Change In Consumer Surplus
Consumer Surplus Formula Guide Examples How To Calculate Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium. Consumer surplus is the benefit that consumers get from paying less than the maximum price they are willing to pay for a good or service. learn how to calculate consumer surplus, see an example, and understand its relationship with producer surplus and total economic surplus.

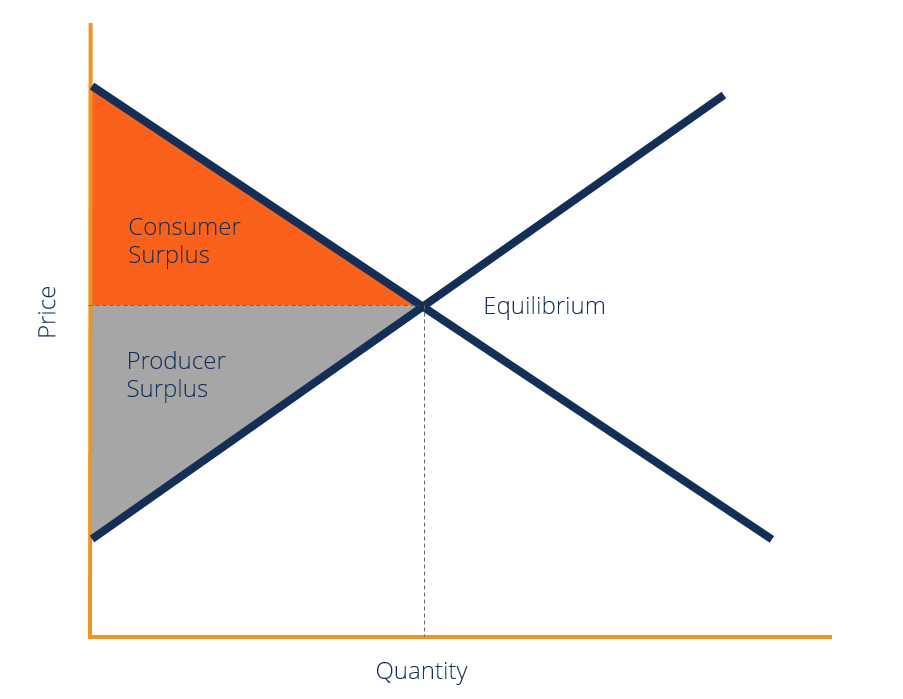
Consumer And Producer Surplus Edexcel Economics Revision Consumer surplus is calculated by finding the difference between the amount a consumer is willing to pay for a product and the actual price they pay. to find the total consumer surplus, you sum up these differences for all units sold. in some cases this can be simplified to finding the area between the demand curve and the price line. Learn how to measure consumer surplus, the economic benefit of a customer's willingness to pay for a product or service. find out how consumer surplus changes with price elasticity of demand and the law of diminishing marginal utility. Learn how to measure the monetary gains a consumer obtains as they can purchase a product at a price lesser than the highest price they are willing to pay. see graphical and mathematical representations, examples, and the rule of one half for changes in consumer surplus due to shifts in supply. Consumer surplus is an indicator of the economic welfare and satisfaction derived by consumers from market transactions. used by policymakers to evaluate the impact of regulations, taxes, and subsidies on consumer welfare. a decrease in market price increases consumer surplus, while an increase in price reduces it.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Economics Tutor2u Learn how to measure the monetary gains a consumer obtains as they can purchase a product at a price lesser than the highest price they are willing to pay. see graphical and mathematical representations, examples, and the rule of one half for changes in consumer surplus due to shifts in supply. Consumer surplus is an indicator of the economic welfare and satisfaction derived by consumers from market transactions. used by policymakers to evaluate the impact of regulations, taxes, and subsidies on consumer welfare. a decrease in market price increases consumer surplus, while an increase in price reduces it. Microeconomics. course: microeconomics > unit 4. lesson 1: consumer and producer surplus. demand curve as marginal benefit curve. consumer surplus introduction. total consumer surplus as area. producer surplus. equilibrium, allocative efficiency and total surplus. lesson overview: consumer and producer surplus. Consumer surplus is an economic measurement to calculate the benefit (i.e., surplus) of what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus its market price. the consumer surplus formula is based on an economic theory of marginal utility. the theory explains that spending behavior varies with the preferences of individuals.

Explaining Consumer Surplus Tutor2u Economics Microeconomics. course: microeconomics > unit 4. lesson 1: consumer and producer surplus. demand curve as marginal benefit curve. consumer surplus introduction. total consumer surplus as area. producer surplus. equilibrium, allocative efficiency and total surplus. lesson overview: consumer and producer surplus. Consumer surplus is an economic measurement to calculate the benefit (i.e., surplus) of what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus its market price. the consumer surplus formula is based on an economic theory of marginal utility. the theory explains that spending behavior varies with the preferences of individuals.

Comments are closed.