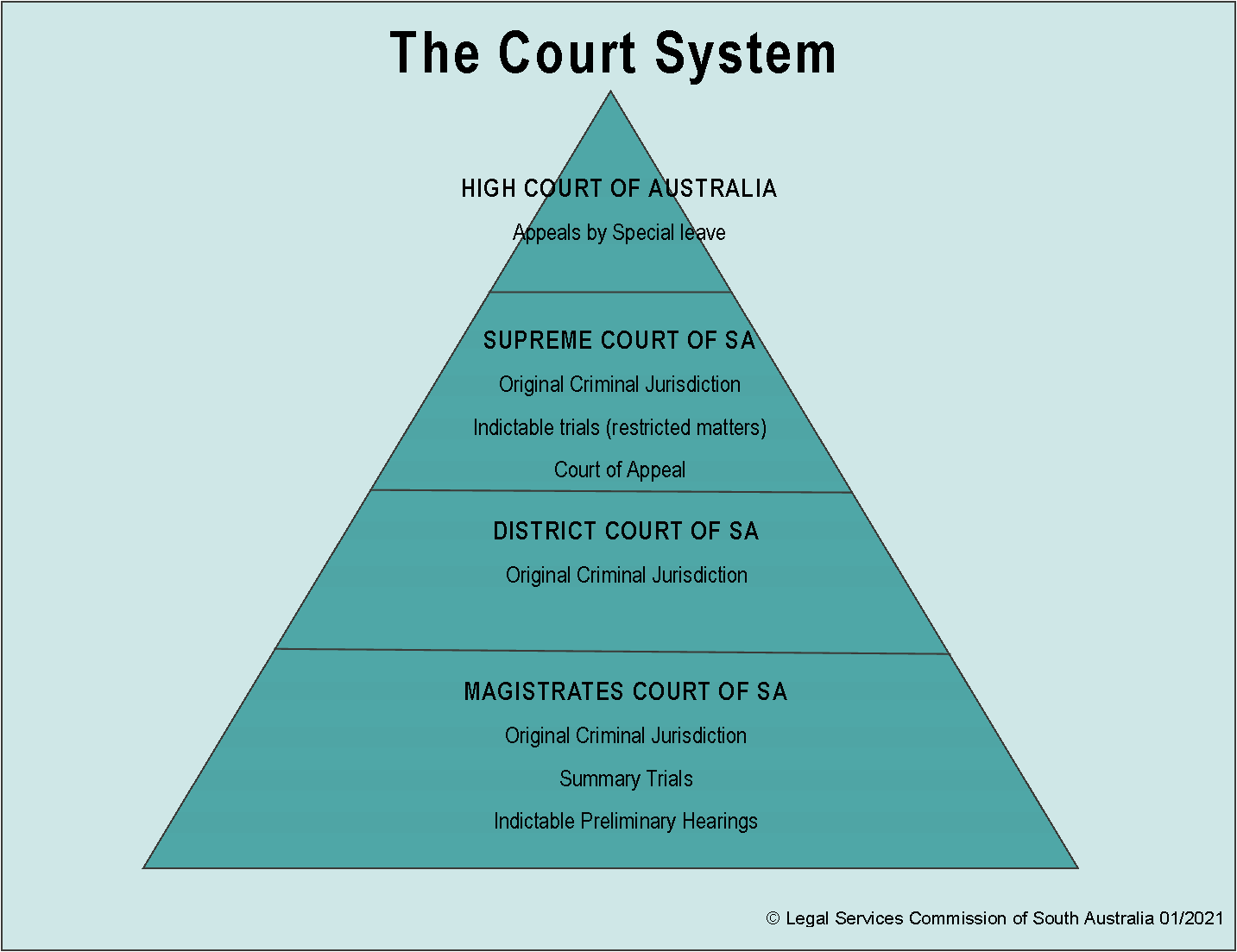
Courts Court role and structure. federal courts hear cases involving the constitutionality of a law, cases involving the laws and treaties of the u.s. ambassadors and public ministers, disputes between two or more states, admiralty law, also known as maritime law, and bankruptcy cases. the federal judiciary operates separately from the executive and. The state court system: the state court system largely mirrors the structure of the federal court system in that it is generally composed of three main levels: trial courts, state appellate courts and a state supreme court. on rare occasions, a decision on federal matters made in a state supreme court will be petitioned to the u.s. supreme court.
