Chart Of Angles Degrees
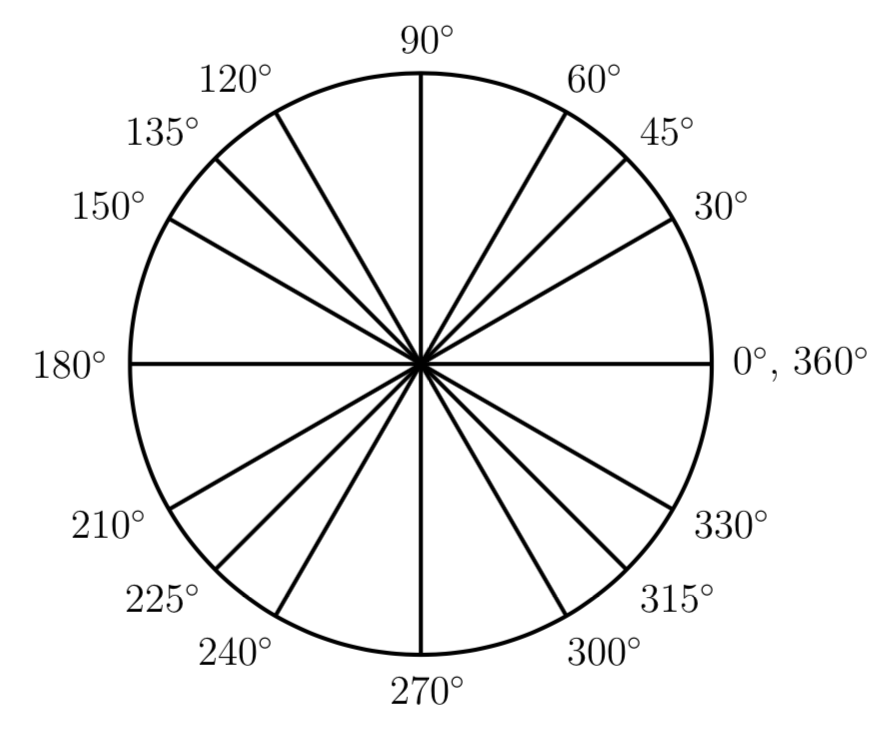
Chart Of Angles Degrees (note: "degree" is also used for temperature, but here we talk about angles) the degree symbol ° we use a little circle ° following the number to mean degrees. for example 90° means 90 degrees. one degree. this is how large 1 degree is. the full circle. a full circle is 360° half a circle is 180° (called a straight angle) quarter of a. Answer: the measure of the angle in degrees between the two arms of the scissors is 30 degrees. example 3: help jack to convert the 60 degree angle into radians. solution: the formula for the conversion of degrees into radians is, 1 degree = π 180 rad. now multiply 60 on both sides, 1 degree = π 180 rad.
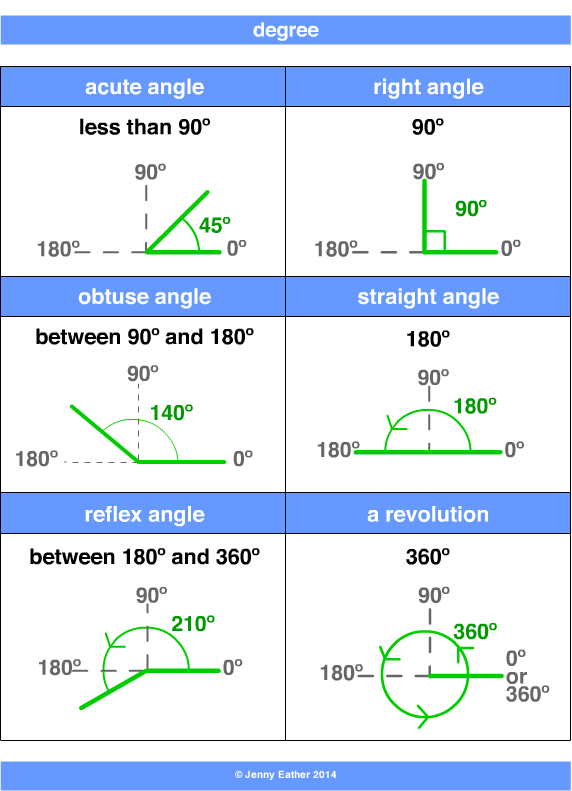
Chart Of Angles Degrees Parts of an angle. the corner point of an angle is called the vertex. and the two straight sides are called arms. the angle is the amount of turn between each arm. how to label angles. there are two main ways to label angles: 1. give the angle a name, usually a lower case letter like a or b, or sometimes a greek letter like α (alpha) or θ (theta). An angle in degrees is denoted by a tiny circle (°) that is often placed in the superscript position after the number (at the top right corner of a number). for example, 40 degrees = 40°. note that this symbol is to be used after the numerical value representing the measurement of an angle (angle measure), and not after the name of an angle. A chart to convert between degrees and radians. in most mathematical work beyond practical geometry, angles are typically measured in radians rather than degrees. this is for a variety of reasons; for example, the trigonometric functions have simpler and more "natural" properties when their arguments are expressed in radians. these. Trig table of common angles; angle (degrees) 0 30 45 60 90 120 135 150 180 210 225 240 270 300 315 330 360 = 0; angle (radians) 0 pi 6 pi 4 pi 3 pi 2 2 3pi 3 4pi 5 6pi pi.
