Costs In The Short Run 2023
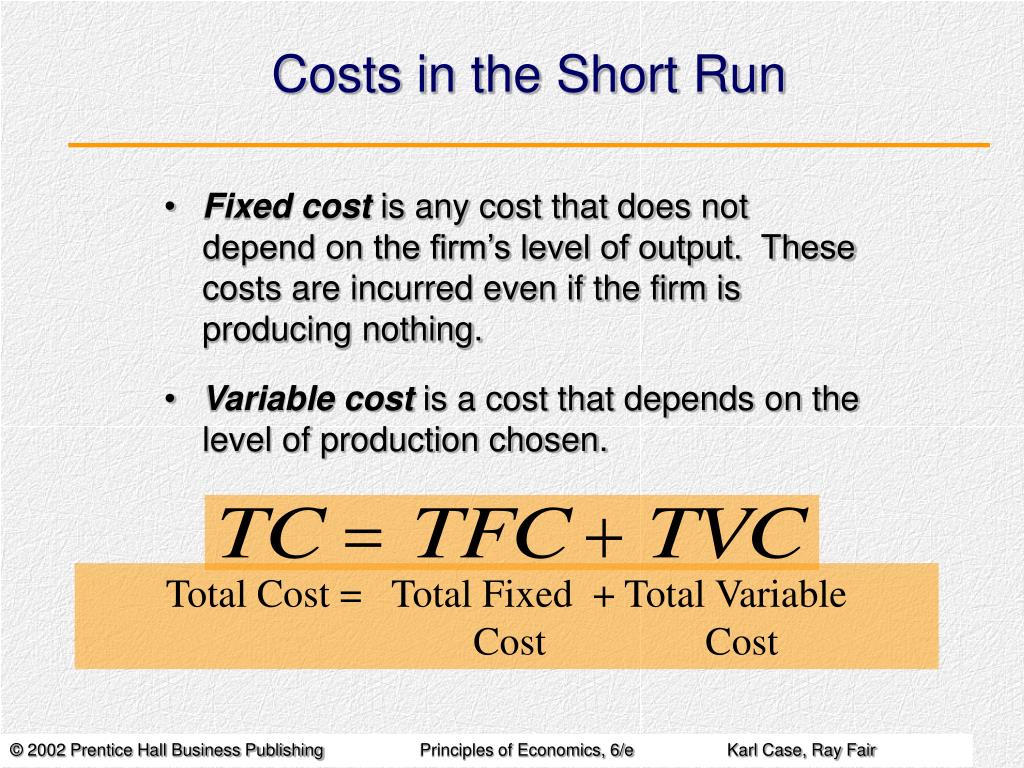
Costs In The Short Run 2023 Following are the cost concepts that are taken into consideration in the short run: i. total fixed costs (tfc): refer to the costs that remain fixed in the short period. these costs do not change with the change in the level of output. for example, rents, interest, and salaries. in the words of ferguson, “total fixed cost is the sum of the. Summary of the main points all the important short run cost relations may now be summed up: the total cost function may be expressed as: advertisements: tc = k ƒ (q) where k is total fixed cost which is a constant, and ƒ (q) is total variable cost which is a function of output. atc = k q ƒ (q) q = afc avc.
Ppt Short Run Costs And Output Decisions Powerpoint Presentation Equation 8.1. m p l = Δq Δl m p l = Δ q Δ l. in addition we can define the average product of a variable factor. it is the output per unit of variable factor. the average product of labor (apl), for example, is the ratio of output to the number of units of labor (q l). Average cost is the cost on average of producing a given quantity. we define average cost as total cost divided by the quantity of output produced. ac = tc q a c = t c q if producing two widgets costs a total of $44, the average cost per widget is $44 2 = $22 $44 2 = $22 per widget. In summary, the short run and the long run in terms of cost can be summarized as follows: short run: fixed costs are already paid and are unrecoverable (i.e. "sunk"). long run: fixed costs have yet to be decided on and paid, and thus are not truly "fixed." the two definitions of the short run and the long run are really just two ways of saying. In the short run, capital is fixed. after a certain point, increasing extra workers leads to declining productivity. therefore, as you employ more workers the marginal cost increases. diagram of marginal cost because the short run marginal cost curve is sloped like this, mathematically the average cost curve will be u shaped.

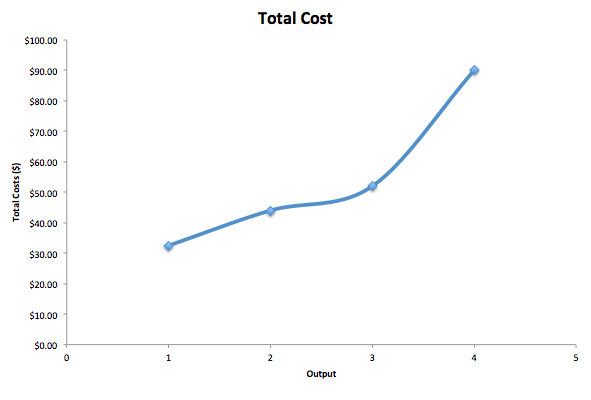
Eco 2023 Microeconomics Chapter 7 04 Production In The Short Run In summary, the short run and the long run in terms of cost can be summarized as follows: short run: fixed costs are already paid and are unrecoverable (i.e. "sunk"). long run: fixed costs have yet to be decided on and paid, and thus are not truly "fixed." the two definitions of the short run and the long run are really just two ways of saying. In the short run, capital is fixed. after a certain point, increasing extra workers leads to declining productivity. therefore, as you employ more workers the marginal cost increases. diagram of marginal cost because the short run marginal cost curve is sloped like this, mathematically the average cost curve will be u shaped. Even if the firm cuts production to zero, it must still pay $200 per day in the short run. acme’s total cost is its total fixed cost of $200 plus its total variable cost. we add $200 to the total variable cost curve in figure 8.5 to get the total cost curve shown in figure 8.6. Mathematically, marginal cost is the change in total cost divided by the change in output: \displaystyle mc=\delta tc \delta q m c = Δt c Δq. if the cost of the first widget is $32.50 and the cost of two widgets is $44, the marginal cost of the second widget is. $44 −$32.50 = $11.50 $ 44 − $ 32.50 = $ 11.50.

Comments are closed.