Classification Of Bacteria On The Basis Of Gram Stain And Shapes Of

Classification Of Bacteria Microbe Online 1. classification on the basis of gram stain and bacterial cell wall . of all the different classification systems, the gram stain has withstood the test of time. discovered by h.c. gram in 1884 it remains an important and useful technique to this day. A gram stain smear suffices to show the gram reaction, size, shape and grouping of the bacteria, and the arrangement of any endospores. an unstained wet film may be examined with dark ground illumination in the microscope to observe the morphology of delicate spirochaetes; an unstained wet film, or ‘hanging drop’, preparation is examined.
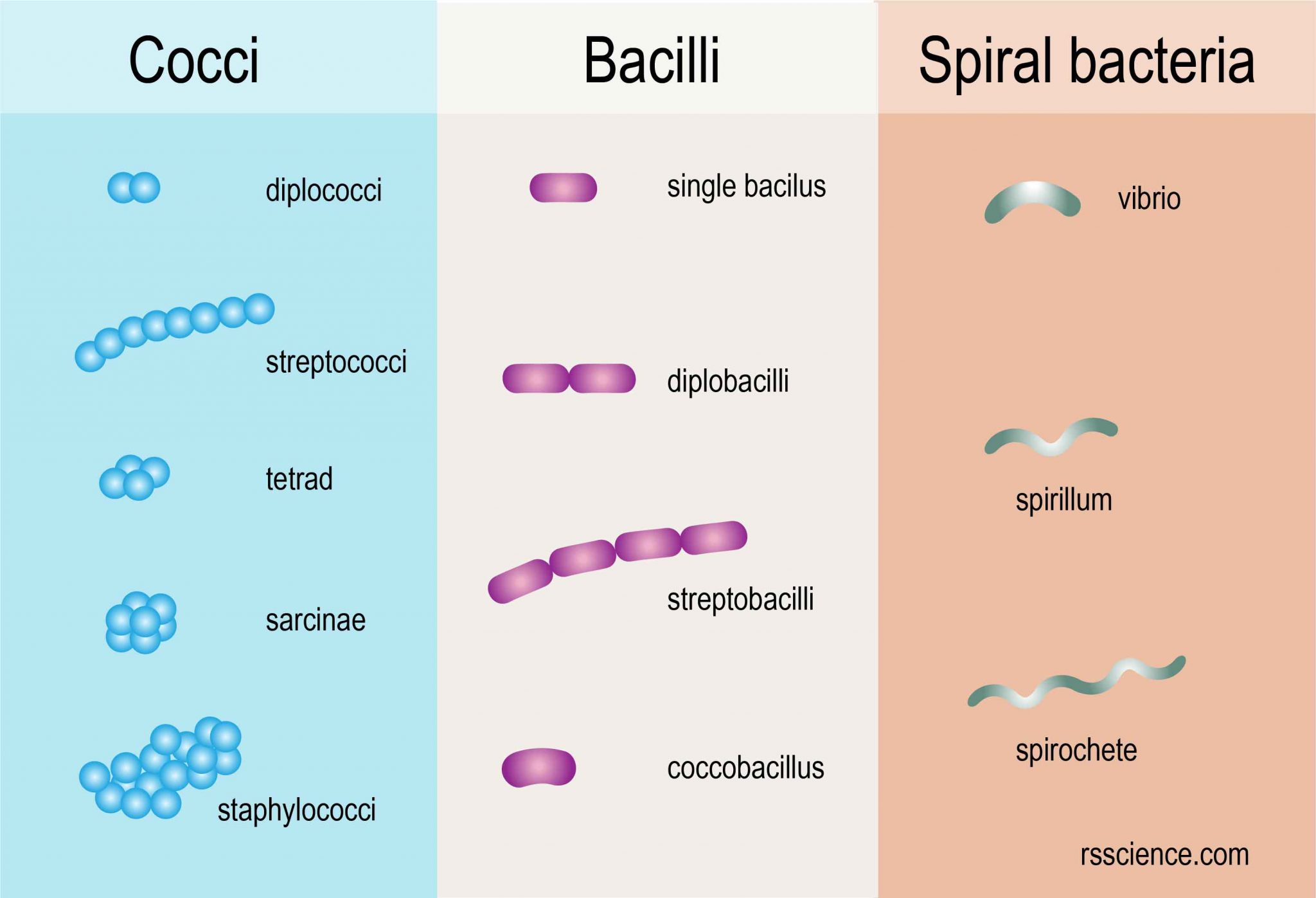
Observing Bacteria Under The Microscope Gram Stain Steps Rs Science Bacteria are classified into five groups based on the basis of their shapes. they are; cocci (round), bacilli (rod), spiral, vibrios (comma), and spirochetes. shapes of bacteria. you can find more about the shapes of bacterial cells and their arrangements in this post: size, shape, arrangement of bacteria. Bacteria are classified based on their response to the gram staining technique, which helps differentiate them into two main categories: gram positive and gram negative bacteria. this classification is fundamental in microbiology and has implications for bacterial cell wall structure, as well as their response to antibiotics and various aspects. 1. cover different classification schemes for grouping bacteria, especially the use of the gram stain 2. describe the different types of bacteria 3. discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components 4. discuss the distinguishing characteristics of gram positive and gram negative bacteria. The first stain is crystal violet which stains all bacteria blue purple followed by an iodine fixative. the critical step is then the decolorizer which is methanol. methanol fixes the cells causing the pores in the walls of gram positive cells to collapse and become sealed thus retaining the blue dye.

Classification Of Bacteria On The Basis Of Gram Stain Shapes 1. cover different classification schemes for grouping bacteria, especially the use of the gram stain 2. describe the different types of bacteria 3. discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components 4. discuss the distinguishing characteristics of gram positive and gram negative bacteria. The first stain is crystal violet which stains all bacteria blue purple followed by an iodine fixative. the critical step is then the decolorizer which is methanol. methanol fixes the cells causing the pores in the walls of gram positive cells to collapse and become sealed thus retaining the blue dye. Principle of gram staining. when the bacteria is stained with primary stain crystal violet and fixed by the mordant, some of the bacteria are able to retain the primary stain and some are decolorized by alcohol. the cell walls of gram positive bacteria have a thick layer of protein sugar complexes called peptidoglycan and lipid content is low. The gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. it gets its name from the danish bacteriologist hans christian gram, who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.[1] often, the first test performed, gram staining, involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color.[2] the term for organisms that retain.

Classification Of Bacteria On Basis Of Gram Stain Gram Stain Gram Principle of gram staining. when the bacteria is stained with primary stain crystal violet and fixed by the mordant, some of the bacteria are able to retain the primary stain and some are decolorized by alcohol. the cell walls of gram positive bacteria have a thick layer of protein sugar complexes called peptidoglycan and lipid content is low. The gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. it gets its name from the danish bacteriologist hans christian gram, who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.[1] often, the first test performed, gram staining, involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color.[2] the term for organisms that retain.

Comments are closed.