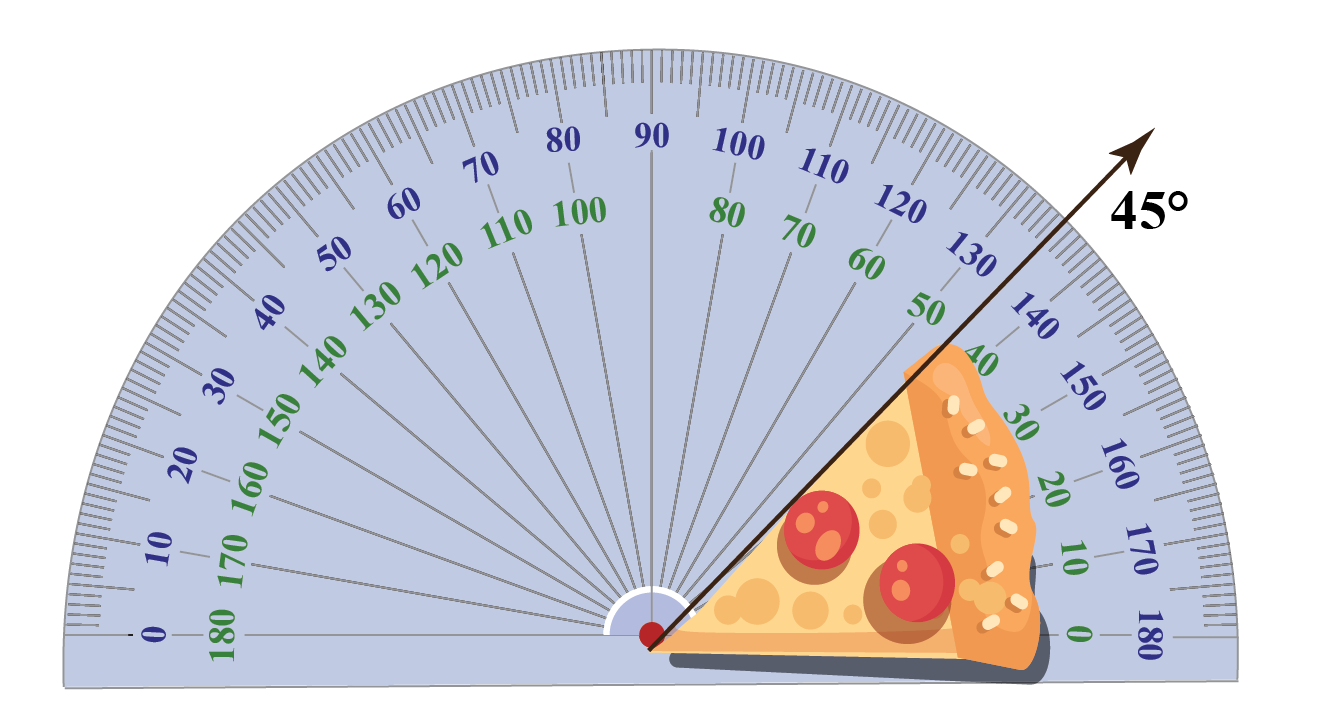
Chart Of Angles Degrees A chart to convert between degrees and radians. in most mathematical work beyond practical geometry, angles are typically measured in radians rather than degrees. this is for a variety of reasons; for example, the trigonometric functions have simpler and more "natural" properties when their arguments are expressed in radians. these. Trig table of common angles; angle (degrees) 0 30 45 60 90 120 135 150 180 210 225 240 270 300 315 330 360 = 0; angle (radians) 0 pi 6 pi 4 pi 3 pi 2 2 3pi 3 4pi 5 6pi pi. The acute angles: these are angles measuring less than 90 ∘. imagine the sharpness of a pizza slice which typically forms an acute angle. angle type. degree measure. property. acute. <90 ∘. sharp and narrow. right angles are the cornerstones of geometry and are exactly 90 ∘. Angles are formed when two lines intersect at a point. the measure of the 'opening' between these two rays is called an 'angle'. it is represented by the symbol ∠. angles are usually measured in degrees and radians, which is a measure of circularity or rotation. angles are a part of our day to day life. engineers and architects use angles for.