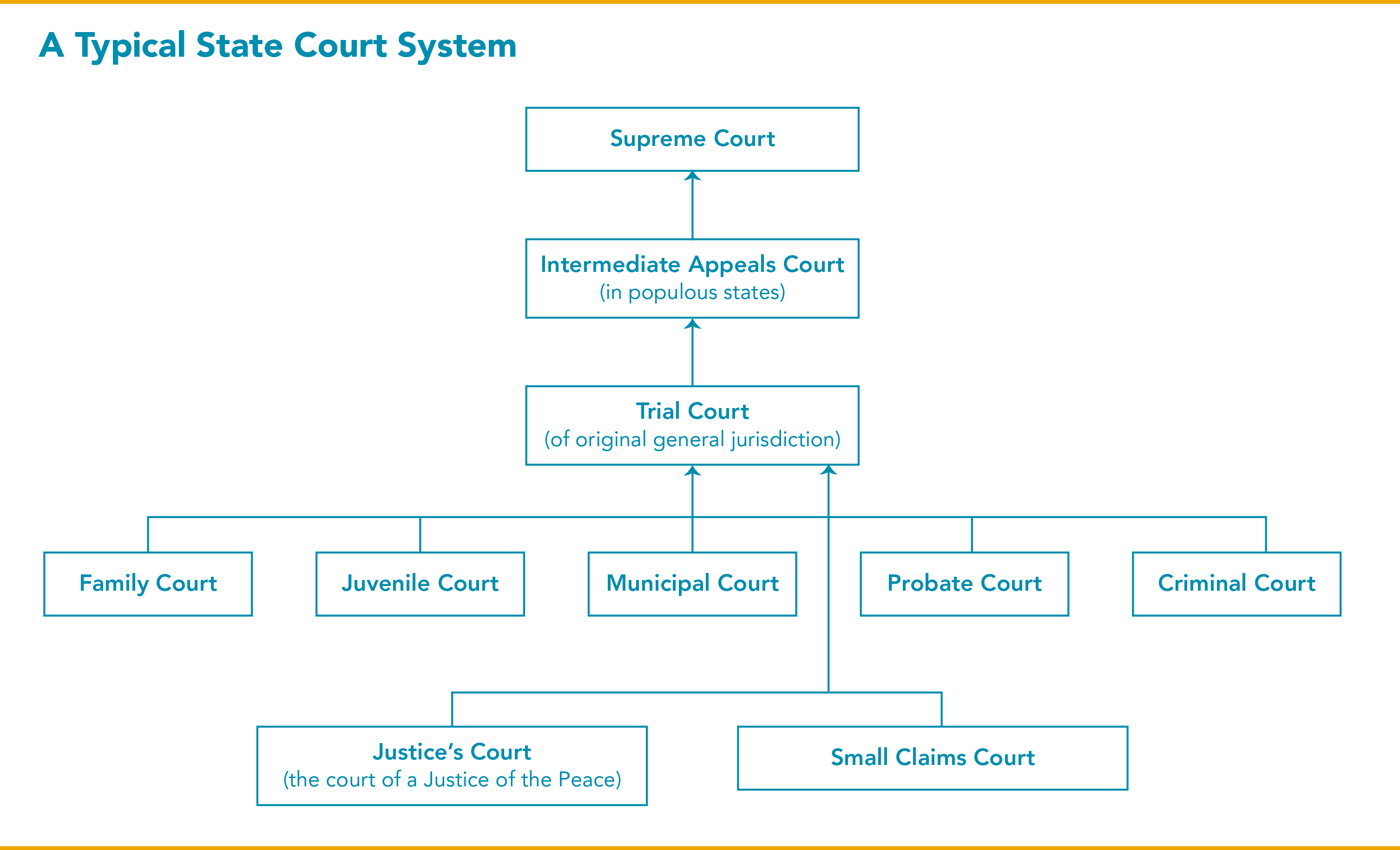
Pennsylvania Court System Chart Federal claims. congress passed a law in 1968 establishing the position of u.s. magistrate judge. they are federal judges of the district courts who serve 8 year terms. they handle preliminary criminal matters such as setting bail and issuing search warrants, and they assist the district judges with all types of cases. State court system . the organizational structure of a state court is determined by individual state constitutions – none are exactly the same – but the following levels of courts, discussed in greater detail in later sections, exist in the majority of states. see . appendix b for state court structure diagrams. courts of limited jurisdiction. The federal courts and most state courts are structured the same way. however, state and federal courts handle different types of cases, each with its own exclusive jurisdiction and original jurisdiction. state courts mainly handle cases involving state laws. this includes criminal matters, civil matters such as personal injury claims, matters. Comparing federal & state courts. the u.s. constitution is the supreme law of the land in the united states. it creates a federal system of government in which power is shared between the federal government and the state governments. due to federalism, both the federal government and each of the state governments have their own court systems.
