Children Free Full Text Development Of The Gut Microbiome In

Children Free Full Text Development Of The Gut Microbiome In In this cohort of children that are at risk for developing islet autoimmunity (ia) or t1d, we aimed to (1) characterize definitively the longitudinal gut microbiome development from 3 to 46 months. The composition of the intestinal microbiome affects health from the prenatal period throughout childhood, and many diseases have been associated with dysbiosis. the gut microbiome is constantly changing, from birth throughout adulthood, and several variables affect its development and content. features of the intestinal microbiota can affect development of the brain, immune system, and lungs.
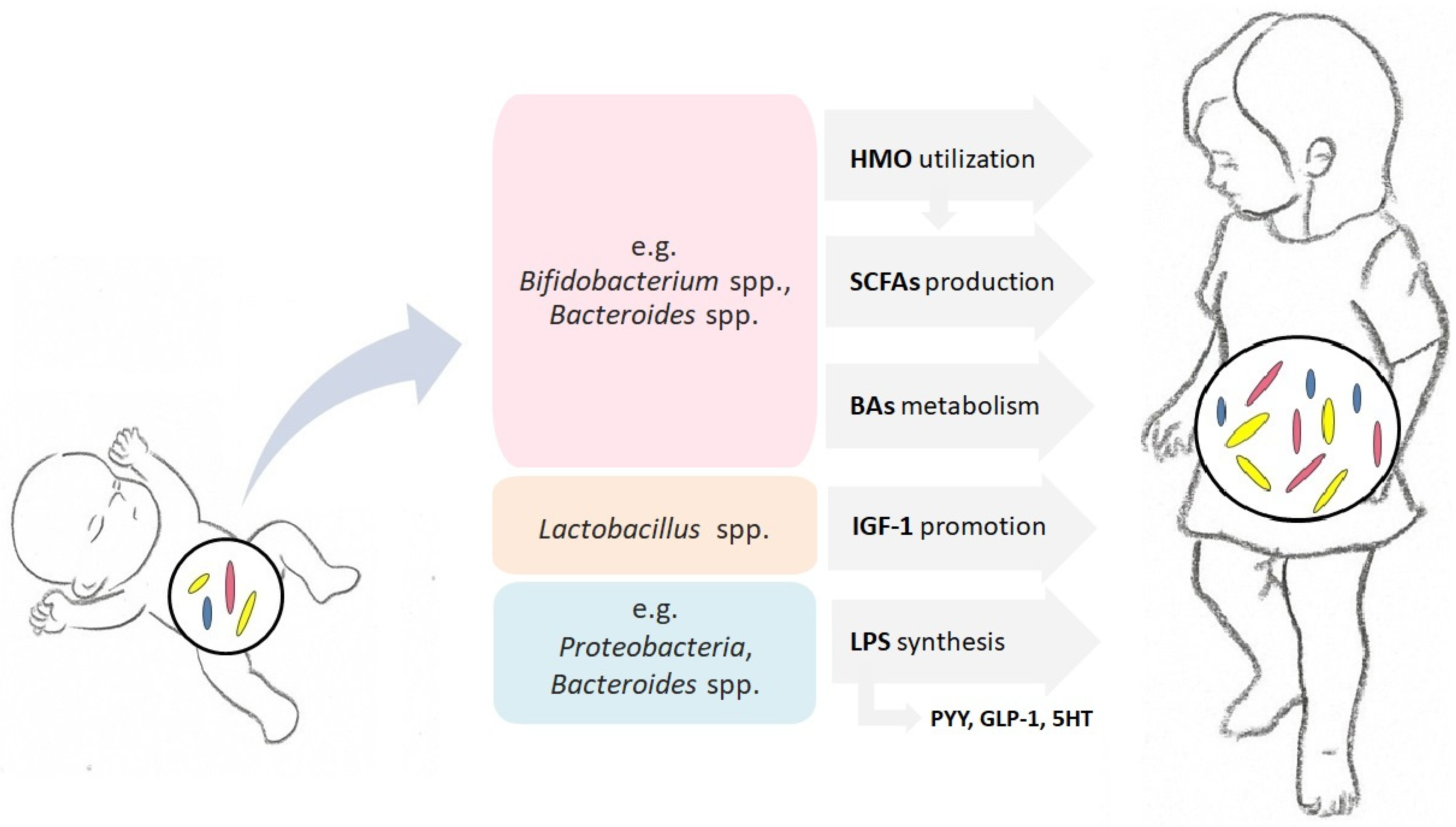
Life Free Full Text The Mediating Role Of The Gut Microbiota In The Due to the important role the gut microbiome plays in the development of the immune system, it has been hypothesized that the gut flora may influence the host response to vaccines. while there have been relatively few studies investigating microbiome composition and vaccination, the data indicate that microbiota play a role in vaccine response. The gut microbiota undergoes most of its development very early in life and major changes in the composition of the gut microbiota have been observed until the child is 2 to 3 years of age 2, 6, 7. In this review, we describe the development of the pediatric microbiome, starting in utero and progressing through infancy, childhood and adolescence. we then discuss the impact of the microbiome on the developing brain and neural function through the gut brain axis. we conclude with a discussion on the impact of dysbiosis on disease. The human gut microbiome develops during the first years of life, followed by a relatively stable adult microbiome. day care attendance is a drastic change that exposes children to a large group.

