Chapter 4 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand What Factors Affect
Chapter 4 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand What Factors Affect A market in which there are many buyers and many sellers so that each has a negligible impact on the market price. perfectly competitive markets. 1. the goods offered for sale are all the same 2. the buyers and sellers are so numerous that no one buyer or seller can influence the price. price takers. Chapter 4: the market forces of supply and demand principles of economics, 8th edition n. gregory mankiw page 3 price of one good leads to a decrease in the demand for the other good. p. 70. iii. tastes (1) while economists do not normally try to explain people’s tastes, they do examine what happens when tastes change. iv. expectations.

Chapter 4 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand Pdf Chapter 4: supply and demand. supply, demand, and equilibrium. step 1: identify which curve shifts (or both) step 2: identify what direction did it shift. step 3: use the s d graph to find how equilibrium price and quantity change. homework:. Market demand is the sum of all of the individual demands for a particular good or service. individual demand curves are summed horizontally – quantities demanded are added up for each level of price. market demand curve shows how the total quantity demanded of a good varies with the price of the good, ceteris paribus. Ndch. 4: the market forces of supply and demanda market is a gr. a particular product.(trading places: 1:45 3:15)a competitive market is one with many buyers. in a perfectly competitive market. and sellers are so numerous that no one can. a•ect market price each is a \price taker".quantity demanded: the total quantity of a. Microeconomists use the theory of supply and demand to understand: 1. how buyers and sellers in an individual market for a particular good behave. 2. how the interactions between those buyers and sellers work to determine the quantity of the good that gets produced and the price at which the good gets bought and sold.

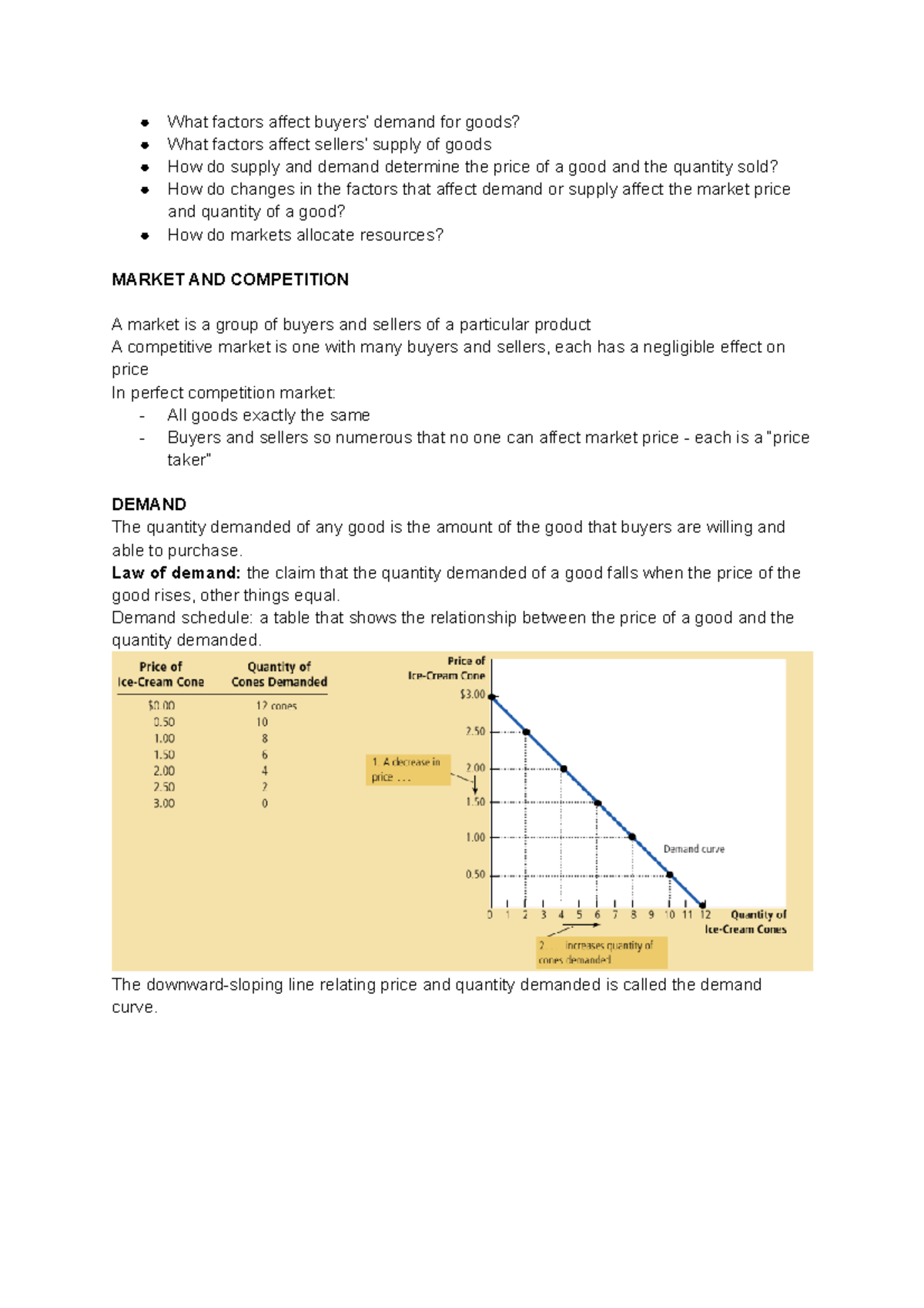
Chapter 04 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand Pdf Chapter 4 Ndch. 4: the market forces of supply and demanda market is a gr. a particular product.(trading places: 1:45 3:15)a competitive market is one with many buyers. in a perfectly competitive market. and sellers are so numerous that no one can. a•ect market price each is a \price taker".quantity demanded: the total quantity of a. Microeconomists use the theory of supply and demand to understand: 1. how buyers and sellers in an individual market for a particular good behave. 2. how the interactions between those buyers and sellers work to determine the quantity of the good that gets produced and the price at which the good gets bought and sold. The demand schedule demand schedule: a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded example: helen’s demand for lattes. notice that helen’s preferences obey the law of demand. price of lattes quantity of lattes demanded $0.00 16 1.00 14 2.00 12 3.00 10 4.00 8 5.00 6 6.00 4. The supply and demand model of perfect competition is treated as a generic model that can be used as a typical market in a market economy ; mankiw begins the chapter by writing: “supply and demand are the forces that make market economies work. they determine the quantity of each good produced and the price at which it is sold.

Ppt Ch 4 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand Pdf Supply And The demand schedule demand schedule: a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded example: helen’s demand for lattes. notice that helen’s preferences obey the law of demand. price of lattes quantity of lattes demanded $0.00 16 1.00 14 2.00 12 3.00 10 4.00 8 5.00 6 6.00 4. The supply and demand model of perfect competition is treated as a generic model that can be used as a typical market in a market economy ; mankiw begins the chapter by writing: “supply and demand are the forces that make market economies work. they determine the quantity of each good produced and the price at which it is sold.

Comments are closed.