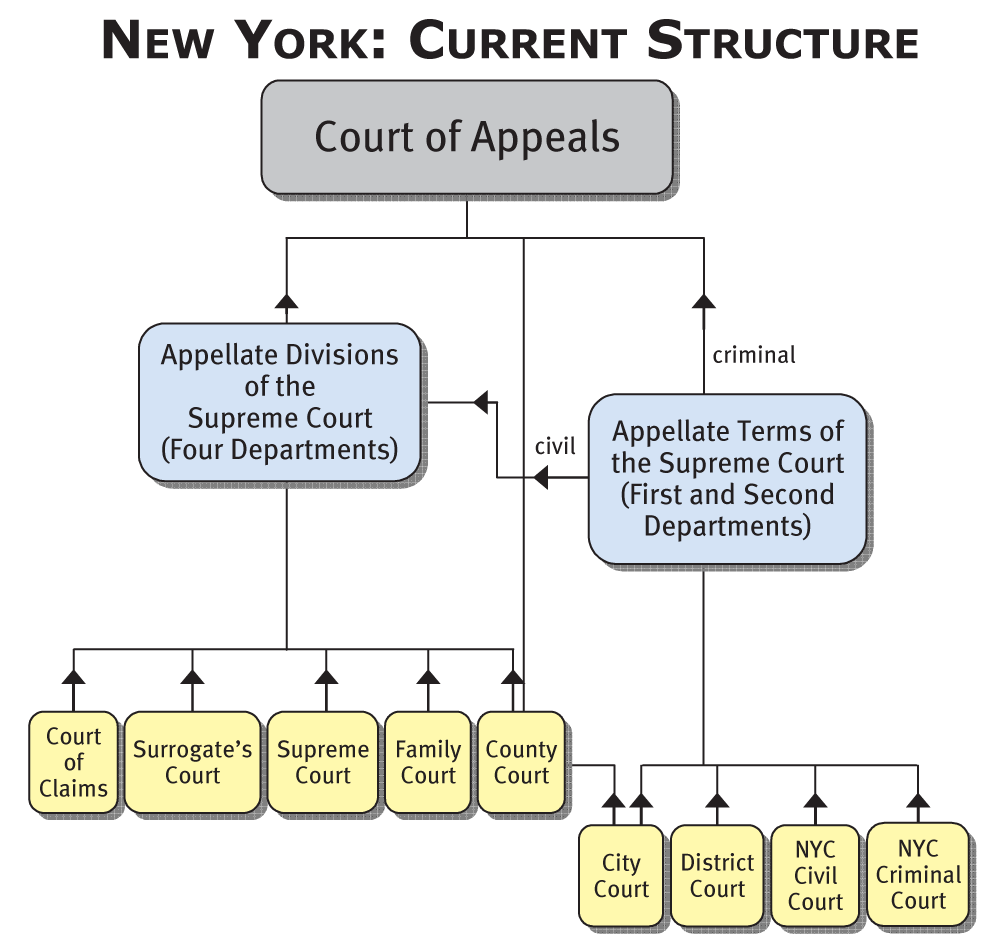
Structure Of The Courts The Fund For Modern Courts The federal courts and most state courts are structured the same way. however, state and federal courts handle different types of cases, each with its own exclusive jurisdiction and original jurisdiction. state courts mainly handle cases involving state laws. this includes criminal matters, civil matters such as personal injury claims, matters. Comparing federal & state courts. the u.s. constitution is the supreme law of the land in the united states. it creates a federal system of government in which power is shared between the federal government and the state governments. due to federalism, both the federal government and each of the state governments have their own court systems. Understanding the federal courts. administrative office of the u.s. courts. this publication was developed by the administrative office of the united. states courts to provide an introduction to the federal judicial system, its organization and administration, and its relationship to the legislative and executive branches of the government. The court structure charts summarize in one page diagrams the key features of each state’s court organization. the format meets two objectives: (1) it is comprehensive, indicating all court systems in the state and their interrelationship, and (2) it describes the subject matter jurisdiction of the court systems, using a standard set of.
