Consumer Preferences And Choice Chapter 3 Pdf Utility Marginal

Consumer Preferences And Choice Chapter 3 Pdf Utility Marginal 2. ns. mers face constraints (budget) that limit their choices3.consumers maximize their well being or pleas. re from consumption, subject to the constraints they face.we want our. odel to be realistic so we can predict consu. possible. 3description of consumer preferencesconsumer preferences tell us how the consumer would rank any two basket. 3. consumer choices chapter 3 consumer behavior . chairat aemkulwat . economics i: 2900111 3 3.1 consumer preferences • market baskets market basket (or bundle) list with specific quantities of one or more goods. to explain the theory of consumer behavior, we will ask whether consumers prefer one market basket to another. 4.

Chapter 3 Consumer Preferences And Choice Some basic assumptions about preferences. 1. completeness: preferences are assumed to be complete. in other words, consumers can compare and rank all possible baskets. thus, for any two market baskets a and b, a consumer will prefer a to b, will prefer b to a, or will be indifferent between the two. Choice,preference,orutility,thisconglomerate(withthetwopairsofassumptions) is the standard model of consumer choice in microeconomics. a much used piece of terminology concerns display (1.3), which connects a utility function u and a preference relation ⌫. when (1.3) holds, we say that the utility function u represents the preference relation. 1) the document discusses consumer preferences and choice, specifically analyzing utility through concepts of total utility and marginal utility. 2) it introduces indifference curves as a way to represent consumer tastes, and examines how consumers are constrained by budgets that reflect their limited income. 3) the key questions addressed are how consumers maximize satisfaction given their. Consumers have a preference for diversity in consumption. consumers value more the first unit of any good they own, compared to the hundredth unit. everyone gets tired of consuming the same thing eventually. these are all appropriate ways to capture the intuition behind the principle of diminishing marginal utility.
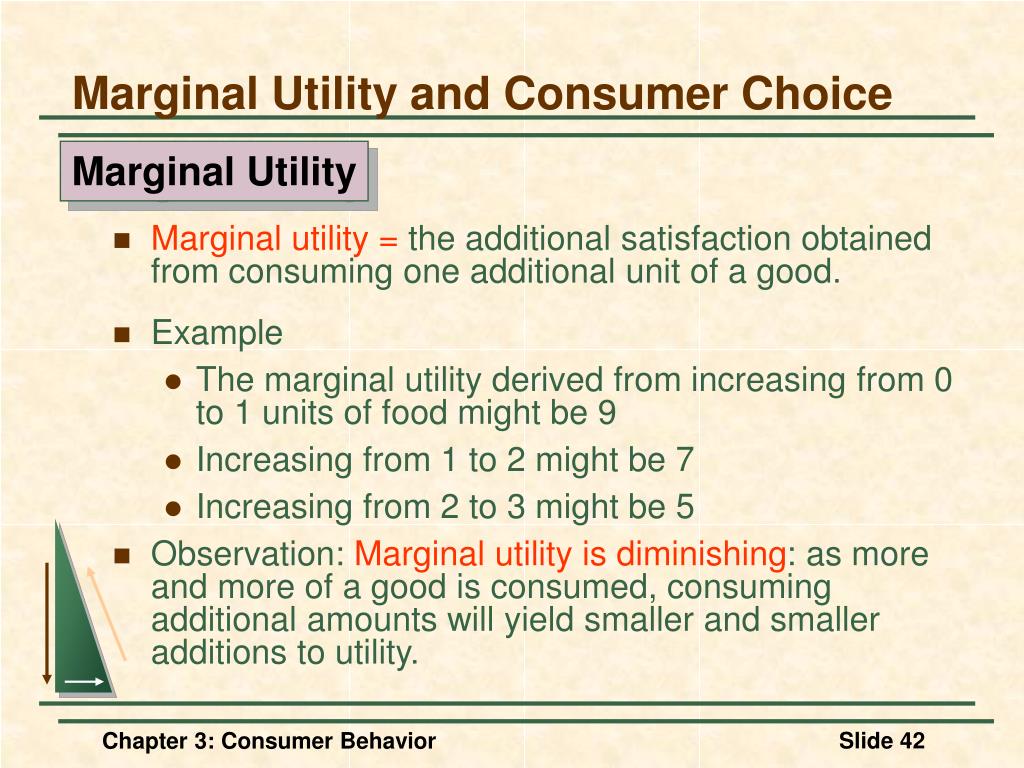
Ppt Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 495261 1) the document discusses consumer preferences and choice, specifically analyzing utility through concepts of total utility and marginal utility. 2) it introduces indifference curves as a way to represent consumer tastes, and examines how consumers are constrained by budgets that reflect their limited income. 3) the key questions addressed are how consumers maximize satisfaction given their. Consumers have a preference for diversity in consumption. consumers value more the first unit of any good they own, compared to the hundredth unit. everyone gets tired of consuming the same thing eventually. these are all appropriate ways to capture the intuition behind the principle of diminishing marginal utility. Chapter. consumer behavior. 63. chapter outline. 3.1 consumer preferences 65 3.2 budget constraints 79 3.3 consumer choice 83 3.4 revealed preference 89 3.5 marginal utility and consumer choice 92 *3.6 cost of living indexes 97. list of examples. 3.1 designing new automobiles (i) 74 3.2 can money buy happiness? 78 3.3 designing new automobiles. Utility represents an individual’s choices. individual choices are primitive data that economists can observe. choices are taken to reveal individual’s preferences. utility is a convenient mathematical construction for modeling choices and preferences. “u (apple) = 7, u (banana) = 12” = individual prefers bananas to apples.

Marginal Utility Consumer Choice Marginal Utility Consumer Choice Chapter. consumer behavior. 63. chapter outline. 3.1 consumer preferences 65 3.2 budget constraints 79 3.3 consumer choice 83 3.4 revealed preference 89 3.5 marginal utility and consumer choice 92 *3.6 cost of living indexes 97. list of examples. 3.1 designing new automobiles (i) 74 3.2 can money buy happiness? 78 3.3 designing new automobiles. Utility represents an individual’s choices. individual choices are primitive data that economists can observe. choices are taken to reveal individual’s preferences. utility is a convenient mathematical construction for modeling choices and preferences. “u (apple) = 7, u (banana) = 12” = individual prefers bananas to apples.

Understanding Consumer Preferences An Introduction To Utility Theory

Consumer Preferences And Choice Pdf Utility Economic Surplus

Comments are closed.