Chapter 15 Lecture Notes 7 Chapter 15 Monopoly Ex Of Monopoly

Chapter 15 Lecture Notes 7 Chapter 15 Monopoly Ex Of Monopoly Chapter 15: monopoly ex. of monopoly— microsoft corporation owner of windows microsoft corporation is a price maker o market price is approximately 10 times the marginal cost (p > mc) o profit is not unlimited (a high price reduces the quantity that its customers buy) why monopolies arise. Chapter 15: monopoly. definitions monopoly – a firm that is the sole seller of a product without any close substitutes natural monopolies – a type of monopoly that arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a lower cost than could two or more firms price discrimination – the business practice of selling the same good at different prices to different.

Chapter 15 Notes Student Version Chapter 15 Monopoly In This Figure 1 economies of scale as a cause of monopoly. when a firm’s average total cost curve continually declines, the firm has what is called a natural monopoly. in this case, when production is divided among more firms, each firm produces less, and average total cost rises. as a result, a single firm can produce any given amount at the lowest. Econ 1101 lecture notes chapter 15 chapter 15 monopoly monopoly means one firm that has all the power market power alters the relationship between costs and the. Introduction. a monopoly is a firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes. in this chapter, we study monopoly and contrast it with perfect competition. the key difference: a monopoly firm has market power, the ability to influence the market price of the product it sells. Characteristics of monopoly 1:33 a monopoly is a price maker 2:57sources of barriers to entry 4:22the monopoly faces the market demand curve 12:53the reve.
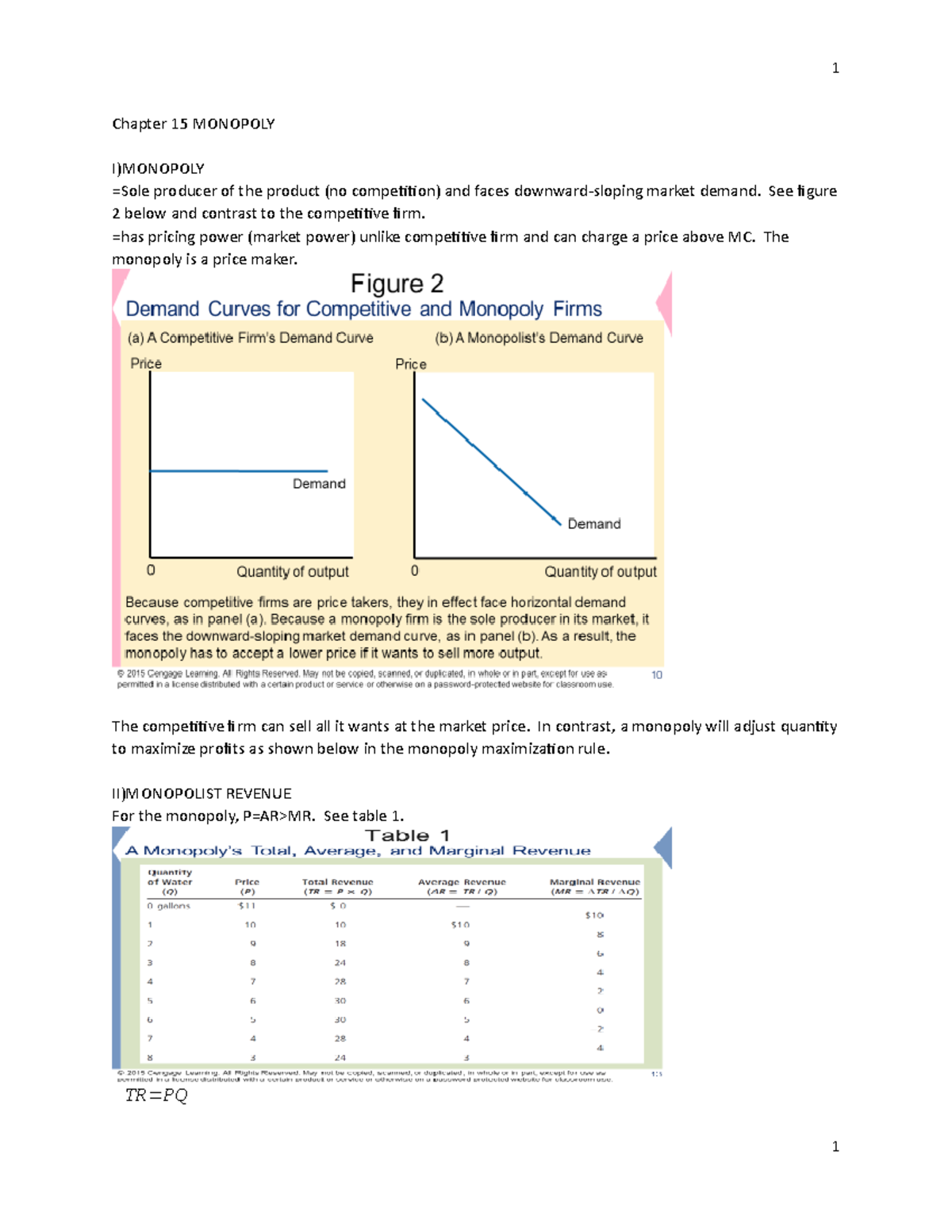
Chapter 15 Monopoly Lecture Notes 15 17 Chapter 15 Monopoly I Introduction. a monopoly is a firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes. in this chapter, we study monopoly and contrast it with perfect competition. the key difference: a monopoly firm has market power, the ability to influence the market price of the product it sells. Characteristics of monopoly 1:33 a monopoly is a price maker 2:57sources of barriers to entry 4:22the monopoly faces the market demand curve 12:53the reve. 1. government restrictions on entry. 2. control over a key resource. 3. network externalities. 4. natural monopoly. what are the four main reasons for barriers to entry in a monopoly? patent. government restriction. government granted permission to be the sole producer and seller of a good. copyright. Chapter 15 monopoly solutions to course manual problems quick quizzes 1. what are the three reasons why a market might have a monopoly? • give two examples of monopolies, and explain the reason for each. a market might have a monopoly because: (1) a key resource is owned by a single firm; (2) the.

Chapter 15 Monopoly Lecture Notes 16 Chapter 15 Monopoly Monopoly A 1. government restrictions on entry. 2. control over a key resource. 3. network externalities. 4. natural monopoly. what are the four main reasons for barriers to entry in a monopoly? patent. government restriction. government granted permission to be the sole producer and seller of a good. copyright. Chapter 15 monopoly solutions to course manual problems quick quizzes 1. what are the three reasons why a market might have a monopoly? • give two examples of monopolies, and explain the reason for each. a market might have a monopoly because: (1) a key resource is owned by a single firm; (2) the.

Chapter 15 Monopoly

Chapter 15 Monopoly Chapter 15 Monopoly Multiple Choice Which Of The

Comments are closed.