Common Laplace Transform Pairs Pdf
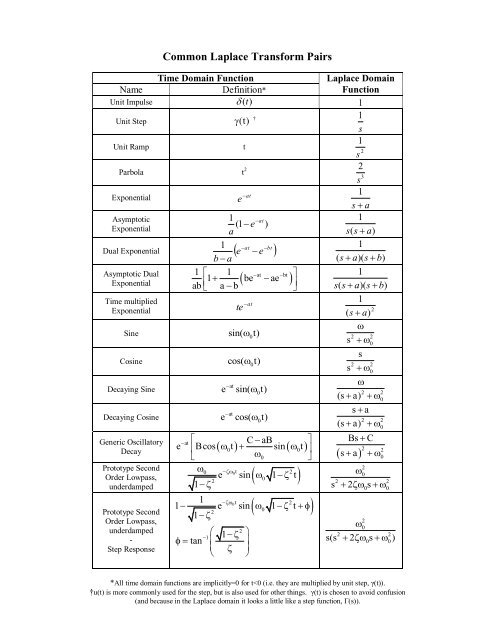
Common Laplace Transform Pairs Common laplace transform pairs. *all time domain functions are implicitly=0 for t<0 (i.e. they are multiplied by unit step, γ(t)). †u(t) is more commonly used for the step, but is also used for other things. γ(t) is chosen to avoid confusion (and because in the laplace domain it looks a little like a step function, Γ(s)). Common laplace transform pairs time domain function name definition* laplace domain function unit impulse δt( ) 1 unit step u t ( ) s 1 unit ramp t 2 1 s exponential e−at s a.

Basic Laplace Transform Pairs Pdf The laplace transform †deflnition&examples †properties&formulas { linearity { theinverselaplacetransform { timescaling { exponentialscaling { timedelay { derivative { integral { multiplicationbyt { convolution 3{1. A.3 common laplace transform pairs and properties the next three subsections present tables of common laplace transform pairs and laplace transform prop erties. the information in these tables has been adapted from: • signals and systems, 2nd ed. simon haykin and barry van veen. john wiley & sons, hoboken, nj, 2005. pp. 781 783. The laplace transform of f, f = l[f]. in the study of laplace transforms. we now turn to laplace transforms. the laplace transform of a function f(t) is defined as f(s) = l[f](s) = z¥ 0 f(t)e st dt, s > 0.(5.2) this is an improper integral and one needs lim t!¥ f(t)e st = 0 to guarantee convergence. Summarized in table 4.1, and the table of common laplace transform pairs, table 4.2. the use of the partial fraction expansion method is sufficient for the purpose of this course. however, in general, in order to find the laplace transform of any laplace transformable function we must learn the complex variable integration and.

Solved Table 6 2 Common Laplace Transform Pairs 1 U T S 1 Chegg Kernel of the transform. one of the two most important integral transforms1 is the laplace transform l, which is de ned according to the formula (1) l[f(t)] = f(s) = z 1 0 e stf(t)dt; i.e. ltakes a function f(t) as an input and outputs the function f(s) as de ned above. 1the other is the fourier transform; we’ll see a version of it later. 1. 2. 13. damped sinusoid (complex poles) 2 k e − α t cos ( β t ∠ k ) u ( t ) k k. ( s − p ) ( s − p. ) where p = −α j β.

Comments are closed.