Figure 1 From Development Of The Gut Microbiota And Dysbiosis In In this review, we describe the development of the pediatric microbiome, starting in utero and progressing through infancy, childhood and adolescence. we then discuss the impact of the microbiome on the developing brain and neural function through the gut brain axis. we conclude with a discussion on the impact of dysbiosis on disease. The human gut microbiome develops during the first years of life, followed by a relatively stable adult microbiome. day care attendance is a drastic change that exposes children to a large group. Ana m valdes and colleagues discuss strategies for modulating the gut microbiota through diet and probiotics microbiome refers to the collective genomes of the micro organisms in a particular environment, and microbiota is the community of micro organisms themselves (box 1). approximately 100 trillion micro organisms (most of them bacteria, but also viruses, fungi, and protozoa) exist in the. The factors that influence gut microbiome development are thought to impact signaling along the microbiome gut brain axis, which has been implicated in a variety of neurological outcomes late in life including neurodegenerative diseases such as parkinson’s disease and alzheimer’s (16–18), neuropsychiatric illness such as anxiety and.
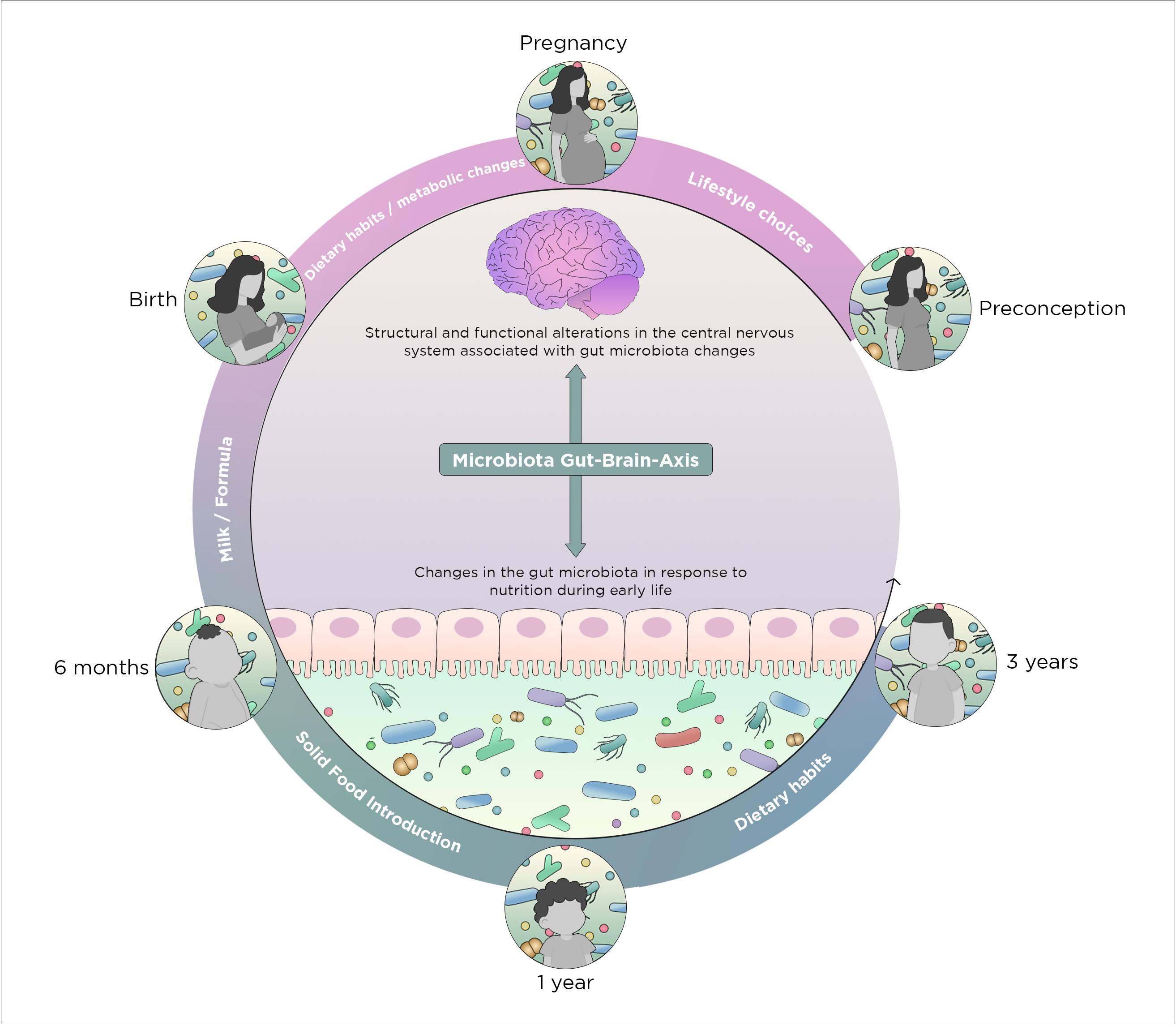
Nutrients Free Full Text Priming For Life Early Life Nutrition And Ana m valdes and colleagues discuss strategies for modulating the gut microbiota through diet and probiotics microbiome refers to the collective genomes of the micro organisms in a particular environment, and microbiota is the community of micro organisms themselves (box 1). approximately 100 trillion micro organisms (most of them bacteria, but also viruses, fungi, and protozoa) exist in the. The factors that influence gut microbiome development are thought to impact signaling along the microbiome gut brain axis, which has been implicated in a variety of neurological outcomes late in life including neurodegenerative diseases such as parkinson’s disease and alzheimer’s (16–18), neuropsychiatric illness such as anxiety and.

Infographic Gut Microbiota Development And Probiotics In Children Exden

Comments are closed.