Corresponding Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples
Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Example 1: corresponding angles. calculate the size of the missing angle θ. justify your answer. highlight the angle (s) that you already know. 2 use corresponding angles to find a missing angle. here we can label the corresponding angle on the diagram as 75°. 3 use a basic angle fact to calculate the missing angle. Free angles gcse maths revision guide, including step by step examples, exam questions and free worksheet. maths tutoring for schools. example 11: corresponding.
Corresponding Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Firstly, we will use the fact that angles on a straight line add to 180 degrees. specifically, \angle efc and \angle cfg add to make 180\degree. which means we can do the following: \angle cfg = 180\degree 32\degree = 148\degree. now, looking at the diagram we can see that angle \angle cfg and the missing angle x are corresponding angles. Show step. co interior angles add up to 180^o 180o. here 180 110=70^o 180 − 110 = 70o. state the alternate angle, co interior angle or corresponding angle fact to find a missing angle in the diagram. show step. θ θ is corresponding to 70 35 70 35 so θ = 70 35 = 105^o θ = 70 35 = 105o. After covering the basics we run through the alternate angles (z a this video covers the angle rules when you have a transversal crossing two parallel lines. The other corresponding pairs of angles in the above diagram are: b and f; c and g; a and e. (corresponding angles found in a f shaped figure) example: in the following diagram, all the lines shown are straight lines. line m is parallel to line n. list a pair of corresponding angle. solution: d and h are corresponding angles.
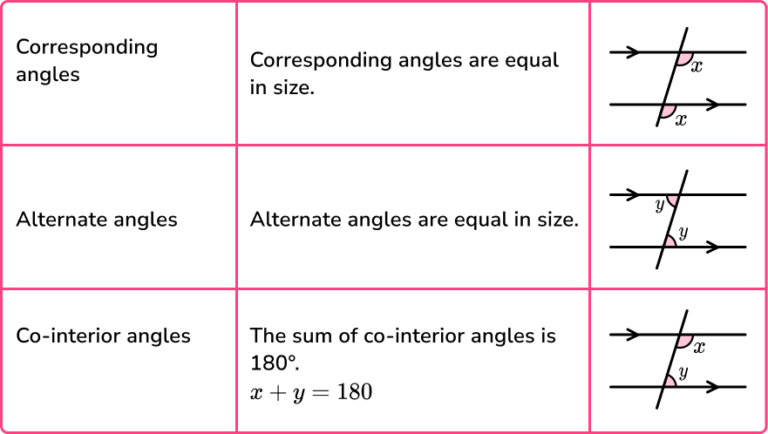
Corresponding Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples After covering the basics we run through the alternate angles (z a this video covers the angle rules when you have a transversal crossing two parallel lines. The other corresponding pairs of angles in the above diagram are: b and f; c and g; a and e. (corresponding angles found in a f shaped figure) example: in the following diagram, all the lines shown are straight lines. line m is parallel to line n. list a pair of corresponding angle. solution: d and h are corresponding angles. Corresponding angles. when you have a pair of parallel lines, with one line crossing them, the corresponding angles are equal. basically the angles in the same position on each parallel line will be equal to the angle in that position on the other parallel line. this rule is sometimes remembered as “f angles” because the angles make an f shape. Vertically opposite angles can also be used in problems involving parallel lines. the below diagram shows how identifying angle x, can lead to knowing information about several other angles. the green angle opposite is also x, as it is vertically opposite. the orange angle must be 180 x as angles on a straight line sum to 180°.
Corresponding Angles Gcse Maths Steps Examples Corresponding angles. when you have a pair of parallel lines, with one line crossing them, the corresponding angles are equal. basically the angles in the same position on each parallel line will be equal to the angle in that position on the other parallel line. this rule is sometimes remembered as “f angles” because the angles make an f shape. Vertically opposite angles can also be used in problems involving parallel lines. the below diagram shows how identifying angle x, can lead to knowing information about several other angles. the green angle opposite is also x, as it is vertically opposite. the orange angle must be 180 x as angles on a straight line sum to 180°.

Comments are closed.