Circulatory System And Pathway Of Blood Through The Heart
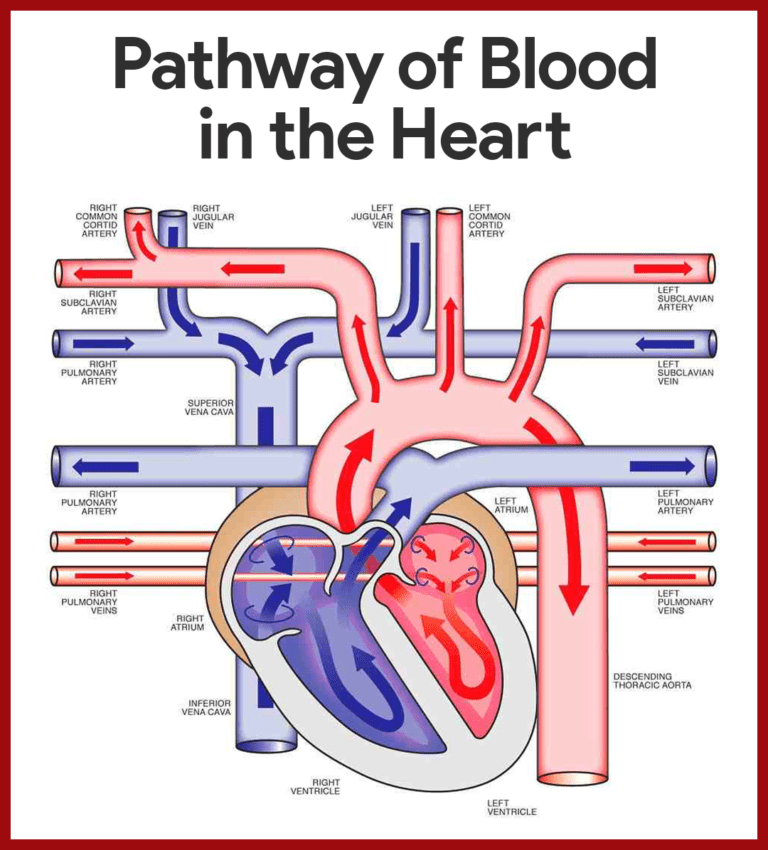
Cardiovascular System Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide For Nurses This circulation of blood continues over and over, every second of every day. your heart and blood vessels make it all happen, and that’s why together they’re known as your circulatory system. the many parts of your circulatory system work together like a top notch delivery service to keep blood moving through your body on schedule. The path of blood flow through the heart and lungs is pulmonary circulation, while the blood supply to the heart itself is coronary circulation. pulmonary circulation: purpose: pulmonary circulation is responsible for oxygenating the blood. it involves the movement of deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and then.

What Is The Path Of Blood Through The Circulatory System Adding oxygen to blood. oxygen poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. the blood enters the heart's right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs. the pulmonary artery then carries the oxygen poor blood from your heart to the. Oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart gets pumped out of the aorta. from there, blood flows through arteries, arterioles, and then capillaries (tiny blood vessels that transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen to cells). deoxygenated blood from the capillaries then flows back to the heart through venules, veins, and ultimately through. Join the amoeba sisters in their introduction to the circulatory system and follow the pathway of blood as it travels through the heart! this video explains. The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) pumps blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen. the heart then sends oxygenated blood through arteries to the rest of the body. the veins carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart to start the circulation process over. your circulatory system is critical to healthy organs, muscles and tissues.

Blood Flow In The Heart Mcat Biology Medschoolcoach Join the amoeba sisters in their introduction to the circulatory system and follow the pathway of blood as it travels through the heart! this video explains. The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) pumps blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygen. the heart then sends oxygenated blood through arteries to the rest of the body. the veins carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart to start the circulation process over. your circulatory system is critical to healthy organs, muscles and tissues. Pulmonary circulation. recall that blood returning from the systemic circuit enters the right atrium (figure 20.5.2) via the superior and inferior venae cavae and the coronary sinus, which drains the blood supply of the heart muscle. these vessels will be described more fully later in this section. The main function of the circulatory (or cardiovascular) system is to deliver oxygen to the body tissues, whilst simultaneously removing carbon dioxide produced by metabolism. oxygen is bound to molecules called haemoglobin that are on the surface of the red blood cells in the blood. beginning in the heart, deoxygenated blood (containing carbon.

The Path Of Blood Through The Heart And Circulatory System Human Steam Pulmonary circulation. recall that blood returning from the systemic circuit enters the right atrium (figure 20.5.2) via the superior and inferior venae cavae and the coronary sinus, which drains the blood supply of the heart muscle. these vessels will be described more fully later in this section. The main function of the circulatory (or cardiovascular) system is to deliver oxygen to the body tissues, whilst simultaneously removing carbon dioxide produced by metabolism. oxygen is bound to molecules called haemoglobin that are on the surface of the red blood cells in the blood. beginning in the heart, deoxygenated blood (containing carbon.
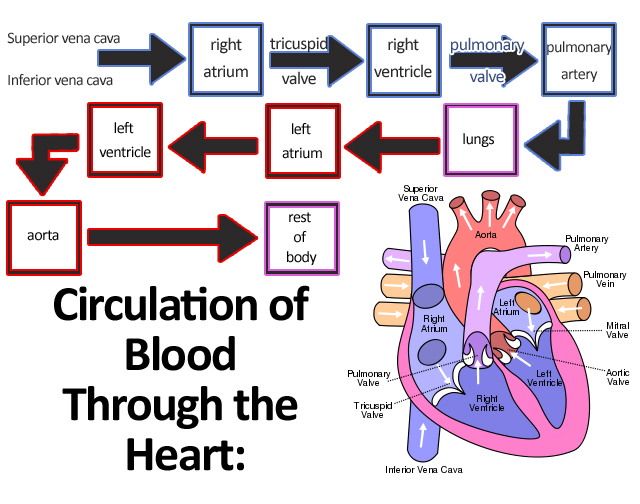
File Circulation Of Blood Through The Heart Jpg Wikimedia Commons

14 3 Heart Human Biology

Comments are closed.