Chapter 14 1 Ans Versus Somatic Nervous System Bio201

Chapter 14 1 Ans Versus Somatic Nervous System Bio201 Youtube Bio 201: lesson 15 chapter 14. identify the differences between the structure and function of the components of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. click the card to flip 👆. ans is a part of the pns. uses 2 motor neurons, first one is in the brain spine, second one has its cell body in an autonomic ganglion. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright.

Ans Versus Somatic Nervous System Channels For Pearson The autonomic nervous system also has two divisions: the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. these two divisions have antagonistic (opposing) effects on the internal organs they innervate (send nerves to = act on). the sympathetic division, shown at the left, is the emergency system adrenergic receptors. Chapter 14 the somatic nervous system ops for this assignment, please read the chapter and answer the questions below. please type your answers in red or blue color. please note that points may be deducted if answers are not submitted in these colors. Cerebrospinal fluid (csf) clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of the cns and bathes the external surface. brain produces ~500 ml of csf per day. flows through spaces in the brain, and the central canal in the spinal cord. blockage of csf exiting the brain can lead to hydrocephalus. A. the autonomic nervous system (ans) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral nervous system (pns), also known as the. division. the ans is divided into two separate divisions, the and nervous systems, which work together constantly to maintain homeostasis. the ans oversees most vital functions including: , , and .

Bio 201 Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous System Assignment Ops Chapter 14 Cerebrospinal fluid (csf) clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of the cns and bathes the external surface. brain produces ~500 ml of csf per day. flows through spaces in the brain, and the central canal in the spinal cord. blockage of csf exiting the brain can lead to hydrocephalus. A. the autonomic nervous system (ans) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral nervous system (pns), also known as the. division. the ans is divided into two separate divisions, the and nervous systems, which work together constantly to maintain homeostasis. the ans oversees most vital functions including: , , and . The somatic nervous system (sons) is the part of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of body movements through the skeletal muscles and mediation of involuntary reflex arcs. the autonomic nervous system (ans) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls visceral functions that occur below the level. Thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. the seat of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses; forms surface layer, cortex, over cerebrum and cerebellum; forms nuclei deep within the brain. bundle of axons; lies deep to cortical gray matter; composed of tracts, bundles of axons, that connect one part of.

Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System And Homeostasis Pdf Chapter 14 The somatic nervous system (sons) is the part of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of body movements through the skeletal muscles and mediation of involuntary reflex arcs. the autonomic nervous system (ans) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls visceral functions that occur below the level. Thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. the seat of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses; forms surface layer, cortex, over cerebrum and cerebellum; forms nuclei deep within the brain. bundle of axons; lies deep to cortical gray matter; composed of tracts, bundles of axons, that connect one part of.
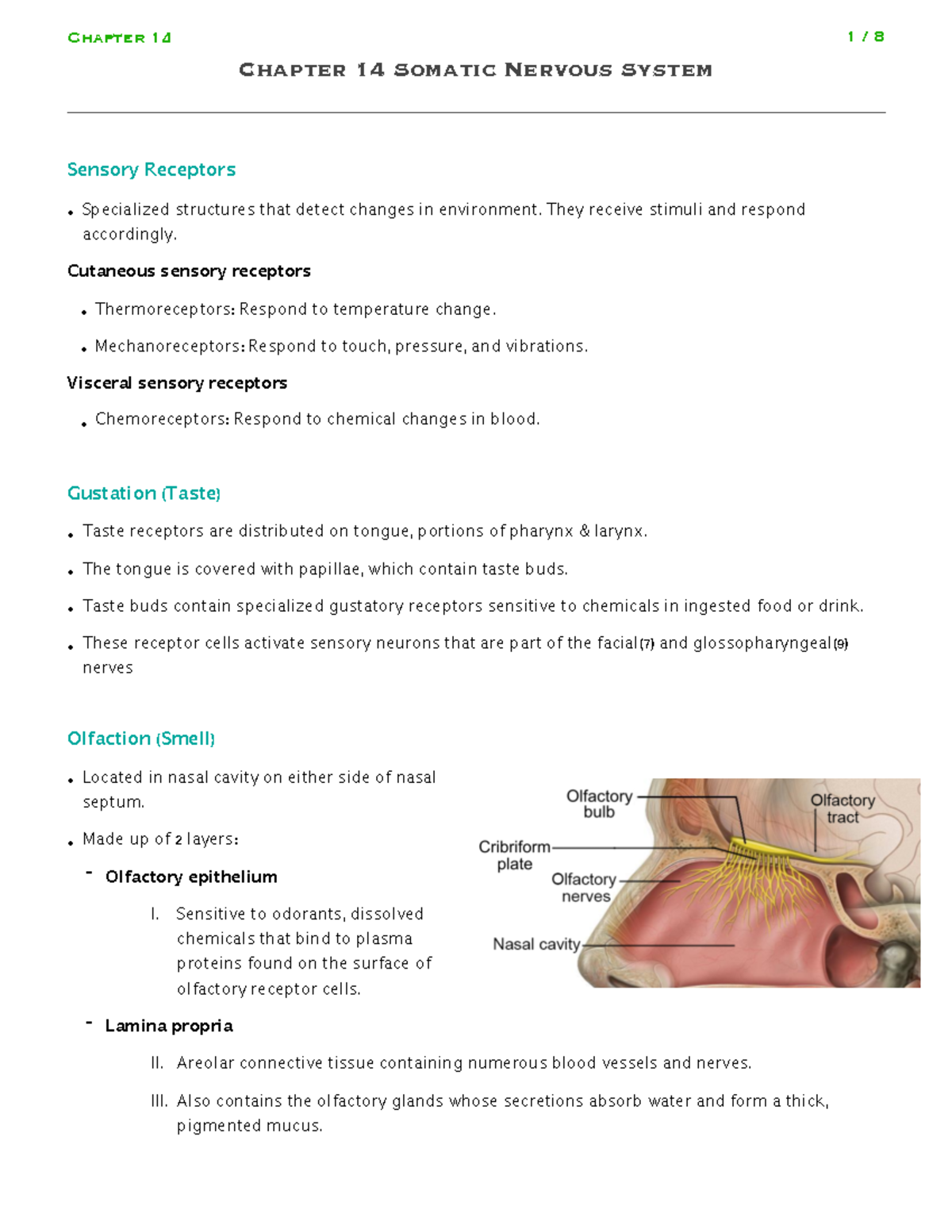
Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous System Chapter 14 Somatic Nervous System

Comments are closed.