Conduction Convection Radiation With Example

Modes Of Heat Trnsfer The three types of heat transfer with examples. the three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: conduction requires contact. convection requires fluid flow. radiation does not require any medium. conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. Comparison: convection, conduction, and radiation. convection, conduction, and radiation are three heat transfer processes: convection: heat transfer via fluid movement, requiring a fluid medium. conduction: heat transfer through direct contact within or between solid materials. an example is the end of a metal spoon becoming hot when stirring.

Conduction Convection Radiation The space between earth and the sun is largely empty, so the sun warms us without any possibility of heat transfer by convection or conduction. similarly, you can sometimes tell that the oven is hot without touching its door or looking inside—it may just warm you as you walk by. in these examples, heat is transferred by radiation (figure 1.28. Convection heat transfer occurs partly due to the actual movement of molecules or due to the mass transfer. for example. heating of milk in a pan. 3. radiation of heat. it is the process in which heat is transferred from one body to another body without involving the molecules of the medium. Example 13.4.1 13.4. 1: calculating heat transfer by convection: convection of air through the walls of a house. most houses are not airtight: air goes in and out around doors and windows, through cracks and crevices, following wiring to switches and outlets, and so on. the air in a typical house is completely replaced in less than an hour. Figure 1.7.1: in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. heat transfer also occurs through conduction into the room, but much slower.

Famous Conduction Convection And Radiation Definitions With Examples Example 13.4.1 13.4. 1: calculating heat transfer by convection: convection of air through the walls of a house. most houses are not airtight: air goes in and out around doors and windows, through cracks and crevices, following wiring to switches and outlets, and so on. the air in a typical house is completely replaced in less than an hour. Figure 1.7.1: in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. heat transfer also occurs through conduction into the room, but much slower. An obvious example is the warming of the earth by the sun. a less obvious example is thermal radiation from the human body. figure 1. in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. A less obvious example is thermal radiation from the human body. figure 14.12 in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. heat transfer also occurs through conduction into the room, but at a much slower rate.
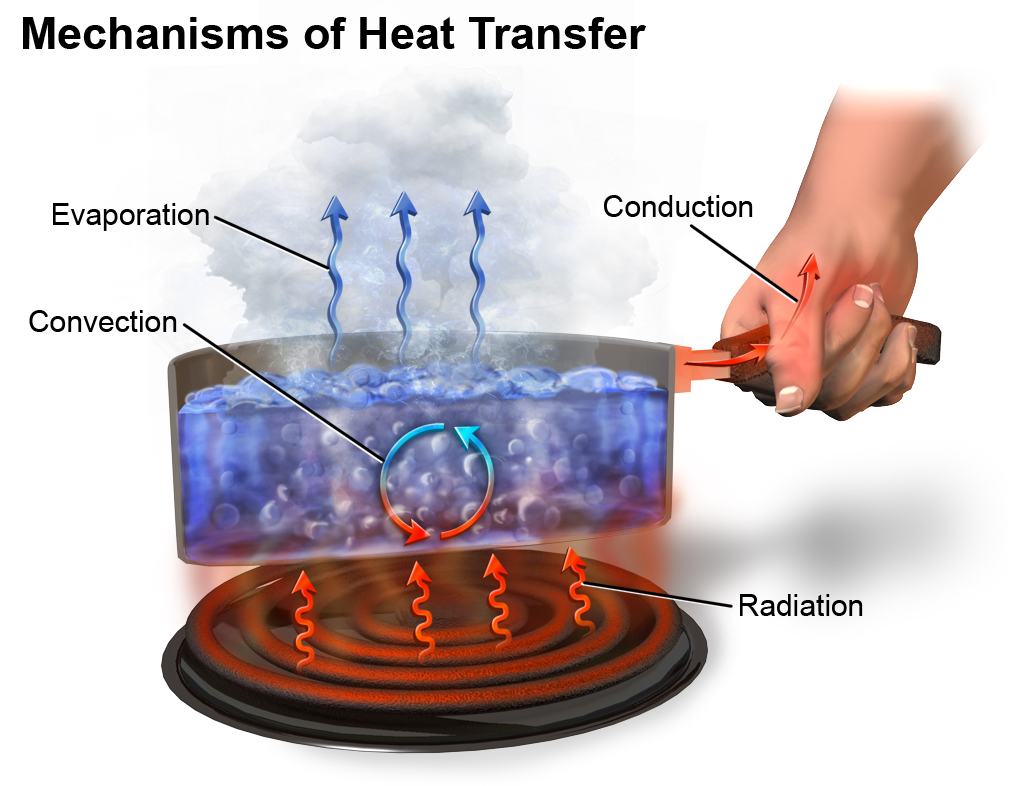
What Is Conduction Convection And Radiation With Example Linquip An obvious example is the warming of the earth by the sun. a less obvious example is thermal radiation from the human body. figure 1. in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. A less obvious example is thermal radiation from the human body. figure 14.12 in a fireplace, heat transfer occurs by all three methods: conduction, convection, and radiation. radiation is responsible for most of the heat transferred into the room. heat transfer also occurs through conduction into the room, but at a much slower rate.

Comments are closed.