Correlation Coefficient Maths

Correlation Correlation Coefficient Types Formulas Example The sample correlation coefficient uses the sample covariance between variables and their sample standard deviations. sample correlation coefficient formula. explanation. rxy = strength of the correlation between variables x and y. cov (x, y) = covariance of x and y. sx = sample standard deviation of x. The mini lesson targeted the fascinating concept of the correlation coefficient. the math journey around correlation coefficient started with what a student already knew and went on to creatively crafting a fresh concept in the young minds. done in a way that not only it is relatable and easy to grasp, but also will stay with them forever.
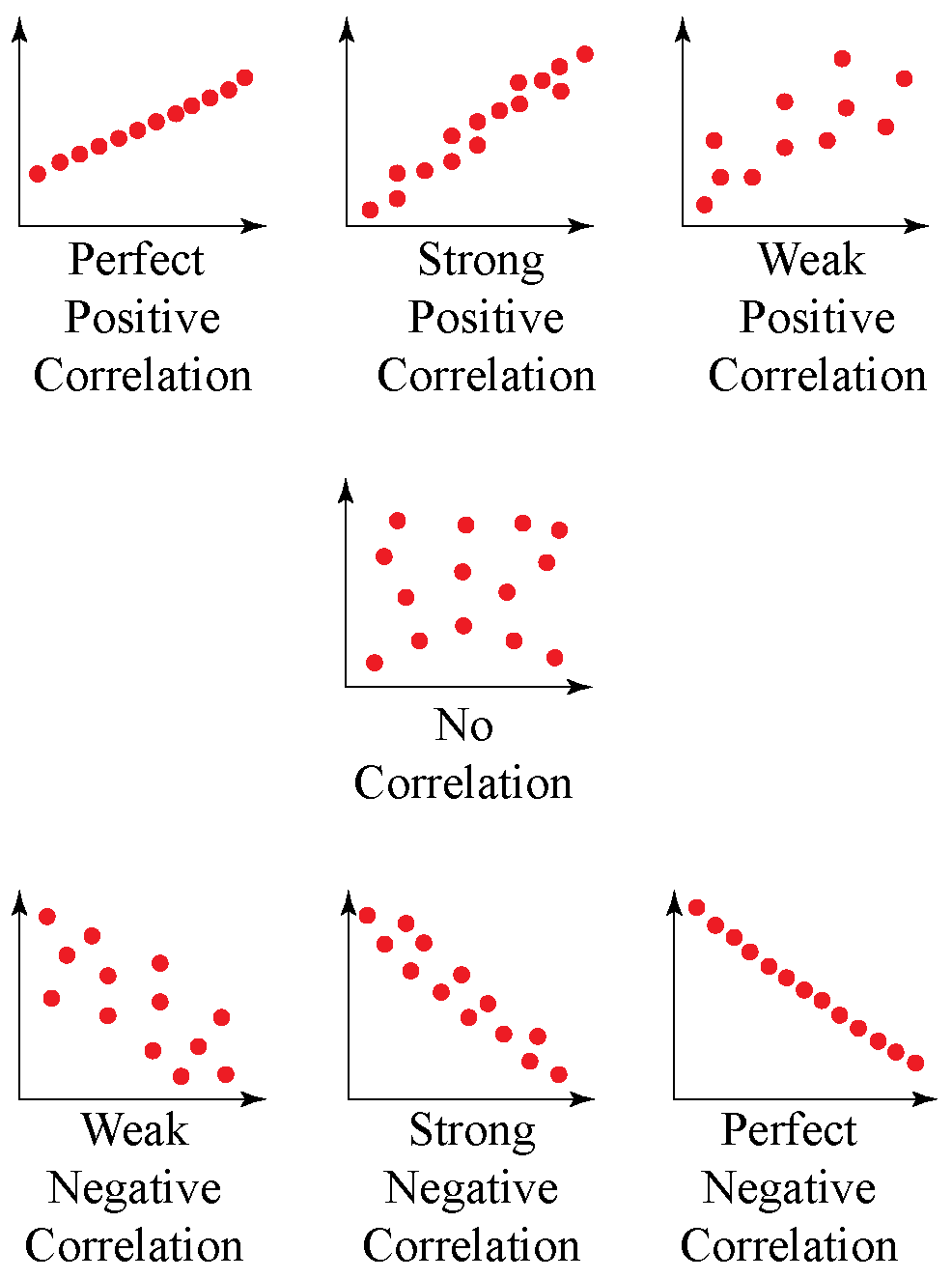
Correlation Coefficient Definition Formula Properties Examples A correlation is assumed to be linear (following a line). correlation can have a value: 1 is a perfect positive correlation; 0 is no correlation (the values don't seem linked at all) 1 is a perfect negative correlation; the value shows how good the correlation is (not how steep the line is), and if it is positive or negative. example: ice cream. X̄ = (3 5 2 7 4) 5 = 4.2. Ȳ = (70 80 60 90 75) 5 = 75. then, follow these steps to calculate the numerator in the correlation coefficient formula: calculate the differences between the observed x and y values and each variable’s mean. multiply those differences for each x and y pair. Correlation is a measure of relationship between two variables. there are several relations involving variables such as: linear, (in general) non linear, and others. also, variables can have differing quantities of correlation to each other. pearson's correlation coefficient or pcc is the most common linear coefficient measuring the degree of correlation between two variables. the pcc. Statisticians consider pearson’s correlation coefficients to be a standardized effect size because they indicate the strength of the relationship between variables using unitless values that fall within a standardized range of 1 to 1. effect sizes help you understand how important the findings are in a practical sense.
