Ch 17 The Heart Part 2

Chap 17 Heart Part 2 Pre Reading Docx Guiding Questions Chapter 17 Convey (s) the impulse down the interventricular septum. set (s) the pace for entire heart. electrical link (s) between atria and ventricles. convey (s) the impulse throughout the ventricular walls. which part of the intrinsic conduction system normally initiates the depolarizing impulse that causes a heartbeat?. The heart is a transport system divided into what 2 side by side pumps? 1. right side: receives oxygen poor blood from tissues. pumps to lungs to get rid of co2, pick up o2, via pulmonary circuit. 2. left side: receives oxygenated blood from lungs. pumps to body tissues via systemic circuit.

Ch 17 Heart Pptx Chapter The17 Cardiovascular System The Course Hero 18.0 l minute. 11.1 l minute. 2.8 l minute. 2.8 l minute. sv = (edv esv) beat => 40 ml beat; cardiac output= sv x hr => 40 ml beat x 70 beats minute. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the apex of the heart is . inferior anterior posterior superior, what surface groove separates the right and left. 17.2: heart anatomy. the vital importance of the heart is obvious. if one assumes an average rate of contraction of 75 contractions per minute, a human heart would contract approximately 108,000 times in one day, more than 39 million times in one year, and nearly 3 billion times during a 75 year lifespan. Subject bears down and tries to expire against a closed glottis (airway in larynx), as occurs during coughing, sneezing, defecation, and heavy lifting. raises pressure in thoracic cavity and reduces return of venous blood to heart. à drop in bp; should trigger baroreceptor reflex and generate increased hr. Chapter 17: the heart. functions of the heart a. generating blood pressure contraction of the heart generates blood pressure, which is required for blood flow through the blood vessels b. routing blood the heart is two pumps moving blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulations i. pulmonary moves blood to and from the lungs. ii.
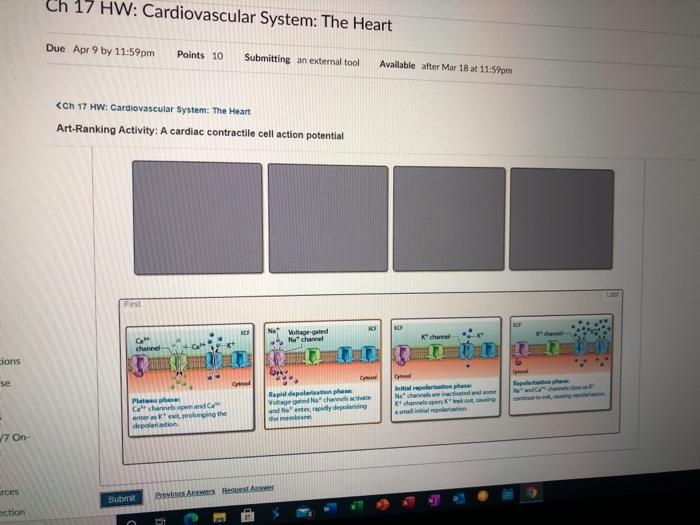
Solved Ch 17 Hw Cardiovascular System The Heart Due Apr 9 Chegg Subject bears down and tries to expire against a closed glottis (airway in larynx), as occurs during coughing, sneezing, defecation, and heavy lifting. raises pressure in thoracic cavity and reduces return of venous blood to heart. à drop in bp; should trigger baroreceptor reflex and generate increased hr. Chapter 17: the heart. functions of the heart a. generating blood pressure contraction of the heart generates blood pressure, which is required for blood flow through the blood vessels b. routing blood the heart is two pumps moving blood through the pulmonary and systemic circulations i. pulmonary moves blood to and from the lungs. ii. Heart. the heart is a muscular organ in the chest. it consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. as shown in figure 17.2.3 17.2. 3, the heart has four inner chambers: a right atrium and ventricle and a left atrium and ventricle. Heart sounds: the stethoscope is a clinical device that can be used to listen to, or auscultate, the rhythmic “lub dub” made by the heart sounds (figure 17). there are two heart sounds: (1) , or the “lub,” is heard when the av valves close, and (2) , the “dub,” is heard when the semilunar valves close.

Heart Part 2 Diagram Quizlet Heart. the heart is a muscular organ in the chest. it consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. as shown in figure 17.2.3 17.2. 3, the heart has four inner chambers: a right atrium and ventricle and a left atrium and ventricle. Heart sounds: the stethoscope is a clinical device that can be used to listen to, or auscultate, the rhythmic “lub dub” made by the heart sounds (figure 17). there are two heart sounds: (1) , or the “lub,” is heard when the av valves close, and (2) , the “dub,” is heard when the semilunar valves close.

Comments are closed.