Chapter 1 Micro Biology Chapter 1 Microbiology Various Types Of
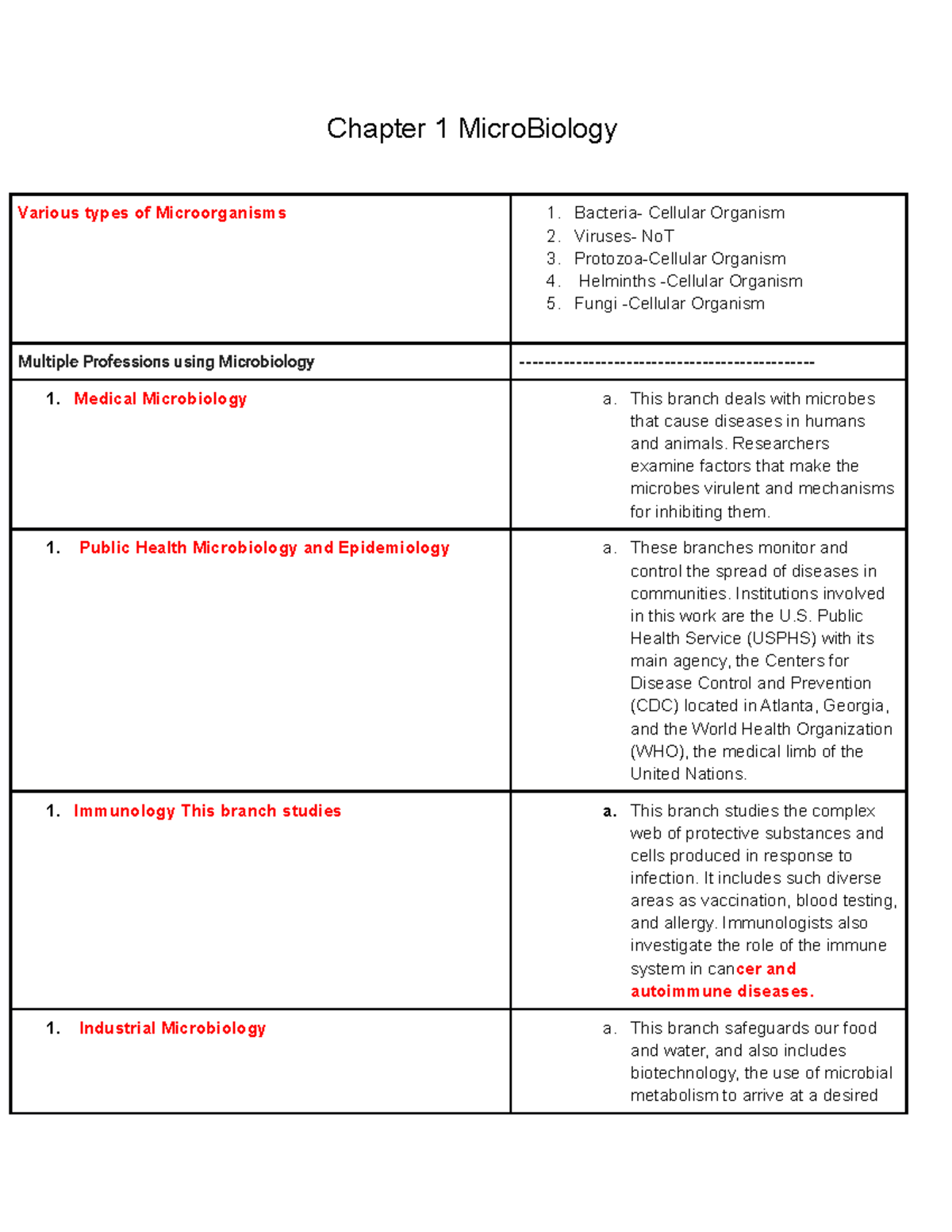
Chapter 1 Micro Biology Chapter 1 Microbiology Various Types Of 2. they are producers in the ecosystem by photosynthesis. 3. they produce industrial chemicals such as ethanol and acetone. 4. produce fermented foods such as vinegar, cheese, and bread. 5. produce products used in manufacturing and treatment (insulin) 6. This chapter explores how various types of microscopes manipulate light in order to provide a window into the world of microorganisms. by understanding how various kinds of microscopes work, we can produce highly detailed images of microbes that can be useful for both research and clinical applications. section 1.e: an invisible world (exercises).

Chapter 1 Microbiology And Parasitology Pdf Microorganism Chapter 1 microbiology. various types of microorganisms 1. bacteria cellular organism 2. viruses not 3. protozoa cellular organism 4. helminths cellular organism 5. fungi cellular organism. multiple professions using microbiology medical microbiology a. 4. industrial microbiology. 5. agricultural microbiology. 6. environmental microbiology. medical microbiology. study of microbes as they relate to medicine, deals with microbes that causes disease in humans and animals. public health microbiology and epidemiology. Microbial growth refers to the increase in the number of microorganisms in a population over time. microbes can reproduce rapidly under favorable conditions, leading to exponential growth. factors that affect microbial growth include nutrient availability, temperature, ph, oxygen levels, and moisture. 1.3 types of microorganisms from boiling thermal hot springs to deep beneath the antarctic ice, microorganisms can be found almost everywhere on earth in great quantities. microorganisms (or microbes, as they are also called) are small organisms.

Micro Chapter 1 Pdf Microbiology Bacteria Microbial growth refers to the increase in the number of microorganisms in a population over time. microbes can reproduce rapidly under favorable conditions, leading to exponential growth. factors that affect microbial growth include nutrient availability, temperature, ph, oxygen levels, and moisture. 1.3 types of microorganisms from boiling thermal hot springs to deep beneath the antarctic ice, microorganisms can be found almost everywhere on earth in great quantities. microorganisms (or microbes, as they are also called) are small organisms. See table 1.1 for units of length used in microbiology. figure 1.12 the relative sizes of various microscopic and nonmicroscopic objects. note that a typical virus measures about 100 nm, 10 times smaller than a typical bacterium (~1 µm), which is at least 10 times smaller than a typical plant or animal cell (~10–100 µm). Applications of microbiology (table 1.1): within the field of microbiology there are many sub disciplines: 1. immunology – study of how the body defends itself against infection. 2. epidemiology – monitoring and controlling the spread of disease. 3. medical microbiology & pathology – focuses disease causing microbes. 4.

Chapter 1 History Of Microbiology Chapter 1 Stuvia Us See table 1.1 for units of length used in microbiology. figure 1.12 the relative sizes of various microscopic and nonmicroscopic objects. note that a typical virus measures about 100 nm, 10 times smaller than a typical bacterium (~1 µm), which is at least 10 times smaller than a typical plant or animal cell (~10–100 µm). Applications of microbiology (table 1.1): within the field of microbiology there are many sub disciplines: 1. immunology – study of how the body defends itself against infection. 2. epidemiology – monitoring and controlling the spread of disease. 3. medical microbiology & pathology – focuses disease causing microbes. 4.
The History And Scope Of Microbiology Microbiology Chapter 1

Microbiology Mcqs Chapter 1 Medical Laboratory Scientist Mls

Comments are closed.