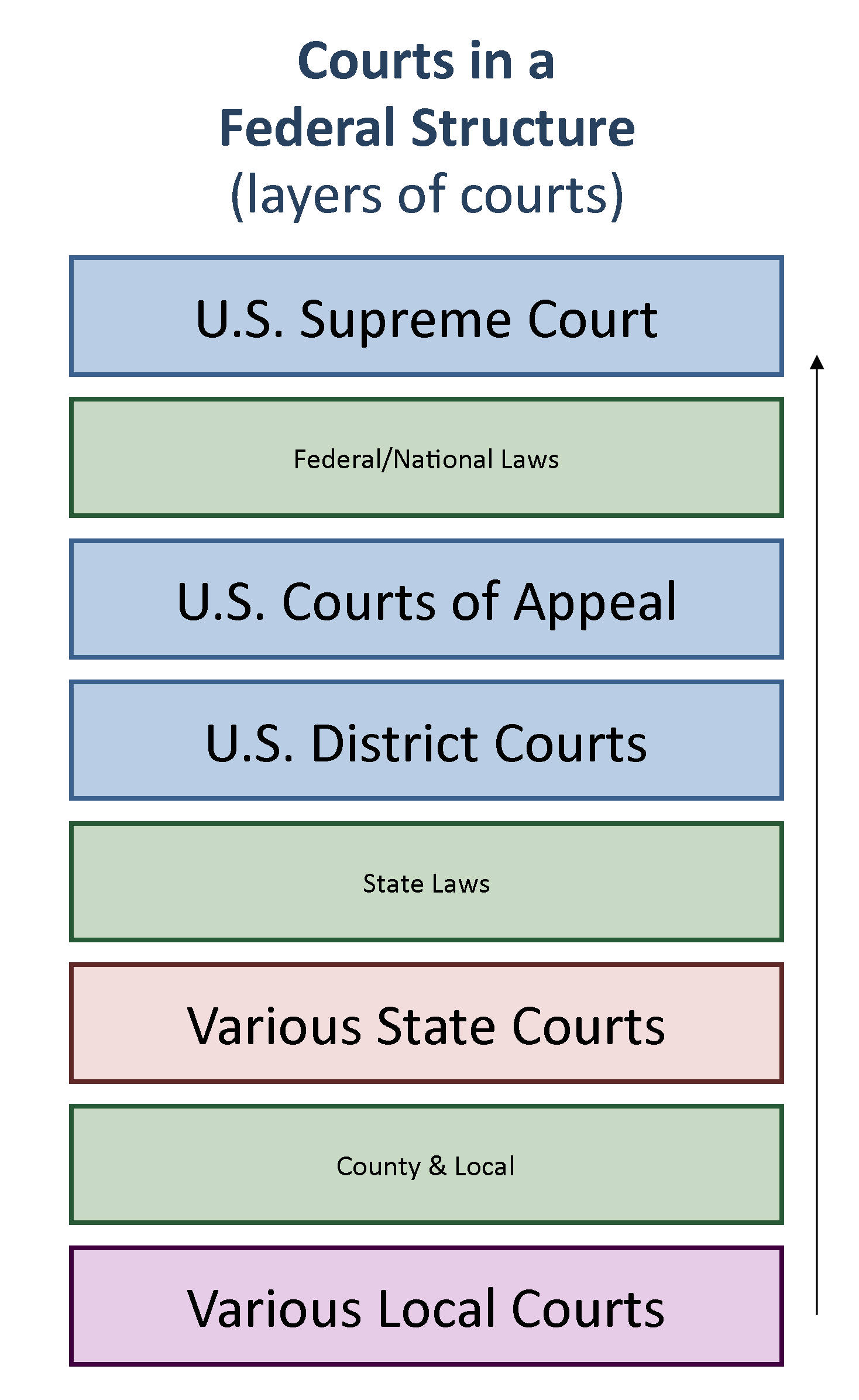
U S Courts Structure And Procedure United States Government Understanding the federal courts. administrative office of the u.s. courts. this publication was developed by the administrative office of the united. states courts to provide an introduction to the federal judicial system, its organization and administration, and its relationship to the legislative and executive branches of the government. The court structure charts summarize in one page diagrams the key features of each state’s court organization. the format meets two objectives: (1) it is comprehensive, indicating all court systems in the state and their interrelationship, and (2) it describes the subject matter jurisdiction of the court systems, using a standard set of.

Comments are closed.