Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia

Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia It is the iconic western work of architecture. it served as a temple to athena and a treasury to the athenian empire. there was a parthenon before this one but the persians destroyed it. so, they built this one instead. later, in the 5th century ce, they converted this temple to athena into a temple to mary. C. patriarchal forms of social organization developed in both pastoralist and agrarian societies. from about 5,000 years ago, urban societies developed, laying the foundations for the first civilizations. the term civilization is normally used to designate large societies with cities and powerful states.

Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia This is the post classical era. the major world powers come from places you might not expect. there are some powers that are similar to the ones before and the ones after (byzantine, china). but, the major players in the post classical era come from totally backwards places. one sprouts out of a cave in the arabian desert. Apush unit ix: conservatism, terrorism and the modern era (1980 to present) unit ii: the classical era (600 b.c.e. to 600 c.e.) the foundations unit (unit i) will only be approximately 5% of the ap world exam in the spring, the classical era is where what the average person thinks of as history really starts. The postclassical era => regional and transregional interactions ca 600 c.e. to 1450 c.e. key concept 3.1: expansion & intensification of communication & exchange networks although afro eurasia and the americas remained separate from one another, this era witnessed a deepening and widening of old and new networks of human interaction within and. Regional and transregional interactions (600ce to 1450 ce) the classical era set the scene. it brought us the major civilizations, religions, and trade routes. but, what happens when all of the major world powers collapse? this is the post classical era. the major world powers come from places you might not expect.

Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia The postclassical era => regional and transregional interactions ca 600 c.e. to 1450 c.e. key concept 3.1: expansion & intensification of communication & exchange networks although afro eurasia and the americas remained separate from one another, this era witnessed a deepening and widening of old and new networks of human interaction within and. Regional and transregional interactions (600ce to 1450 ce) the classical era set the scene. it brought us the major civilizations, religions, and trade routes. but, what happens when all of the major world powers collapse? this is the post classical era. the major world powers come from places you might not expect. Classical period: 600 bce 600 ce. term. 1 78. satrapies. click the card to flip 👆. definition. 1 78. persian states each was headed by a governor appointed by the emperor. click the card to flip 👆. Classical (600 bce 600 ce) post classical (600 ce to 1450 ce) early modern (1450 1750) modern (1750 1900) freemanpedia.@neiltyson breaks down yesterday’s.
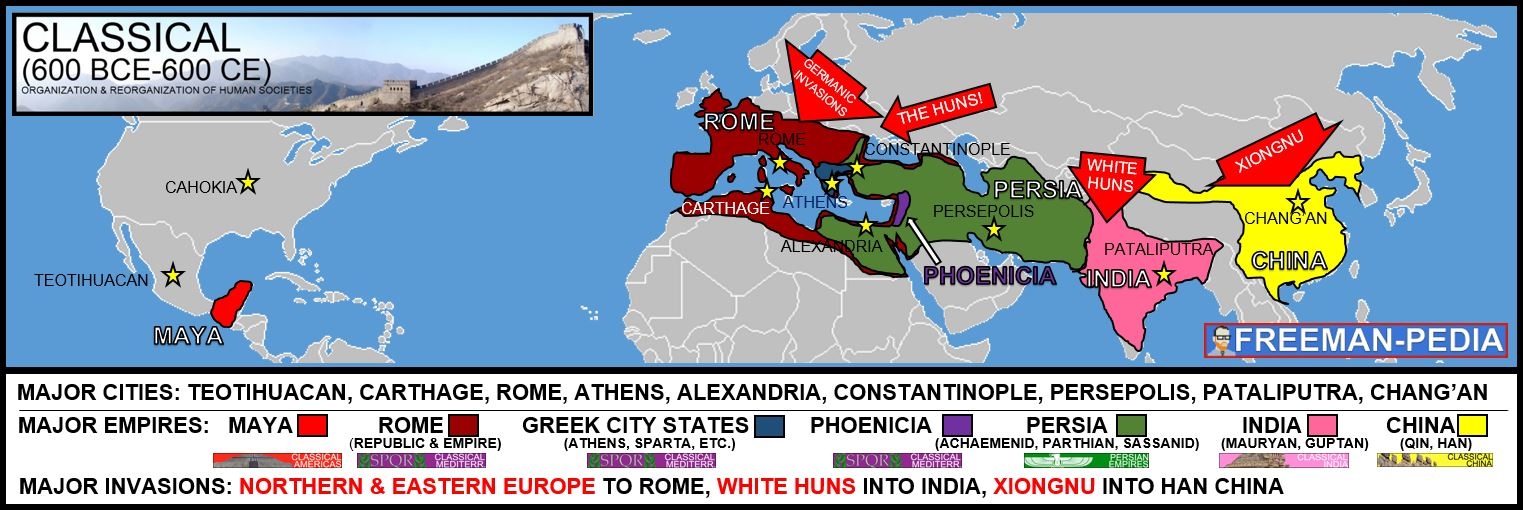
Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia Classical period: 600 bce 600 ce. term. 1 78. satrapies. click the card to flip 👆. definition. 1 78. persian states each was headed by a governor appointed by the emperor. click the card to flip 👆. Classical (600 bce 600 ce) post classical (600 ce to 1450 ce) early modern (1450 1750) modern (1750 1900) freemanpedia.@neiltyson breaks down yesterday’s.

Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia

Classical 600 Bce 600 Ce Freemanpedia

Comments are closed.