Consumer Credit Legislation
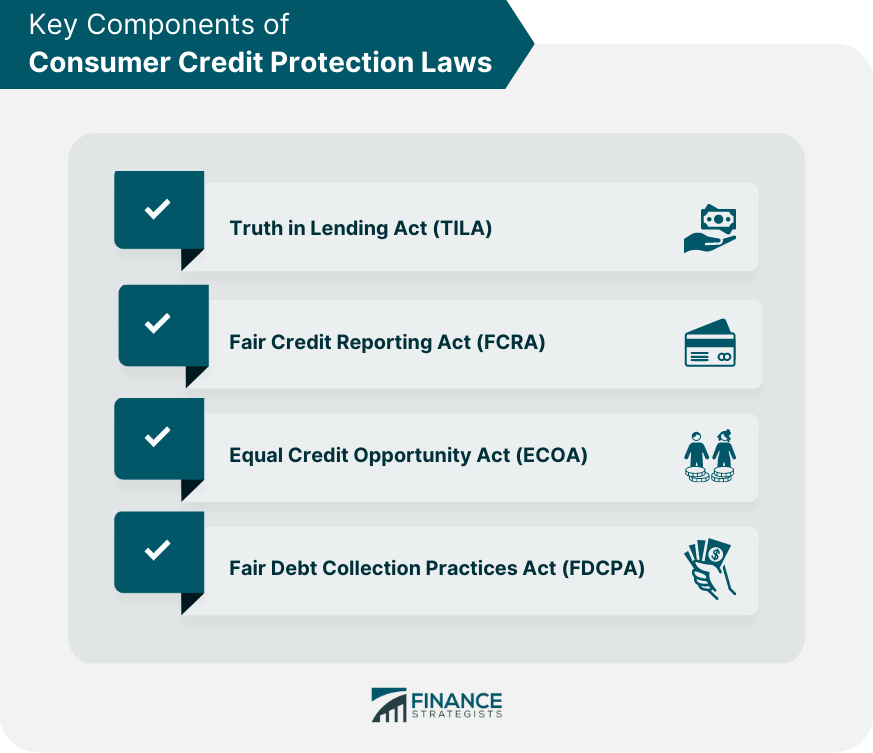
Consumer Credit Protection Laws Meaning History Components It started with the consumer credit protection act of 1968, when congress moved to shield consumers and their financial records from abuse. in the years following, other laws refined consumer rights, spelling out how the government can access bank customers’ information, how banks treat borrowers and the way banks handle customer deposits. Your consumer credit rights are protected in large part by the consumer credit protection act (ccpa), which became effective in the late 1960s. this act is made up of several laws which each protect an aspect of your personal credit, such as banning discrimination or requiring honest credit reports. since its inception, the ccpa has grown to.

Consumer Credit Legislation By Joshua Robinson On Prezi The consumer credit protection act of 1968 (ccpa) is federal legislation that created protections for consumers from banks, credit card companies, and other lenders. the act mandates disclosure. Subchapter i—consumer credit cost disclosure (§§ 1601 – 1667f) subchapter ii—restrictions on garnishment (§§ 1671 – 1677) subchapter ii–a—credit repair organizations (§§ 1679 – 1679j) subchapter iii—credit reporting agencies (§§ 1681 – 1681x) subchapter iv—equal credit opportunity (§§ 1691 – 1691f). The consumer credit protection act (ccpa) is a united states law pub. l. 90–321, 82 stat. 146, enacted may 29, 1968, composed of several titles relating to consumer credit, mainly title i, the truth in lending act, title ii related to extortionate credit transactions, title iii related to restrictions on wage garnishment, and title iv related to the national commission on consumer finance. The law of consumer credit is primarily embodied in federal and state statutes. these laws protect consumers and provide guidelines for the credit industry. states have passed various statutes regulating consumer credit. for example, the uniform consumer credit code (uccc) has been adopted as law in eleven states and guam. its purpose is to.

Ppt Chapter 6 Using Credit Powerpoint Presentation Free Download The consumer credit protection act (ccpa) is a united states law pub. l. 90–321, 82 stat. 146, enacted may 29, 1968, composed of several titles relating to consumer credit, mainly title i, the truth in lending act, title ii related to extortionate credit transactions, title iii related to restrictions on wage garnishment, and title iv related to the national commission on consumer finance. The law of consumer credit is primarily embodied in federal and state statutes. these laws protect consumers and provide guidelines for the credit industry. states have passed various statutes regulating consumer credit. for example, the uniform consumer credit code (uccc) has been adopted as law in eleven states and guam. its purpose is to. Fcra may2023 508.pdf (652.93 kb) the act (title vi of the consumer credit protection act) protects information collected by consumer reporting agencies such as credit bureaus, medical information companies and tenant screening services. information in a consumer report cannot be provided to anyone who does not have a purpose specified in the act. Consumer credit law & practice in the u.s.1. 1. introduction. consumer credit is an important element of the united states economy. a consumer’s ability to borrow money easily allows a well managed economy to function more efficiently and stimulates economic growth.
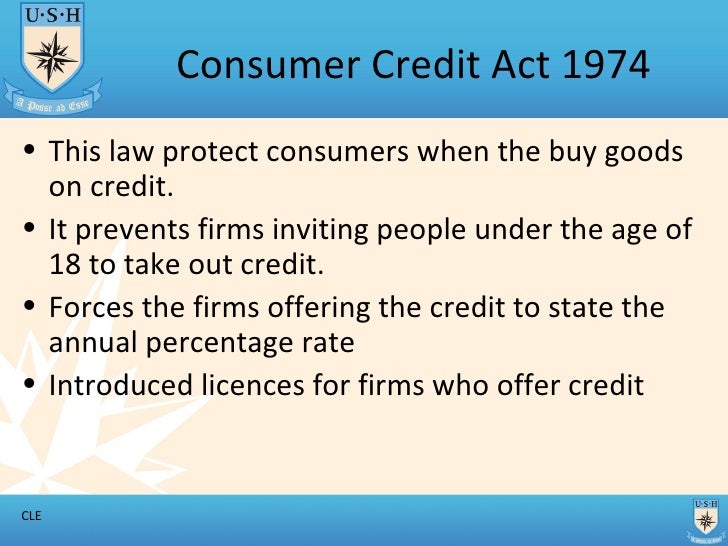
Consumer Legislation1 T2 Fcra may2023 508.pdf (652.93 kb) the act (title vi of the consumer credit protection act) protects information collected by consumer reporting agencies such as credit bureaus, medical information companies and tenant screening services. information in a consumer report cannot be provided to anyone who does not have a purpose specified in the act. Consumer credit law & practice in the u.s.1. 1. introduction. consumer credit is an important element of the united states economy. a consumer’s ability to borrow money easily allows a well managed economy to function more efficiently and stimulates economic growth.

Comments are closed.