Cellular Level Research Into How Autism And Dementia May Be Connected

Single Cell Genomics Identifies Cell Type Specific Molecular Changes In Most neuropsychiatric disorders lack biomarkers that can provide insights into pathophysiology, inform clinical diagnosis, or guide management ().high throughput genomic profiling technologies—applied to bulk tissue or single cells—may provide insights at scale: interrogating genome wide molecular features (e.g., gene expression or dna methylation) across large numbers of brain samples. The growing interest in the relationship between autism and dementia stems from observations of cognitive changes in older adults with autism and the recognition of shared neurological features between the two conditions. this intersection has opened up new avenues for research and has important implications for diagnosis, treatment, and care.

Autism And Dementia S Surprising Connection Autism spectrum disorder (asd) has captured the attention of scientists and clinicians, as well as the lay public, in part because the clinical profile is so striking [1,2,3].affected individuals. Research suggests a link between autism and early onset alzheimer’s disease. in a 2021 study of public health records, researchers found that autistic middle aged adults appear to be more likely. Functional genomic analyses of multiple brain regions across three major neurodegenerative disorders involving tau pathology, ad, bvftd, and psp, at the single cell level enables the identification of markers of neuronal vulnerability, glial states that vary across disease, and disorder specific cellular differences in the expression and regulation of known risk genes. A key consideration includes methods of identifying ‘missing groups’ of individuals with autism who do not self refer for research and who may be lost in the community. these may include, for example, individuals over the age of 21 years who are no longer in social or health related services; those with co existing id; or older autistic.
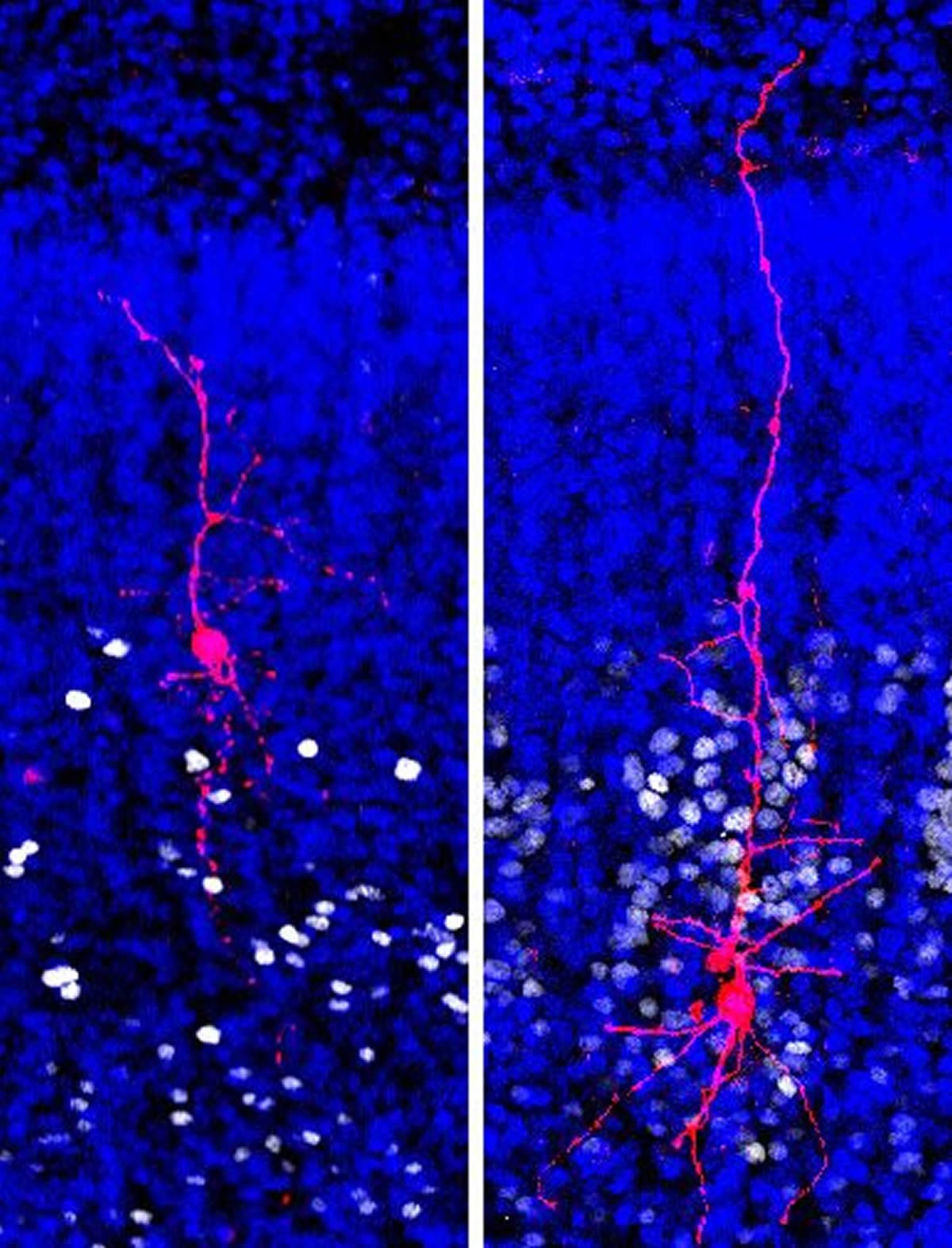
Brain Changes In Autism Traced To Specific Cell Types Neuroscience News Functional genomic analyses of multiple brain regions across three major neurodegenerative disorders involving tau pathology, ad, bvftd, and psp, at the single cell level enables the identification of markers of neuronal vulnerability, glial states that vary across disease, and disorder specific cellular differences in the expression and regulation of known risk genes. A key consideration includes methods of identifying ‘missing groups’ of individuals with autism who do not self refer for research and who may be lost in the community. these may include, for example, individuals over the age of 21 years who are no longer in social or health related services; those with co existing id; or older autistic. Geschwind's study on autism, one of nine published in the may 24 issue of science, builds on decades of his group's research profiling the genes that increase the susceptibility to autism spectrum. Autism spectrum disorder (asd) is a heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorder associated with both genetic and environmental risks. neuroimaging approaches have been widely employed to parse the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying asd, and provide critical insights into the anatomical, functional, and neurochemical changes. we reviewed recent advances in neuroimaging studies that focused.

The Alzheimer S Research Uk Stem Cell Research Centre Alzheimer S Geschwind's study on autism, one of nine published in the may 24 issue of science, builds on decades of his group's research profiling the genes that increase the susceptibility to autism spectrum. Autism spectrum disorder (asd) is a heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorder associated with both genetic and environmental risks. neuroimaging approaches have been widely employed to parse the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying asd, and provide critical insights into the anatomical, functional, and neurochemical changes. we reviewed recent advances in neuroimaging studies that focused.

Researchers Begin To Map Neurogenetic Pathway Find New Cell Is

Molecular And Cellular Basis Of Cognitive Flexibility In Autism

Comments are closed.