Classical Greece And The Roman Empire James Timmins

Classical Greece And The Roman Empire James Timmins Aris messinis afp getty images. the term “classical greece” refers to the period between the persian wars at the beginning of the fifth century b.c. and the death of alexander the great in. Classical greece 480 323 bce. classical greece, also known as the golden age, became fundamental both to the later roman empire and western civilization, in philosophy, politics, literature, science, art, and architecture. the great greek historian of the era thucydides, called the general and populist statesman pericles "athens's first citizen.".

The Roman Empire Reconsidered Vision A major new history of classical greece—how it rose, how it fell, and what we can learn from it lord byron described greece as great, fallen, and immortal, a characterization more apt than he knew. through most of its long history, greece was poor. but in the classical era, greece was densely populated and highly urbanized. many surprisingly healthy greeks lived in remarkably big houses and. Josiah ober. a major new history of classical greece—how it rose, how it fell, and what we can learn from it. series: the princeton history of the ancient world. hardcover. price: $35.00 £30.00. isbn: 9780691140919. Updated on june 07, 2024. both greece and ancient roman empire had climates similar enough latitudinally for both to grow wine and olives. however, their terrains were quite different. the ancient greek city states were separated from each other by hilly countryside and all were near the water. rome was inland, on one side of the tiber river. Greece in the roman era. greece in the roman era (greek: Έλλάς, latin: graecia) describes the roman conquest of ancient greece (roughly, the territory of the modern nation state of greece) as well as that of the greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. [1][2][3] it covers the periods when greece was dominated first.

Classical Greece Updated on june 07, 2024. both greece and ancient roman empire had climates similar enough latitudinally for both to grow wine and olives. however, their terrains were quite different. the ancient greek city states were separated from each other by hilly countryside and all were near the water. rome was inland, on one side of the tiber river. Greece in the roman era. greece in the roman era (greek: Έλλάς, latin: graecia) describes the roman conquest of ancient greece (roughly, the territory of the modern nation state of greece) as well as that of the greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. [1][2][3] it covers the periods when greece was dominated first. The parthenon, in athens, a temple to athena. classical greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries bc) in ancient greece, [1] marked by much of the eastern aegean and northern regions of greek culture (such as ionia and macedonia) gaining increased autonomy from the persian empire; the peak flourishing of democratic athens; the first and second peloponnesian wars; the. Hemingway, colette. “africans in ancient greek art.” (january 2008) hemingway, colette. “ancient greek colonization and trade and their influence on greek art.” (july 2007) hemingway, colette. “architecture in ancient greece.” (october 2003).

Biblio Timeline Of The Roman Empire Laminated Poster By Parthenon The parthenon, in athens, a temple to athena. classical greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries bc) in ancient greece, [1] marked by much of the eastern aegean and northern regions of greek culture (such as ionia and macedonia) gaining increased autonomy from the persian empire; the peak flourishing of democratic athens; the first and second peloponnesian wars; the. Hemingway, colette. “africans in ancient greek art.” (january 2008) hemingway, colette. “ancient greek colonization and trade and their influence on greek art.” (july 2007) hemingway, colette. “architecture in ancient greece.” (october 2003).
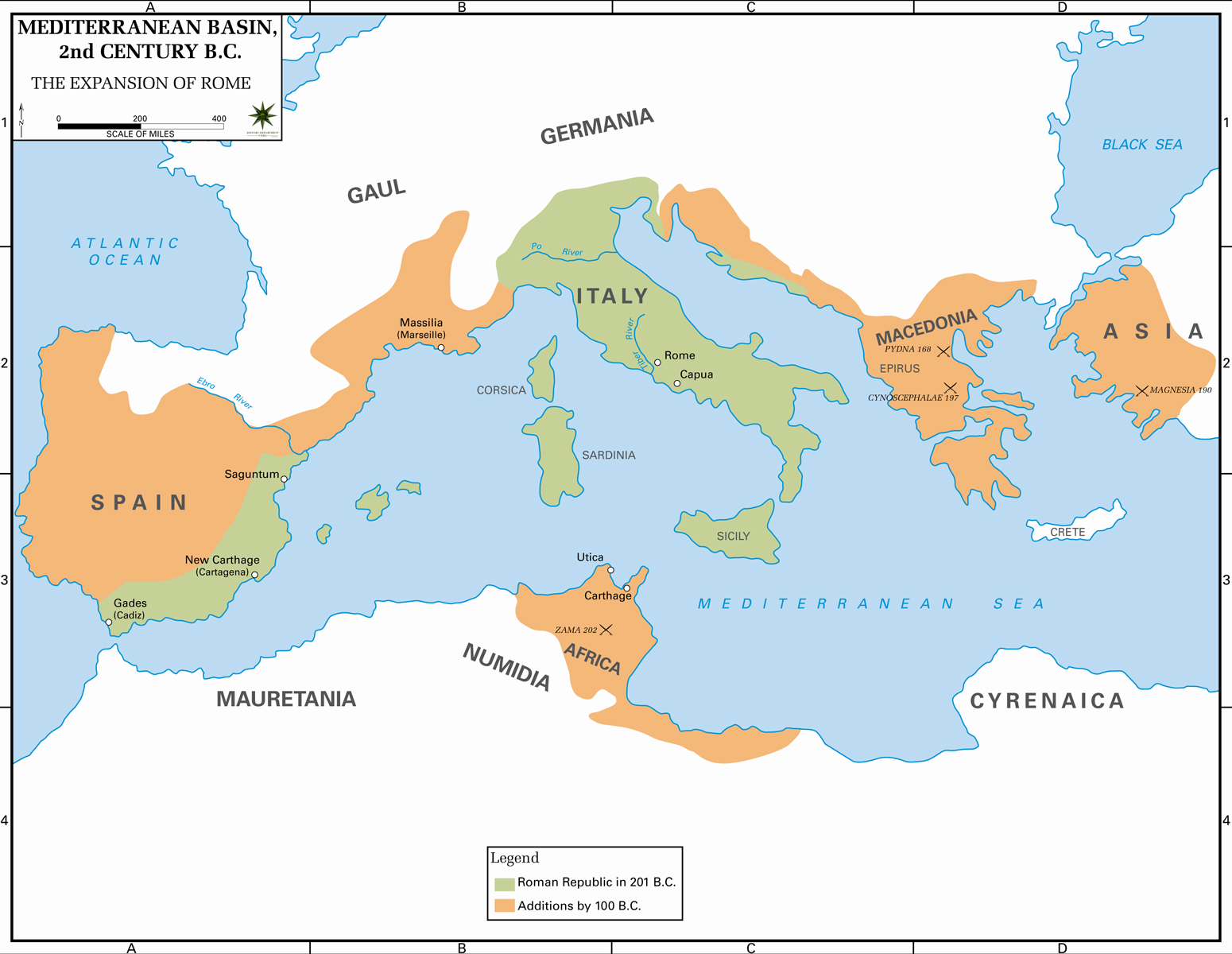
Timelines And Maps Greco Roman Religions
Ancient Egypt A Concise Overview Of The Egyptian History And Mythology

Comments are closed.