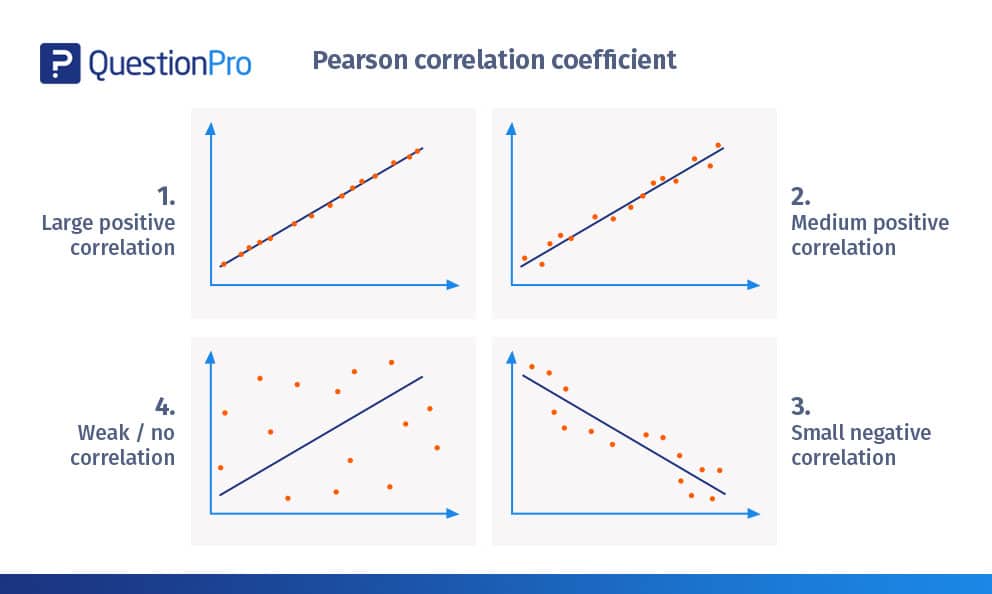
Pearson Correlation Coefficient Calculation Examples Correlation is a measure of relationship between two variables. there are several relations involving variables such as: linear, (in general) non linear, and others. also, variables can have differing quantities of correlation to each other. pearson's correlation coefficient or pcc is the most common linear coefficient measuring the degree of correlation between two variables. the pcc. Statisticians consider pearson’s correlation coefficients to be a standardized effect size because they indicate the strength of the relationship between variables using unitless values that fall within a standardized range of 1 to 1. effect sizes help you understand how important the findings are in a practical sense. Revised on february 10, 2024. the pearson correlation coefficient (r) is the most common way of measuring a linear correlation. it is a number between –1 and 1 that measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. when one variable changes, the other variable changes in the same direction. The correlation coefficient (sometimes also denoted ) is then defined by. the correlation coefficient is also known as the product moment coefficient of correlation or pearson's correlation. the correlation coefficients for linear fits to increasingly noisy data are shown above. the correlation coefficient has an important physical interpretation.