Chart Of Angles Degrees The acute angles: these are angles measuring less than 90 ∘. imagine the sharpness of a pizza slice which typically forms an acute angle. angle type. degree measure. property. acute. <90 ∘. sharp and narrow. right angles are the cornerstones of geometry and are exactly 90 ∘. Angles are formed when two lines intersect at a point. the measure of the 'opening' between these two rays is called an 'angle'. it is represented by the symbol ∠. angles are usually measured in degrees and radians, which is a measure of circularity or rotation. angles are a part of our day to day life. engineers and architects use angles for.
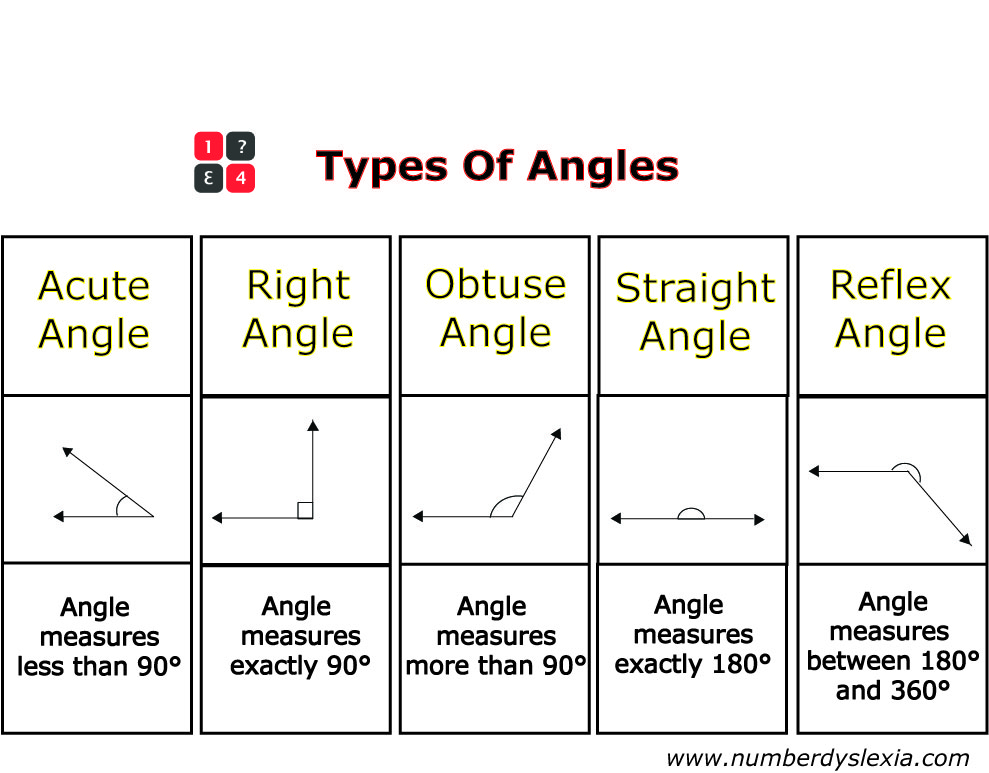
Free Printable Angles Anchor Chart For Classroom Pdf Number Dyslexia

Comments are closed.