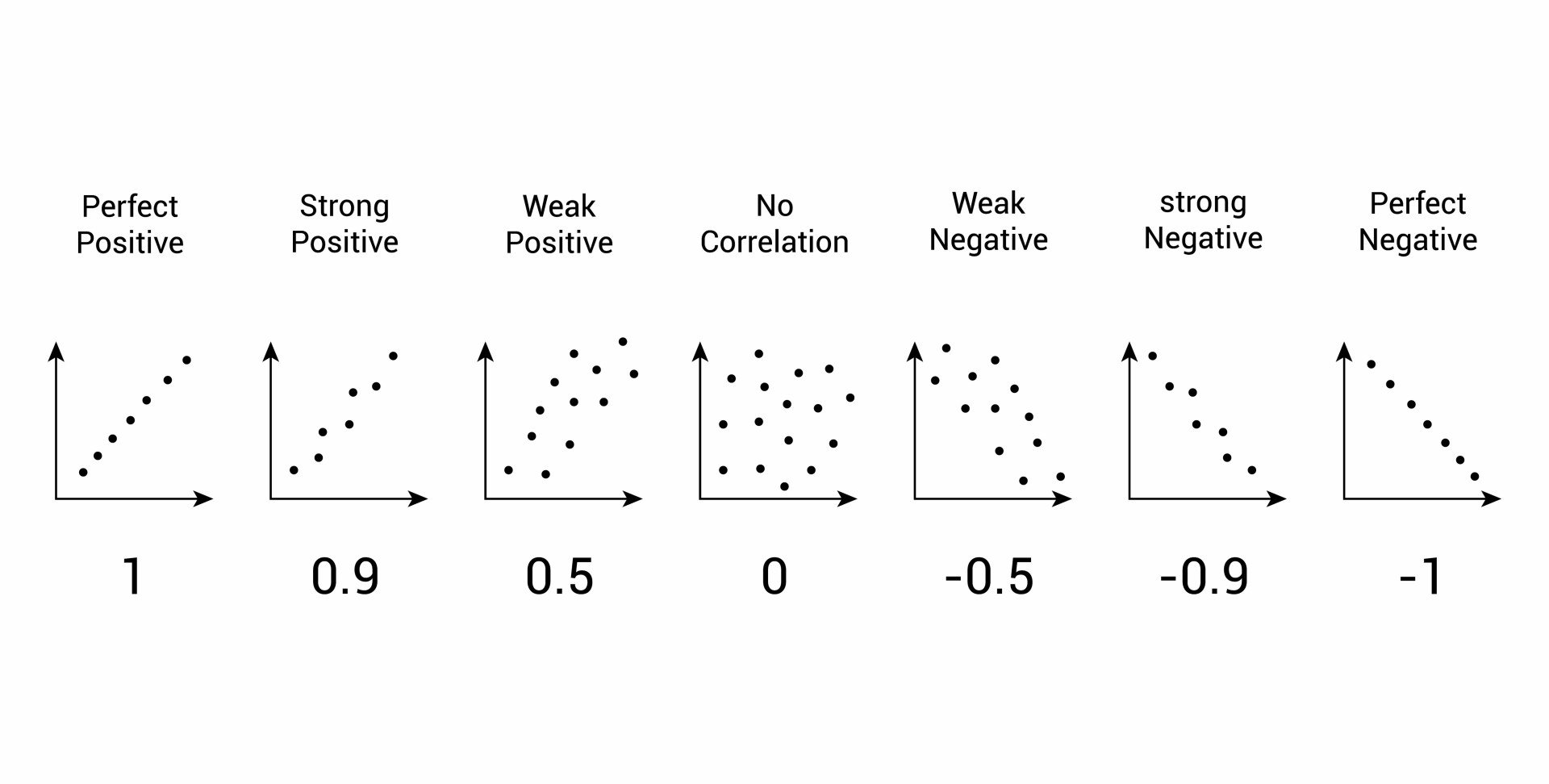
Correlation Meaning Types Examples Coefficient Revised on february 10, 2024. the pearson correlation coefficient (r) is the most common way of measuring a linear correlation. it is a number between –1 and 1 that measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. when one variable changes, the other variable changes in the same direction. The correlation coefficient (sometimes also denoted ) is then defined by. the correlation coefficient is also known as the product moment coefficient of correlation or pearson's correlation. the correlation coefficients for linear fits to increasingly noisy data are shown above. the correlation coefficient has an important physical interpretation.

Correlation Formula Learn The Correlation Formula Cuemath

Comments are closed.